
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
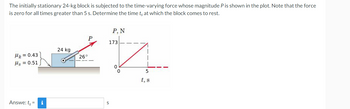
Transcribed Image Text:The initially stationary 24-kg block is subjected to the time-varying force whose magnitude P is shown in the plot. Note that the force
is zero for all times greater than 5 s. Determine the time t, at which the block comes to rest.
P, N
24 kg
26°
T
Mk=0.43
Hg = 0.51
Answe: ts = i
173
S
5
t, s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A mass that weighs 8 lb stretches a spring 24 inches. The system is acted on by an external force of 4 sin(4t) lb. If the mass is pulled down 6 inches and then released, determine the position of the mass at any time t. Assume that the u-axis is directed downwards and ft = g 32 Express your answer as a linear combination of sin(at) $² and cos(at), where u is in feet and t is in seconds. u(t) = Determine the first four times at which the velocity of the mass is zero. Exclude t = 0 as trivial, and enter exact answers. First zero: t = Third zero: t = Second zero: t = Fourth zero: t =arrow_forwardUnder the man's pushing force P= 34.8 lb, the uniform cabinet is sliding on the ground with a constant acceleration of a. If the uniform cabinet has weight of 150 lb, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the cabinet and the ground is μk = 0.12, determine the normal force reaction under leg A. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point and proper unit. Take g = 32.2 ft/s². -1 ft- -1 ft- Your Answer: Answer P 4 ft units A 3.5 ft Barrow_forwardThe initially stationary 24-kg block is subjected to the time-varying force whose magnitude P is shown in the plot. Note that the force is zero for all times greater than 5 s. Determine the time to at which the block comes to rest. P, N P 173 *Z 24 kg 26° H₂ = 0.43 Hs = 0.51 0 0 5 t, s i 4.181 S Answe: ts =arrow_forward
- The roller coaster car has a mass of 900 kg, including its passenger. It is released from rest at the top of the hill A. Neglect friction, the mass of the wheels, and the size of the car. Take hp = 19 m, PB = 9.5 m, hc = 14 m, and pc = 7 m. (Figure 1) Figure h hB B hc C BRE 1 of 1 Part A Determine the minimum height of the hill crest so that the car travels around both inside the loops without leaving the track. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. h = Submit Part B NB = Submit Part C 0 Nc = Value Submit What is the normal reaction on the car when the it is at B? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. μᾶ Request Answer Di μA Value Request Answer LO ☛ μA Units What is the normal reaction on the car when the it is at C? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Value www Request Answer Units ? Units wwwww ? ?arrow_forwardalso determine the force exerted by loop ABCD on the block at point C is _____ N.arrow_forwardA heavy crate with a weight of 160 lbs rests on a floor for which μS = 0.2. Find the minimum force P necessary for impending motion and determine whether the crate slides or tips, given:L1 = 4.4 ft, L2 = 2 ft, θ = 30 °arrow_forward
- = The smooth pin P has a mass of 80 g. It is attached to an elastic cord extending from 0 to P and, due to the slotted arm guide, moves along the horizontal circular path r = (0.8 sin ) m. If the cord has a stiffness k 30 kN/m and an unstretched length of 0.25 m, determine the force of the guide and the normal force of the circular path on the pin when 0 = 60°. The guide has a constant angular velocity è = 5 rad/s. T P ė = 5 rad/s 0.arrow_forwardThe homogeneous cylinder A has a mass of 80 kg, and the mss of the hub can be neglected. The magnitude of the variable force P, is in newtons when t is in sec- onds. The velocity of body B changes from 2 m/s downward when t = 0 to 4 m/s downward t = 5 s. Determine the mass of B. Solve all questions using Impulse and Momentum methodsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY