
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
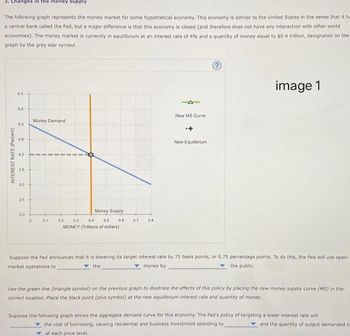
Transcribed Image Text:Changes in the money supply
The following graph represents the money market for some hypothetical economy. This economy is similar to the United States in the sense that it ha
a central bank called the Fed, but a major difference is that this economy is closed (and therefore does not have any interaction with other world
economies). The money market is currently in equilibrium at an interest rate of 4% and a quantity of money equal to $0.4 trillion, designated on the
graph by the grey star symbol.
INTEREST RATE (Percent)
6.0
5.5
5.0
45
4.0
35
3.0
25
20
0
Money Demand
0.1
Money Supply
0.2 03 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7
MONEY (Trillions of dollars)
08
4
New MS Curve
New Equilibrium
Ⓒ
image 1
Suppose the Fed announces that it is lowering its target interest rate by 75 basis points, or 0.75 percentage points. To do this, the Fed will use open-
market operations to
the
money by
the public.
Use the green line (triangle symbol) on the previous graph to illustrate the effects of this policy by placing the new money supply curve (MS) in the
correct location. Place the black point (plus symbol) at the new equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money.
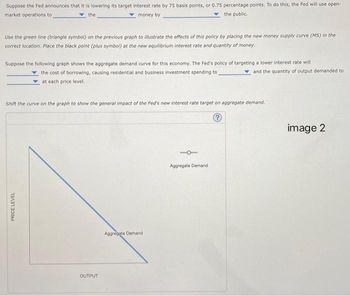
Suppose the following graph shows the aggregate demand curve for this economy. The Fed's policy of targeting a lower interest rate will
the cost of borrowing, causing residential and business investment spending to
at each price level.
and the quantity of output demanded to
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose the Fed announces that it is lowering its target interest rate by 75 basis points, or 0.75 percentage points. To do this, the Fed will use open-
market operations to
money by
the public.
the
Use the green line (triangle symbol) on the previous graph to illustrate the effects of this policy by placing the new money supply curve (MS) in the
correct location. Place the black point (plus symbol) at the new equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money.
Suppose the following graph shows the aggregate demand curve for this economy. The Fed's policy of targeting a lower interest rate will
the cost of borrowing, causing residential and business investment spending to
at each price level.
Shift the curve on the graph to show the general impact of the Fed's new interest rate target on aggregate demand.
?
PRICE LEVEL
OUTPUT
Aggregate Demand
and the quantity of output demanded to
Aggregate Demand
image 2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Briefly explain with the aid of two diagrams: one showing the money market and the second the Treasury bill market, how a Central bank conducts an expansionary open market operation in the money market. In your exposition, be careful to make clear the implications of the operation for the price of Treasury bills and the short-term rate of interest.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardINTEREST RATE (Percent) 3 6 Suppose the money market for some hypothetical economy is given by the following graph, which plots the money demand and money supply curves Assume the central bank in this economy (the Fed) fixes the quantity of money supplied. Suppose the price level decreases from 90 to 75. Shift the appropriate curve on the graph to show the impact of a decrease in the overall price level on the market for money. 18 Money Supply 15 12 0 0 10 20 30 Money Demand 40 50 60 MONEY (Billions of dollars) Money Demand Money Supply Ⓡarrow_forward
- Hey, I need help with the following macro question. Thank you in advance! Imagine that the chair of the Federal Reserve announced that, as of the following day, all currency in circulation in the United States would be worth 10 times its face denomination. For example, a $10 bill would be worth $100; a $100 bill would be worth $1,000; and so forth. Furthermore, the balances in all checking and savings accounts would be multiplied by 10. So, for example, if you had $500 in your checking account, as of the following day your balance would be $5,000. Would you actually be 10 times better off on the day the announcement took effect? Why or why not?arrow_forwardConsider an economy described by the following equations: Y = C + I + G Y = 6100 G = 1100 T = 1100 C = 1000 + .75(Y - T) I = 1100 - 60r in this economy compute private savings, public savings and national savings Find the equilibrium interest rate Now suppose that G rises to 1200. Compute private savings, public savings and national savings. Find the new equilibrium interest rate.arrow_forwardCould you add more information regarding the below statement? "The Federal Reserve System plays a massive role in not only the economy of the united states but alos in the global economy. The US dollar is one of the most popular and well recognized forms of currency all around the world, making it the basis for many financial transactions and trades. This popularity and standardization in regards to the dollar makes it one of if not the most important currency in the world, whose value has implications on nearly every aspect of trade, consumers, and even other countries wellbeing. Because of this, the fed, who has the ability to influence the value of the dollar and the economy, is likely the most important financial institution of the world, because of it's ability to severely impact both positively and negatively the united states economy and the world economy. With the recent inflation, I do think that the fed should take some action to mitigate the risk of any catastrophic…arrow_forward
- Suppose the Federal Reserve wants to fix the U.S. exchange rate with the yen at $0.008 per yen. If the equilibrium market exchange rate were significantly lower at $0.007 per yen, what would the Fed need to do to maintain the fixed rate of $0.008 per yen? What would be the effect of these actions on the money supply in the U.S.? Explain.arrow_forwardConsider the following closed economy: C = 30 + 0.87 x YD. 1= 2400 G = 2000 TR = 30 T = 0,40 x Y If there is a 80 increase in autonomous government expenditures, what is the change in government savings (assuming no change in the price level)? © Do not write the dollar ($) sign, and use a minus (-) in front of a decrease. Round your answer at two (2) decimals if necessary.arrow_forward#27 You saved $900 in currency in your piggy bank to purchase a new iPhone. The $900 you kept in your piggy bank illustrates money’s function as a _______. The iPhone’s price is posted as $900. The $900 price illustrates money’s function as a _____. You use the $900 to purchase the iPhone. This transaction illustrates money’s function as a ______. a medium of exchange, unit of account, store of value b medium of exchange, store of value, unit of account c store of value, medium of exchange, unit of account d store of value, unit of account, medium of exchangearrow_forward
- Let’s assume that the nominal Gross Domestic Product, GDP, of a hypothetical country is $45,000 and that the velocity of money of this country is 5. This implies that the money supply, in this country, is:arrow_forward3. Changes in the money supply The following graph represents the money market for some hypothetical economy. This economy is similar to the United States in the sense that it has a central bank called the Fed, but a major difference is that this economy is closed (and therefore does not have any interaction with other world economies). The money market is currently in equilibrium at an interest rate of 2.5% and a quantity of money equal to $0.4 trillion, designated on the graph by the grey star symbol. INTEREST RATE (Percent) 4.5 4.0 6 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 Money Demand + 0.1 Money Supply 0.3 0.5 0.6 MONEY (Trillions of dollars) 0.2 0.7 0.8 New MS Curve New Equilibrium ? Suppose the Fed announces that it is lowering its target interest rate by 75 basis points, or 0.75 percentage points. To do this, the Fed will use open- market operations to the money by the public. Use the green line (triangle symbol) on the previous graph to illustrate the effects of this policy by placing…arrow_forwardSuppose a hypothetical open economy uses the U.S. dollar as currency. The table below presents data describing the relationship between different real interest rates and this economy's levels of national saving, domestic investment, and net capital outflow. Assume that the economy is currently operating under a balanced government budget. Real Interest Rate (Percent) 7 REAL INTEREST RATE 10 2 0 6 0 5 4 3 2 National Saving (Billions of dollars) 45 40 20 35 30 25 20 Given the information in the table above, use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot the demand for loanable funds. Next, use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the supply of loanable funds. Finally, use the black point (cross symbol) to indicate the equilibrium in this market. Market for Loanable Funds 40 60 QUANTITY OF LOANABLE FUNDS 80 Domestic Investment (Billions of dollars) 30 35 40 45 50 100 55 。 Net Capital Outflow (Billions of dollars) -15 -10 -5 0 Demand Supply + 5 Equilibrium 10arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education