
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
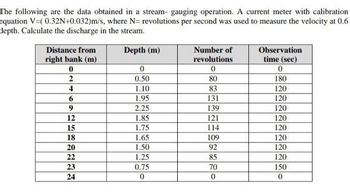
Transcribed Image Text:The following are the data obtained in a stream- gauging operation. A current meter with calibration
equation V=( 0.32N+0.032)m/s, where N= revolutions per second was used to measure the velocity at 0.6
depth. Calculate the discharge in the stream.
Distance from
right bank (m)
Depth (m)
Number of
Observation
revolutions
time (sec)
0
0
0
0
2
0.50
80
180
4
1.10
83
120
6
1.95
131
120
9
2.25
139
120
12
1.85
121
120
15
1.75
114
120
18
1.65
109
120
20
1.50
92
120
22
1.25
85
120
23
0.75
70
150
24
0
0
0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The velocity for an oil flow is defined by V= (0.5y³i+2j) m/s, where y is in meters. Part A What is the equation of the streamline that passes through point (1 m, 3 m)? Express your answer in meters in terms of z. IG] ΑΣΦ. 11 Ivec y = 12x + 15 Submit X Incorrect; Try Again; 9 attempts remaining Part B Previous Answers Request Answer z.y= Submit If a particle is at this point when t=0, at what point is it located when t-3.287 Express your answers in meters to three significant figures separated by a comma. VAX i vec ? Request Answer m ? marrow_forward1. The performance data of a water pump follow the curve fit Havailable =Ho +aV, where the pump's shutoff head Ho="K", coefficient a="Y" m/(Lpm)?, the units of pump head H are meters, and the units of Vare liters per minute (Lpm). The pump is used to pump water from one large reservoir to another large reservoir at a higher elevation. The free surfaces of both reservoirs are exposed to atmospheric pressure. The system curve simplifies to Hrequired =(Z2-Z1)+bV², where elevation difference z2-z1="X" m, and coefficient b = "L" m(Lpm)?. Calculate the operating point of the pump (a) V. operating and (b) Hoperating) in appropriate units (Lpm and meters, respectively). Read the equation carefully. (Zz-Z:) Но b a Y K L 0.0479 4.9 0.029arrow_forwardB. Water flows in a tapering pipe vertically as shown in Fig. 2. Determine the manometer reading 'h'. The flow rate is 100 litter s, take SG mercury = 13.6, and y=9810 N/m Fig. 2 06m d2= 01m Water dia 02m 2 h Mercuryarrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning