
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
The following figure represents a 3-nodes, two-element truss structure with identical cross-sectional area A = 100 mm2 and modulus E = 200 GPa for each element. It is supported by a pin at global node 1, an inclined roller at 135˚ at global node 2 and a horizontal roller at global node 3. A force P = 400 kN is applied at global node 2. Using the direct approach and the minimum number of linear finite elements, what would be the displacement at the global node 2 of the inclined roller in its local coordinate system?
Select one:
û2 = 8.32 mm
û2 = - 6.32 mm
û2 = 3.83 mm
û2 = 2.83 mm
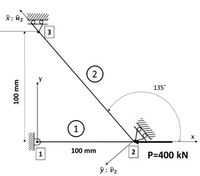
Transcribed Image Text:3
2
135'
1
100 mm
1
P=400 kN
100 mm
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- PE Problem for Module 2.1: Solve the complex truss below by the method of substitution. See component reactions at the supports. Match the axial bar force by ticking the circle that corresponds to your answer according to your solution. * 2m 16KN 4m 16 KN a 1m 4m 4m 10 KN 10 KNarrow_forwardQ1 (а) A hollow circular post ABC as shown in Figure Q1 (a) supports a load P, = 65B5 N acting at the top. P2 is applied around the cap plate at B. The outer diameters and thicknesses of the upper and lower parts of the post are dAB = 30 mm, tu =1A mm, dzc = 50 mm, and t3c =9 mm , respectively. A=1 B=0 (i) Calculate the normal stress o AR on the upper part of the post. (ii) If it is desired that the lower part of the post have the same compressive stress as the upper part, what should be the magnitude of the load P,? (111) If Pi remains at 65B5 N and P2 is now set at 10050 N, what is the new thickness of BC that will result in the same compressive stress in both parts?arrow_forwardplease help solve and explainarrow_forward
- A bridge truss extends x = 206 m across a river (shown in the figure below) where 8 = 39º. The structure is free to slide horizontally to permit thermal expansion. The structural components are connected by pin joints, and the masses of the bars are small compared with the mass of a 1340 kg car at the center. Calculate the force of tension or compression in each structural component (in N). B TAB = TAC = TBC = TBD TDE TDC= TEC = 11 N ---Select--- N ---Select--- N ---Select--- N ---Select--- N ---Select--- N ---Select--- N ---Select--- C X D Earrow_forwardThe channel shape cross-section and the rectangular cross-section shown in the Figure Q4 are made of materials with elastic-perfectly plastic behaviour. The yield stress of the material used for the channel shape cross-section is oy = 473 MPa, whereas that used for the rectangular cross- section is 0.850y. Compute the thickness of the web, t, of the channel shape section if the two cross sections have identical plastic bending moment about the z-axis. In Figure 4, h= 77 mm, b=46 mm, a=11 mm, H=77 mm, d= 46 mm N b h a + N a | d Harrow_forwardI need help with this review problem Engineering Statics Take F1 = 40 kN, F2 = 20 kN, and d = 8 m (a) Draw a free body diagram of the entire truss. (b) Find the support reaction at A (Give the x and y components) (c) Consider a cut through members CD, DI and HI. Draw the free body diagram of the left part of cut. (d) Use the FBD of the previous question to find the tensions in members CD, DI and HI.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY