
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
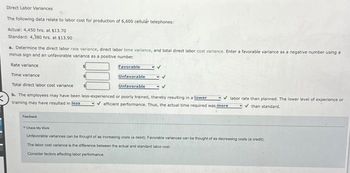
Transcribed Image Text:Direct Labor Variances
The following data relate to labor cost for production of 6,600 cellulár telephones:
Actual: 4,450 hrs. at $13.70
Standard: 4,380 hrs. at $13.90
a. Determine the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a
minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number.
Rate variance
Time variance
Total direct labor cost variance
b. The employees may have been less-experienced or poorly trained, thereby resulting in a lower
training may have resulted in less
Feedback
Favorable
Unfavorable
Unfavorable
✓labor rate than planned. The lower level of experience or
✓than standard.
✔efficient performance. Thus, the actual time required was more
Check My Wor
Unfavorable variances can be thought of as increasing costs (a debit). Favorable variances can be thought of as decreasing costs (a credit)
The labor cost variance is the difference between the actual and standard labor cost.
Consider factors affecting labor performance.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Acme Inc. has the following information available: Actual price paid for material Standard price for material Actual quantity purchased and used in production Standard quantity for units produced Actual labor rate per hour Standard labor rate per hour Actual hours Standard hours for units produced Variance Material Price NOTE: All dollar amounts are rounded to whole dollars and shown with "$" and commas as needed (i.e. $12,345). For the variance conditions, your answer is either "F" (for Favorable) or "U" (for Unfavorable) - capital letter and no quotes. Complete the following table of variances and their conditions: Material Quantity Total DM Cost Variance Labor Rate Labor Efficiency Total DL Cost Variance $1.00 $0.90 100 90 15 14 Variance Amount $ $ 200 190 Favorable (F) or Unfavorable (U)arrow_forwardDirect Materials Variances The following data relate to the direct materials cost for the production of 2,300 automobile tires: Actual: 50,800 Ib. at $2.05 Standard: 49,300 Ib. at $2.10 a. Determine the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. Price variance Favorable Quantity variance Unfavorable Total direct materials cost variance Unfavorable b. The direct materials price variance should normally be reported to the Purchasing Department V. If lower amounts of direct materials had been used because of production efficiencies, the variance would be reported to the Production Supervisor - V. If the favorable use of raw materials had been caused by the purchase of higher-quality raw materials, the variance should be reported to the Purchasing Departmentarrow_forwardPlease answer in text with all workingsarrow_forward
- Determine the variances for A, B, and C.arrow_forwardThe following data relate to the direct materials cost for the production of 1,800 automobile tires: Actual: 60,900 lb. at $1.70 Standard: 59,100 lb. at $1.75 a. Determine the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. Price variance $fill in the blank 1 Quantity variance $fill in the blank 3 Total direct materials cost variance $fill in the blank 5arrow_forwardDirect Materials Variances The following data relate to the direct materials cost for the production of 2,500 automobile tires: Actual: 51,100 lbs. at $1.75 per lb. Standard: 49,600 lbs. at $1.8 per lb. a. Determine the direct materials price variance, direct materials quantity variance, and total direct materials cost variance. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. Direct Materials Price Variance $fill in the blank 1 Direct Materials Quantity Variance $fill in the blank 3 Total Direct Materials Cost Variance $fill in the blank 5 b. The direct materials price variance should normally be reported to the . If lower amounts of direct materials had been used because of production efficiencies, the variance would be reported to the . If the favorable use of raw materials had been caused by the purchase of higher-quality raw materials, the variance should be reported to the .arrow_forward
- $6.00 per hour. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. Variance Amount Favorable/Unfavorable Controllable variance Volume variance Total factory overhead cost variance %24 %24 %24arrow_forwardDirect Labor Variances The following data relate to labor cost for production of 4,800 cellular telephones: Actual: 3,230 hrs. at $16.30 Standard: 3,180 hrs. at $16.60 a. Determine the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. Rate variance Time variance $1 Total direct labor cost variance $ b. The employees may have been less-experienced or poorly trained, thereby resulting in a labor rate than planned. The lower level of experience or training may have resulted in efficient performance. Thus, the actual time required was than standard.arrow_forwardvnfjarrow_forward
- 2. Acme Inc. has the following information available: Actual price paid for material Standard price for material Actual quantity purchased and used in production Standard quantity for units produced Actual labor rate per hour Standard labor rate per hour Actual hours Standard hours for units produced A. Compute the material price and quantity, and the labor rate and B. C. D. E. unfavorable variances. $1.00 $0.90 100 90 15 $ $ 16 200 220 efficiency variances. Describe the possible causes for this combination of favorable andarrow_forwardTrini Company set the following standard costs per unit for its single product Direct materials (30 pounds @ $4.40 per pound) Direct labor (6 hours @ $14 per hour) Variable overhead (6 hours @ $8 per hour) Fixed overhead (6 hours @ $11 per hour) $ 132.00 84.00 48.00 66.00 $ 330.00 Standard cost per unit Overhead is applied using direct labor hours. The standard overhead rate is based on a predicted activity level of 80% of the company's capacity of 50,000 units per quarter. The following additional information is available. Production (in units) Standard direct labor hours (6 DLH per unit) Budgeted overhead (flexible budget) Fixed overhead Variable overhead Operating Levels 70% 80% 90% 35,000 210,000 40,000 240,000 45,000 270,000 $ 2,640,000 $ 1,680,000 $ 2,640,000 $ 2,640,000 $ 1,920,000 $ 2,160,000 During the current quarter, the company operated at 90% of capacity and produced 45,000 units; actual direct labor totaled 266,000 hours. Units produced were assigned the following…arrow_forwardDirect Labor Variances The following data relate to labor cost for production of 6,800 cellular telephones: Actual: 4,610 hrs. at $13.6 Standard: 4,540 hrs. at $13.9 a. Determine the direct labor rate variance, direct labor time variance, and total direct labor cost variance. Enter a favorable variance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positive number. Rate variance $fill in the blank 1 Time variance $fill in the blank 3 Total direct labor cost variance $fill in the blank 5 b. The employees may have been less-experienced or poorly trained, thereby resulting in a labor rate than planned. The lower level of experience or training may have resulted in efficient performance. Thus, the actual time required was than standard.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education