
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
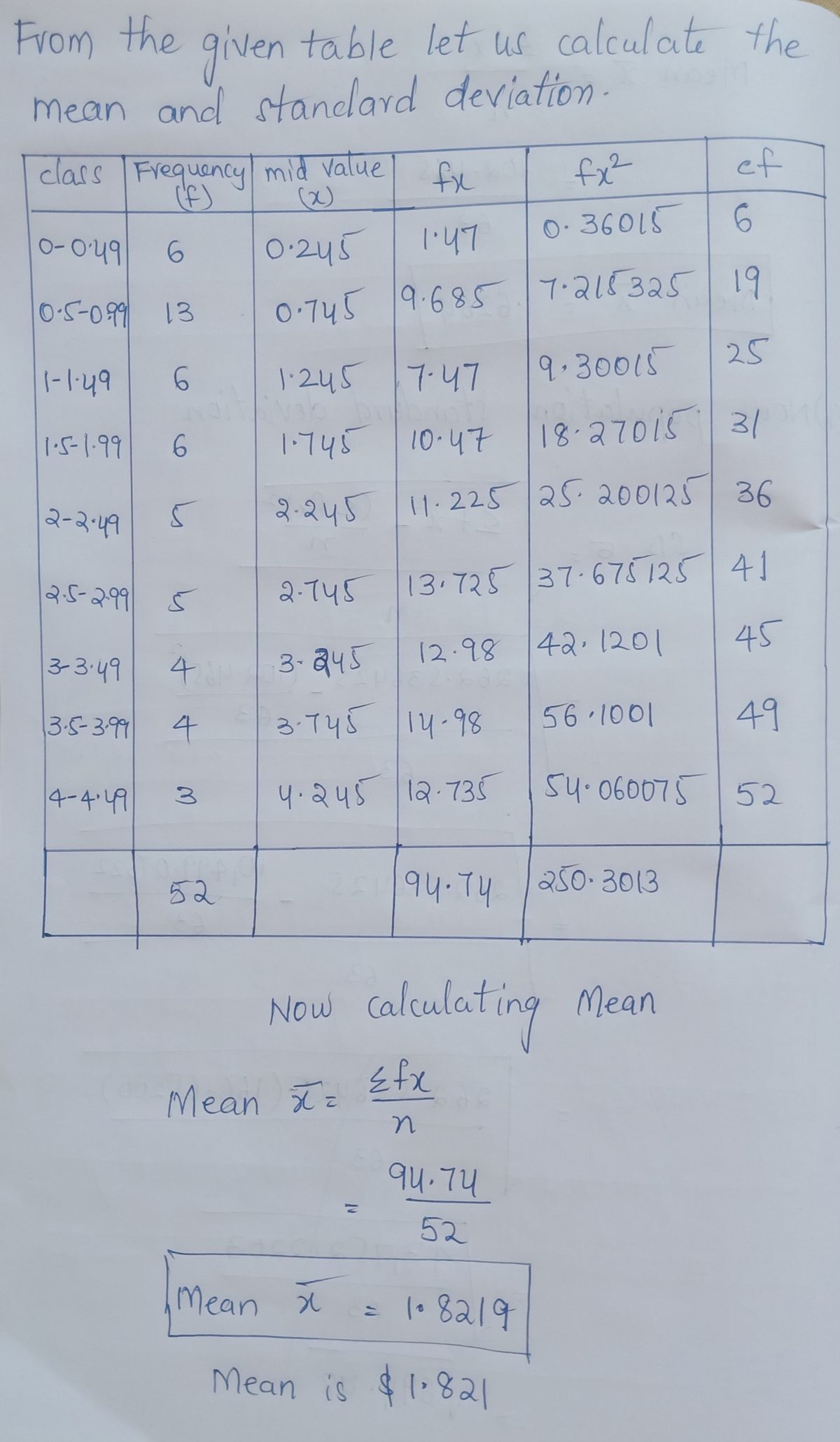
The frequency distribution was obtained using a class width of 0.5 for data on cigarette tax rates. Use the frequency distribution to approximate the population

Transcribed Image Text:The frequency distribution was obtained using a class width of 0.5 for data on cigarette tax rates. Use the frequency distribution to approximate the population mean and population standard deviation. Compare
these results to the actual mean u = $1.786 and standard deviation o = $1.174.
Click the icon to view the frequency distribution for the tax rates.
Frequency distribution of cigarette tax rates
The population mean is $.
Tax Rate
Frequency
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
0.00–0.49
0.50-0.99
13
The population standard deviation is $.
1.00–1.49
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
1.50–1.99
2.00–2.49
Compare these results to the values found using the actual data.
2.50-2.99
5
3.00–3.49
4
O A. The grouped mean is slightly smaller, while the grouped standard deviation is slightly larger.
3.50–3.99
4
B. The grouped values are both slightly larger.
4.00–4.49
O C. The grouped values are both slightly smaller.
D. The grouped mean is slightly larger, while the grouped standard deviation is slightly smaller.
Print
Done
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In a population, the data value 180 has a z score of -0.8. The standard deviation of this population is 32.36. What is the mean of the population?arrow_forwardThe table available below shows the costs per mile (in cents) for a sample of automobiles. At a = 0.01, can you conclude that at least one mean cost per mile is different from the others? E Click on the icon to view the data table. Let uss, HMs: HLS, Hsuv and HMy represent the mean costs per mile for small sedans, medium sedans, large sedans, SUV 4WDS, and minivans respectively. What are the hypotheses for this test? O A. Ho: µss = HMs = HLS = Hsuv = HMV Hạ: Hss HMS HLS HSuv HMv Advertising Scores O B. Ho: Hss = HMs = HLS = Hsuv = HMv Hạ: Not all the means are equal. O C. Ho: Not all the means are equal. Small sedan Medium sedan Large sedan SUV 4WD Minivan Ha: Hss = HMS = HLs= HSuv = HMv 55 62 64 77 63 59 69 69 68 51 O D. Ho: Hss # HMs# HLs HSUV HMV Hạ: Hss = HMS = HLs = Psuv = PMV 58 54 69 80 62 60 64 61 87 59 59 57 62 67 54 65 Click to select your answer and then click Check Answer. Print Done 3 parts remaining Clear All Check Answerarrow_forwardthe average hourly wage of production workers in manufacturing in 2007 was $17.41.Assume the variable is normally distributed. If the standard deviation of earning is$3.72, find the percent of production workers who Earned less than $14.00arrow_forward
- Rachael got a 660 on the analytical portion of the Graduate Record Exam (GRE). If GRE scores are normally distributed and have mean μ = 600 and standard deviation σ = 30, what is her standardized score?arrow_forwardAssume the birth weights at a local hospital have a normal distribution with a mean of 110 oz and a standard deviation of 15 oz. Draw a normal curve and label the mean and each value which is one, two, or three standard deviations above the mean. Then label each value which is one, two, or three standard deviations below the mean.arrow_forwardTable 1.6 A biologist measured the width(in mm) of the upper molar in 40 specimens(population) of a certain mammal. These results are given in the ff. fdt. Mean width(mm) frequency 5.5 3 5.8 10 6.1 15 6.4 8 6.7 3 7.0 1 Calculate the mean deviation(MD) and standard deviation(s) to the nearest hundredths. Choose the relationship which will describe the fdt in terms of variation. Group of answer choices A. None of the measures describes the variation. B. The standard deviation is more variable than the mean deviation. C. Equal variation. D. The mean deviation is more variable than the standard deviation.arrow_forward
- Draw by hand or in Excel fully labelled curves on a common scale to represent two sets of scores where: b. Mean = 50, Standard Deviation = 2, Mean = 50, Standard Deviation = 5. CUAarrow_forwardThe table available below shows the costs per mile (in cents) for a sample of automobiles. At a = 0.01, can you conclude that at least one mean cost per mile is different from the others? Click on the icon to view the data table. Let Hss, µms, HLs, Hsuy and μMy represent the mean costs per mile for small sedans, medium sedans, large sedans, SUV 4WDs, and minivans respectively. What are the hypotheses for this test? A. Ho: Hss HMS HLS="SUV HMV H₂: Not all the means are equal. = B. Ho: Hss HMS = μLS="SUV = HMV Ha: Hss #HMS # μLS *μSUV HMV OC. Ho: Not all the means are equal. Ha: Hss HMS HLS HSUV HMV Ho: Hss #HMS HLS ‡μSUV * µMV Ha: Hss HMS = μLS="SUV=MV What is the test statistic? FSTAT (Round to two decimal places as needed.) =arrow_forwardThe full question didn't fit in one part so I attached 2 photos.arrow_forward
- The table available below shows the weights (in pounds) for a sample of vacuum cleaners. The weights are classified according to vacuum cleaner type. At a = 0.10, can you conclude that at least one mean vacuum cleaner weight is different from the others? Click the icon to view the vacuum cleaner weight data. Let μBU, BLU, and μTC represent the mean weights for bagged upright, bagless upright, and top canister vacuums respectively. What are the hypotheses for this test? A. Ho: At least one of the means is different. Ha: MBUHBLUPTC B. Ho: "BU HBLU HTC # Ha: MBUHBLUPTC C. Ho: MBUHBLU = HTC Ha: At least one of the means is different. D. Ho: MBU - HBLU = μTC Ha: HBU #BLU HTC What is the test statistic? F = 12.56 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) What is the P-value? P-value = 0.000624 (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardSuppose that the distance of fly balls hit to the outfield (in baseball) is normally distributed with a mean of 250 feet and a standard deviation of 44 feet. Let X = distance in feet for a fly ball. Find the 80th percentile of the distribution of fly balls. (Round your answer to one decimal place.)arrow_forwardA successful basketball player has a height of 6 feet 11 inches, or 211 cm. Based on statistics from a data set, his height converts to the z score of 5.17. How many standard deviations is his height above the mean?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman