
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
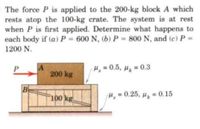
Transcribed Image Text:The force P is applied to the 200-kg block A which
rests atop the 100-kg crate. The system is at rest
when P is first applied. Determine what happens to
each body if (a) P = 600 N, (b) P = 800 N, and (c) P =
1200 N.
H, = 0.5, Hj = 0.3
200 kg
B
100 kg
H, = 0.25, µ̟ = 0.15
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I need help with #2arrow_forwardA 1.40 gram rubber-band starts as 90 mm long; 5.1 N stretches it to 150 mm long, but most kids use 18N to pull them to 300 mm long.The rubber-band used this way can launch a 43 gram chalk-board eraser so it travels 3.15 m (x) while it falls 0.92 m (y). Calculate the rubber-band's elastic PE before launching the eraser.arrow_forwardJum The mass of the block depicted in the image is 1.60 kg. The spring has a spring constant of 76.9 N/m. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the floor is 0.726. Assume that the spring makes no contact with the floor and therefore friction only acts on the block. How far must the block and spring assembly be compressed to just barely overcome the force of static friction acting on the block? Report your result in meters.arrow_forward
- Please answer within 90 minutes.arrow_forwardK L water M A 5.10 kg mass attached to a spring is travelling at a speed v; at point K, as shown above. While it is falling it is also being pushed by a spring (k = 475.00 N/m) compressed by 1.60 m (at point K). The mass travels 1.60 m (between K and L) then hits a pool of water at point L where the water exerts an average force of 54.80 N [upwards]. At point L the spring is no longer pushing and begins to stretch (in other words, at point L, x=0). The mass eventually stops at point M. If the distance between L and M is 7.45 m, determine the initial velocity of the mass (v;). Enter an answer with three digits and in S.I. units.arrow_forwardA spring (k = 1300 N/m) is used to stop a 1320 kg vehicle initially traveling at 4.1 m/s. How much is the spring displaced in doing this task? Δx = marrow_forward
- What is the power in kW produced by the La Rance tidal power station in France if the usable tidal range is 10 m? The barrage is 140m long and the area of the basin behind the barrage is 22 km2. Tidal period is 12h 25minutes. Density of salt water is 1020 kg/m3. Use proper units and 3 significant figures.arrow_forwardFigure MA mc Determine a formula for the magnitude of the force F exerted on the large block (mc) in the figure (Figure 1) so that the mass mA does not move relative to mc. Ignore all friction. Assume mp does not make contact with mc Express your answer in terms of the given quantities and appropriate constants. VE ΑΣΦ +m+m₂) • ( F = (MA !The correct answer does not depend on a. No credit lost. Try again. ?arrow_forwardDesign a "bungee jump" apparatus for adults. A bungee jumper falls from a high platform with two elastic cords tied to the ankles. The jumper falls freely for a while, with the cords slack. Then the jumper falls an additional distance with the cords increasingly tense. Assume that you have cords that are 8 m long, and that the cords stretch in the jump an additional 22 m for a jumper whose mass is 100 kg, the heaviest adult you will allow to use your bungee jump (heavier customers would hit the ground). (a) It will help you a great deal in your analysis to make a series of 5 simple diagrams, like comic strip, showing the platform, the jumper, and the two cords at the following times in the fall and the rebound: 1 while cords are slack (shown here as an example to get you started) 2 when the two cords are just starting to stretch 3 when the two cords are half stretched 4 when the two cords are fully stretched 5 when the two cords are again half stretched, on the way up On each diagram,…arrow_forward
- You have a light spring which obeys Hooke's law. This spring stretches 2.32 cm vertically when a 3.00 kg object is suspended from it. Determine the following. (a) the force constant of the spring (in N/m) _____N/m (b) the distance (in cm) the spring stretches if you replace the 3.00 kg object with a 1.50 kg object ______cm (c) the amount of work (in J) an external agent must do to stretch the spring 9.00 cm from its unstretched position ______Jarrow_forwardn with a force of 100 N, what is the most weight that the large piston can support? t ? GMA MINT 49. How many watts of power do you expend when you exert a force of 50 N that moves a crate 8 m in a time interval of 4 s? 50. Emily holds a banana of mass m over the edge of a bridge of height h. She drops the banana and it falls to the river below. Use conservation of energy to show that the speed of the banana just before hitting the water is v = √2gh. daid vil a. Speed b. KE c. PE 53. The roller coaster ride starts from rest at point A. Rank these quantities from greatest to least point: UJarrow_forwardA cylindrical tank, shown in the figure, has height 8 m and radius 4 m. Suppose the water tank is half-full of water. Determine the work required to empty the tank by pumping the water to a level 6 m above the top of the tank. Use 1000 kg/m³ for the density of water and 9.8 m/s² for the acceleration due to gravity. 4 m Draw a y-axis in the vertical direction (parallel to gravity) and choose the center of the bottom of the tank as the origin. For 0 ≤ y ≤8, find the cross-sectional area A(y). A(y) = (Type an exact answer, using as needed.) 8 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON