
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
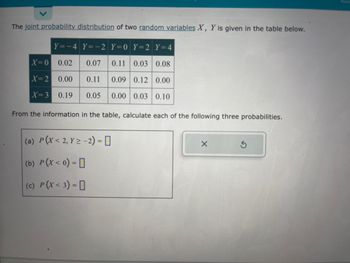
Transcribed Image Text:The joint probability distribution of two random variables X, Y is given in the table below.
Y=-4 Y=-2 Y=0 Y=2 Y = 4
X=0 0.02 0.07 0.11 0.03 0.08
X=2 0.00 0.11 0.09 0.12 0.00
X=3 0.19 0.05 0.00 0.03 0.10
From the information in the table, calculate each of the following three probabilities.
(a) P(X<2, Y> -2) = 0
(b) P(x<0)=
(c) P(X<3) -
Ś
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Fill in the P=Xx values to give a legitimate probability distribution for the discrete random variable X , whose possible values are −1 , 3 , 4 , 5 , and 6 . ValuexofX P=Xx −1 3 0.10 4 5 0.21 6 0.10arrow_forwardFill in the P=Xx values to give a legitimate probability distribution for the discrete random variable X , whose possible values are 1 , 3 , 4 , 5 , and 6 . ValuexofX P=Xx 1 0.15 3 0.29 4 0.21 5 6arrow_forwardThe joint probability distribution of the number X of cars and the number Y of buses per signal cycle at a proposed left-turn lane is displayed in the accompanying joint probability table. y 1 p(x, y) 0 1 0.030 0.020 50 X 3 0.090 0.060 4 0.060 0.040 2 0 0.015 0.010 0.025 0.050 2 0.075 0.050 0.125 0.150 0.100 5 0.030 0.020 0.050 (a) What is the probability that there is exactly one car and exactly one bus during a cycle? 0.020 (b) What is the probability that there is at most one car and at most one bus during a cycle? 0.075 (c) What is the probability that there is exactly one car during a cycle? Exactly one bus? P(exactly one car) = 0.220 x P(exactly one bus) = 0.200 (d) Suppose the left-turn lane is to have a capacity of five cars and one bus is equivalent to three cars. What is the probability of an overflow during a cycle? 0.985 X (e) Are X and Y independent rv's? Explain. O Yes, because p(x, y) = P(x) Py(Y). O Yes, because p(x, y) = Px(x) • P₂(Y). # ● No, because p(x, y) = Px(x) •…arrow_forward
- Fill in the P=Xx values to give a legitimate probability distribution for the discrete random variable X , whose possible values are −4, −3, −2, 5, and 6. ValuexofX P=Xx −4 0.23 −3 0.19 −2 0.30 5 6arrow_forwardFind the variance for the probability distribution 4 0 1 2 3 P(X=x) 0.04 0.18 0.34 0.23 0.21 Select one: а. 1.12 b. 1.26 с. 1.59 d. 3.79arrow_forwardIn the probability distribution to the right, the random variable X represents the number of marriages an individual aged 15 years or older has been involved in. Compute and interpret the mean of the random variable X. Hx = marriages (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) X 0 1 2 3 4 5 P(x) 0.264 0.567 0.136 0.029 0.003 0.001arrow_forward
- The probability distribution of the random variable X represents the number of hits a baseball player obtained in a game for the 2012 baseball season. 1 2 3 4 P(x) 0.1666 0.3437 0.2774 0.1486 0.0384 0.0253arrow_forwardComplete the values of P (X = x) to give a legitimate probability distribution for the discrete random variable, whose possible values are -1, 2, 4, 5, and 6.arrow_forwardPlease calculate the covariance and the correlation coefficient for the two random variables and briefly comment on the resulting correlation between the variables.arrow_forward
- High school students in Michigan sometimes get "snow days" in the winter when the roads are so bad that school is canceled for the day. Define the random variableX = the number of snow days at a certain high school in Michigan for a randomly selected school year. Suppose the table below gives the probability distribution of X. 1. Value x, 1. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Probability p, ? 0.19 0.14 0.10 0.07 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.02 0.01 0.01 (a) Write the event “the school year has O snow days" in terms of X. Then find its probability. (b) At this high school, if more than 5 snow days are used over the course of the year, students are required to make up the time at the end of the school year. What's the probability that a randomly selected school year will require make-up days?arrow_forwardDetermine whether or not the table is a valid probability distribution of a discrete random variable. Explain fully (i). x 0 1 2 3 4 P(x) -0.25 0.50 0.35 0.10 0.30 Soln. (ii). x 1 2 3 P(x) 0.325 0.406 0.164 Soln.(iii). x 25 26 27 28 29 P(x) 0.13 0.27 0.28 0.18 0.14arrow_forwardThe joint probability distribution of two random variables X, Y is given in the table below. Y=-4 Y=0 Y=1_Y=4 X=-4 0.01 0.18 0.00 0.13 X=-1 0.03 0.08 0.20 0.14 X=4 0.00 0.08 0.09 0.06 From the information in the table, calculate each of the following three probabilities. (a) P(Y= -4) = | (b) Р (х < -1, ү 2 0) %3D0 (c) P(x< 5) = []arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman