
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
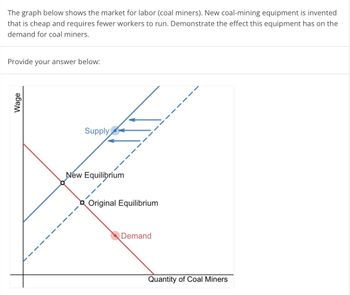
Transcribed Image Text:The graph below shows the market for labor (coal miners). New coal-mining equipment is invented
that is cheap and requires fewer workers to run. Demonstrate the effect this equipment has on the
demand for coal miners.
Provide your answer below:
Wage
Supply
New Equilibrium
Original Equilibrium
Demand
Quantity of Coal Miners
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which one of the following statements is incorrect? a) Equilibrium in a perfectly competitive labour market occurs where the demand for labour is equal to the supply of labour. b) Equilibrium in a perfectly competitive labour market occurs where the quantity of labour demanded is equal to the quantity of labour supplied. c) Equilibrium in a perfectly competitive labour market is the result of the interaction between the demand for labour and the supply of labour. d) The individual supply of labour bends backwards when the income effect becomes stronger than the substitution effect.arrow_forwardThe equilibrium quantity of labor increases and the equilibrium wage decreases when: A) labor supply shifts to the right, if wages are flexible, B) labor supply shifts to the left, if wages are flexible. C) labor demand shifts to the left, if wages are flexible. D) labor demand shifts to the right, if wages are flexible.arrow_forwardWorkers who produce good X were paid w = 2 dollars per hour. They form a union and negotiate a wage of w = 4 dollars per hour. Supply and demand in this market are given by Sx = 0.5px – w and Dx = 8 – 0.5px. Good X is a complement in consumption for good Y where Dy = 40 – 0.5py – px and Sy = 0.5py. Calculate the equilibrium price for good Y after the unionarrow_forward
- Suppose that a firm is producing in the short run with output given by: Q = 55L-L² The firm hires labor at a wage of $45 per hour and sells the good in a competitive market at P = $14 per unit. Find the firm's optimal use of labor. Enter as a value. ROUND TO THE NEAREST WHOLE NUMBER.arrow_forwardPlease answer with work on how to complete this problem.arrow_forwardCandice’s’ Cookies is a new cookie delivery company in Gainesville, Florida. The firm hires local college students to sell cookies door-to-door in higher income neighborhoods. Each of these “Sales Associates” sells cookies, which increases Candice’s Cookies’ total revenue, but must be paid an hourly wage. The graph below depicts Candice’s Cookies’ demand for labor curve when the retail price of a cookie is $2. Show Transcribed Text Part (i): Suppose that the retail price of a cookie is $2.50. What is the marginal product of the 4th Sales Associate? 1 cookie 2 cookies 3 cookies 4 cookies 5 cookies Part (ii): Suppose that the retail price of a cookie is $2.50. What is the marginal product of the 6th Sales Associate? 1 cookie 2 cookies 3 cookies 4 cookies 5 cookies Part (iii): Suppose that the retail price of a cookie is $2. What is the marginal product of the 8th Sales Associate? 1 cookie 2 cookies 3 cookies 4 cookies 5 cookiesarrow_forward
- The labor supply curve: Multiple Choice shows the number of firms that are willing and able to hire workers at each given wage. is made up of firms who want to hire workers at each given wage. shows that the number of firms that want to hire workers decreases as the wage increases. is made up of workers who want to work for firms at each given wage. In 2017, the city of Seattle passed legislation implementing a $15 per hour minimum wage. Critics of the plan argued that this legislation would increase: Multiple Choice cyclical unemployment. structural unemployment. frictional unemployment. real-wage unemployment.arrow_forwardEconomic theory suggests that an increase in the minimum wage will prompt firms to hire fewer low skill workers. true or falsearrow_forwardIn a competitive labor market, employers will not pay less than the market wage because at a wage below the equilibrium A) the equilibrium wage would rise B) they would not be able to hire anyone C) there would be a surplus of workers D) they would be inundated with excess workersarrow_forward
- Suppose the supply curve of lab assistants is given by w = 8 + 6E, while the demand curve is given by w = 40 – 2E. (Assume is in 000s of persons and w is the annual salary in thousands of dollars). Calculate the equilibrium wage and employment level.arrow_forwardQ5 - Q9 are related to the labour market in Australia. The following graph represents this labour market, where the vertical axis is the wage per hour and the horizontal axis is the number of workers employed (in millions). P Supply 30 25 19.84 Demand 8 12 15 The current minimum wage in Australia is $19.84 per hour. This minimum wage is a [ Select ] price floor. Under this minimum wage, the market wage rate is equal to [ Select ] per-hour and the number of workers employed is equal to [ Select ] million.arrow_forwardThe equilibrium wage rate in an industry is determined by a) whether workers or management are better at negotiating. b) finding where the market supply curve indicates that the substitution effect and income effect of a wage increase are offsetting. c) the strength of the substitution effect relative to the elasticity of demand for labor. d) the intersection of the market demand curve for labor and the market supply curve for labor.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education