
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
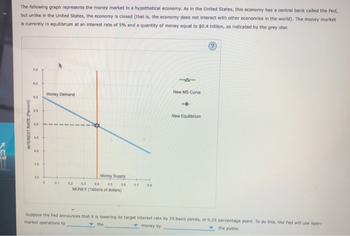
Transcribed Image Text:♫
The following graph represents the money market in a hypothetical economy. As in the United States, this economy has a central bank called the Fed,
but unlike in the United States, the economy is closed (that is, the economy does not interact with other economies in the world). The money market
is currently in equilibrium at an interest rate of 5% and a quantity of money equal to $0.4 trillion, as indicated by the grey star.
INTEREST RATE (Percent)
7.0
6.5
6.0
5.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
3.0
0
Money Demand
0.1
Money Supply
0.2 0.3 04
0.5
MONEY (Trillions of dollars)
0.6
0.7
0.8
14
New MS Curve
+
New Equilibrium
Suppose the Fed announces that it is lowering its target interest rate by 25 basis points, or 0.25 percentage point. To do this, the Fed will use open-
market operations to
money by
the public.
the
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose the money market for some hypothetical economy is given by the following graph, which plots the money demand and money supply curves. Assume the central bank in this economy (the Fed) fixes the quantity of money supplied. Suppose the price level decreases from 150 to 125. Shift the appropriate curve on the graph to show the impact of a decrease in the overall price level on the market for money. ? INTEREST RATE (Percent) 12 10 2 0 0 15 Money Supply Money Demand 30 45 60 MONEY (Billions of dollars) 75 90 Money Demand Money Supplyarrow_forwardSuppose that money demand is given by M = $Y(0.30-i) where $Y is $200 and i denotes the interest rate in decimal form. Also, suppose that the supply of money is $25. Calculate the equilibrium interest rate as a percent. The equilibrium interest rate is %. (Round your response to two decimal places.) If the Federal Reserve wants to increase the interest rate by 10 percentage points (0.1 in decimal form) over and above the equilibrium interest rate determined above, at what level should it set the money supply? The money supply should be set at $ (Round your response to one decimal place.)arrow_forwardThe following graph shows the market for federal reserves. The kinked orange curve Supply FF shows the supply of federal funds. It is vertical at the current amount of available reserves and flattens when the federal funds rate reaches the prevailing discount rate. The blue curve shows the demand for federal funds, which is downward sloping. Suppose that the prevailing federal funds rate is 2% and the discount rate is 4%. The current amount of bank reserves is $2 million. Suppose the Federal Reserve implements a contractionary policy by selling $1 million worth of government securities in open market operations. On the following graph, show the effect of a contractionary OMO on the Fed funds market. (Hint: Use the green points (triangle symbols) to plot the two-part supply curve and the grey point (star symbol) to show the new federal funds rate.) FEDERAL FUNDS RATE 5 0 0 The Market for Federal Reserves Supply FF 2 QUANTITY OF EXCESS RESERVES (Millions of Dollars) 3 As a result of a…arrow_forward
- The Fed has conducted expansionary monetary policy to combat a recession but is running up against the zero lower bound, and the economy is still not recovering. What other steps could the government take to try to stabilize the economy? Steps the government could take to stabilize the economy increase government spending raise real interest rates lower taxes increase transfer payments Steps the government should not or cannot take to stabilize the economy Answer Bank decrease government spending raise taxes lower real interest rates decrease transfer paymentsarrow_forward6. Changes in the money supply The following graph represents the money market for some hypothetical economy. This economy is similar to the United States in the sense that it has a central bank called the Fed, but a major difference is that this economy is closed (and therefore does not have any interaction with other world economies). The money market is currently in equilibrium at an interest rate of 3.5% and a quantity of money equal to $0.4 trillion, designated on the graph by the grey star symbol. INTEREST RATE (Percent) 5.5 5.0 New MS Curve Money Demand 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 0 0.1 0.2 Money Supply 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 MONEY (Trillions of dollars) New Equilibrium (?) Suppose the Fed announces that it is raising its target interest rate by 50 basis points, or 0.5 percentage points. To do this, the Fed will use open- market operations to the money by the public. Use the green line (triangle symbol) on the previous graph to illustrate the effects of this policy by placing…arrow_forward2. The theory of liquidity preference and the downward-slopingaggregate demand curve The following graph shows the money market in a hypothetical economy. The central bank in this economy is called the Fed. Assume that the Fed fixes the quantity of money supplied. Suppose the price level decreases from 90 to 75. Shift the appropriate curve on the graph to show the impact of a decrease in the overall price level on the market for money. 12 Money Supply 10 Money Demand Money Supply MD1 2 MD2 10 20 30 40 50 60 MONEY (Billions of dollars) INTEREST RATE (Percent)arrow_forward
- Part 1: Which of the following Fed actions will increase bank lending? Select one or more answers from the choices shown. The Fed raises the discount rate from 5 percent to 6 percent. The Fed raises the reserve ratio from 10 percent to 11 percent. The Fed buys $400 million worth of Treasury bonds from commercial banks. The Fed lowers the discount rate from 4 percent to 2 percent. (Helpful info)Note that Fed sets a discount rate that it charges to banks for short-term loans, which then contributes to the rate that the banks charge customers on their loans. While the Fed has the ability to issue Federal Reserve Notes, the paper currency used in the U.S. monetary system, they do not print the money. That task is still performed by the U.S. Mint. After the financial crisis of 2007-2008, Congress increased the Fed’s supervisory powers. Part 2: Describe tools that the US Treasury and the Federal Reserve use to undertake restrictive monetary policy today (versus before the…arrow_forwardScenario 2 Suppose the money demand is given by MdYx (0.4 - i) = where i is the interest rate. Suppose income Y totals 250. 9. Refer to Scenario 2. If the money supply is M³ = 25, what is the equilibrium interest rate? 10. Refer to Scenario 2. Suppose the Federal Reserve just met and decided they would like to decrease the interest rate by 4 percentage points (compared to the equilibrium rate you found in the previous question). What kind of monetary policy should it use, and what would the money supply have to equal to achieve that goal? (Your answer should be two items: first is expansion or contraction, the second is the actual amount the money supply should be.)arrow_forwardUse the information in the following table to answer the next question. In the table, investment is in billions. (1) Interest Rate (2) Investment (billions of dollars) (3) Investment (billions of dollars) 4% $100 $80 5 90 70 6 80 60 7 70 50 8 60 40 Suppose the Fed increases the interest rate from 5 percent to 6 percent. As a result of this increase in the interest rate, using column (2) investment will Multiple Choice increase by $20 billion. decrease by $10 billion. increase by $10 billion. decrease by $20 billion.arrow_forward
- Show the impact of the increase in government purchases on the interest rate by shifting one or both of the curves on the following graph. INTEREST RATE 12 10 8 2 0 0 20 Money Supply known as the Money Demand 40 60 80 MONEY (Billions of dollars) 100 120 = Money Demand Money Supply ? Suppose that for every increase in the interest rate of one percentage point, the level of investment spending declines by $0.5 billion. Based on the changes made to the money market in the previous scenario, the new interest rate causes the level of investment spending to by Taking the multiplier effect into account, the change in investment spending will cause the quantity of output demanded to by at every price level. The impact of an increase in government purchases on the interest rate and the level of investment spending is effect. Use the purple line (diamond symbol) on the graph at the beginning of this problem to show the aggregate demand curve (AD3) after accounting for the impact of the increase…arrow_forwardBriefly explain with the aid of two diagrams: one showing the money market and the second the Treasury bill market, how a Central bank conducts an expansionary open market operation in the money market. In your exposition, be careful to make clear the implications of the operation for the price of Treasury bills and the short-term rate of interest.arrow_forwardSuppose that, in an attempt to combat severe unemployment, the government decides to increase the amount of money in circulation in the economy. This monetary policy action ________(Decreases, Increases) demand for goods and services in the economy, leading to ________(Higher, Lower) prices for products. In the short run, the change in prices induces firms to produce ________(Fewer, morer) goods and services. This, in turn, leads to a ___________(Higher, Lower) unemployment level. Based on this analysis, the economy faces the following trade-off between inflation and unemployment: Higher inflation leads to _________(Higher, Lower) unemployment.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education