
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
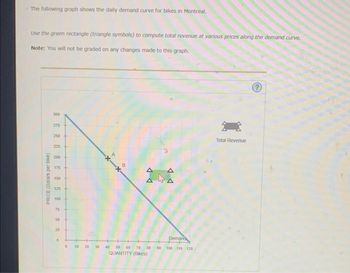
Transcribed Image Text:The following graph shows the daily demand curve for bikes in Montreal.
Use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to compute total revenue at various prices along the demand curve.
Note: You will not be graded on any changes made to this graph.
PRICE (Dollars per bike)
300
275
250
225
200
175
150
125
100
75
50
25+
D
0
10 20
30
4
B
40 50 60 70 00
QUANTITY (Bikes)
90
Demand
100 110 120
Total Revenue
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Define the elasticity of demand and illustrate how it works by giving 2 plausible examples from tourism industry. In addition, briefly answer the following question: Why are elasticities important for strategic decisions even though they are difficult to estimate? Why are elasticities typically not identical for different price and/or income levels?arrow_forwardPlease read attached article and then use it to answer the following questions. Do companies prefer to sell products that are more elastic or more inelastic? Briefly explain. What does the article describe as the best way to calculate price elasticity, and what other information is relevant to inform marketing efforts? Suppose a marketing company runs a market test and finds that the price elasticity equals -0.6. Would a company be more inclined to increase or to decrease price given this elasticity? Explain what would happen to quantity purchased (by how much it would change) and total revenue (would it increase, decrease, or stay the same) if the company were to decrease price by 10%.arrow_forwardThe demand curve for cameras is Q=400-2P where P is the price of a camera and Q is the number of cameras sold per week. Answer the following questions.A. If the vendor has been selling 120 cameras per week, how much revenue has she been collecting?B. What is the price elasticity of demand for cameras?C. Does the law of demand hold?D. If the vendor wants to generate more revenue, should she raise or lower the price of cameras?arrow_forward
- MicroEconomics Practice: Eric has a taco stand in downtown San Francisco. He wants to increase his total revenue. He knows that, when tacos are $1.00, he sells 20 an hour, and when he lowers the price to $0.75, he sells 25 an hour. (a) Calculate the price elasticity of demand for Jose's hotdogs using the midpoint formula. (show the formula and your calculations) (b) Is demand elastic or inelastic? How do you know? Explain your answer. (c) Using the price elasticity of demand calculated in section A, explain whether Eric should raise or lower the price to generate more revenue.arrow_forwardTOPIC: Supply and demandIn the market for widgets, the supply and demand curve are “normal” 45° lines. The equilibrium price is £5 and the equilibrium quantity is 10 widgets. Show in a new graph how your answers would change if the supply curve was infinitely inelastic.arrow_forwardTwo drivers—Kenji and Lucia—each drive up to a gas station. Before looking at the price, each places an order. Kenji says, “I'd like 10 gallons of gas.” Lucia says, “I'd like $10 worth of gas.” Why does Lucia's demand has an unit elasticity instead of an elasticity equal to infinity?arrow_forward
- Price (dollars) 8 7 D. 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Quantity (units per year) In the figure above, when the price falls from $8 to $7, total revenue A) decreases from $210 to $120 so demand is inelastic. B) increases from $120 to $210 so demand is inelastic. C) decreases from $210 to $120 so demand is elastic. D) increases from $120 to $210 so demand is elastic. 6arrow_forward10. Comics The demand curve for original Iguanawoman comics is given by (400 – p)² (0arrow_forwardUsing the midpoint formula and the graph below, calculate the following:i. The price elasticity of demand when the price changes from 9 to 15; andii. The price elasticity of supply when the price changes from $4 to $9arrow_forward6. Elasticity and total revenue The following graph shows the daily demand curve for bikes in San Francisco. Use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to compute total revenue at various prices along the demand curve. Note: You will not be graded on any changes made to this graph. *graph 1* On the following graph, use the green point (triangle symbol) to plot the annual total revenue when the market price is $30, $45, $60, $75, $90, $105, and $120 per bike. *graph 2* According to the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand between points A and B is approximately ___ . Suppose the price of bikes is currently $30 per bike, shown as point B on the initial graph. Because the demand between points A and B is ___ , a $15-per-bike increase in price will lead to ___ in total revenue per day. In general, in order for a price decrease to cause a decrease in total revenue, demand must be ____.arrow_forwardTwo drivers-Kevin and Maria-each drive up to a gas station. Before looking at the price, each places an order. Kevin says, "I'd like 10 gallons of gas." Maria says, "I'd like $10 worth of gas." Who's statement is elastic?arrow_forwardSuppose the own price elasticity of demand for good X is −2, its income elasticity is 3, its advertising elasticity is 4, and the cross-price elasticity of demand between it and good Y is −6. Determine how much the consumption of this good will change if:Instructions: Enter your responses as percentages. If you are entering a negative number, be sure to use a (−) sign.a. The price of good X decreases by 5 percent. percentb. The price of good Y increases by 10 percent. percentc. Advertising decreases by 2 percent. percentd. Income increases by 3 percent. percentarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education