
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%

Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
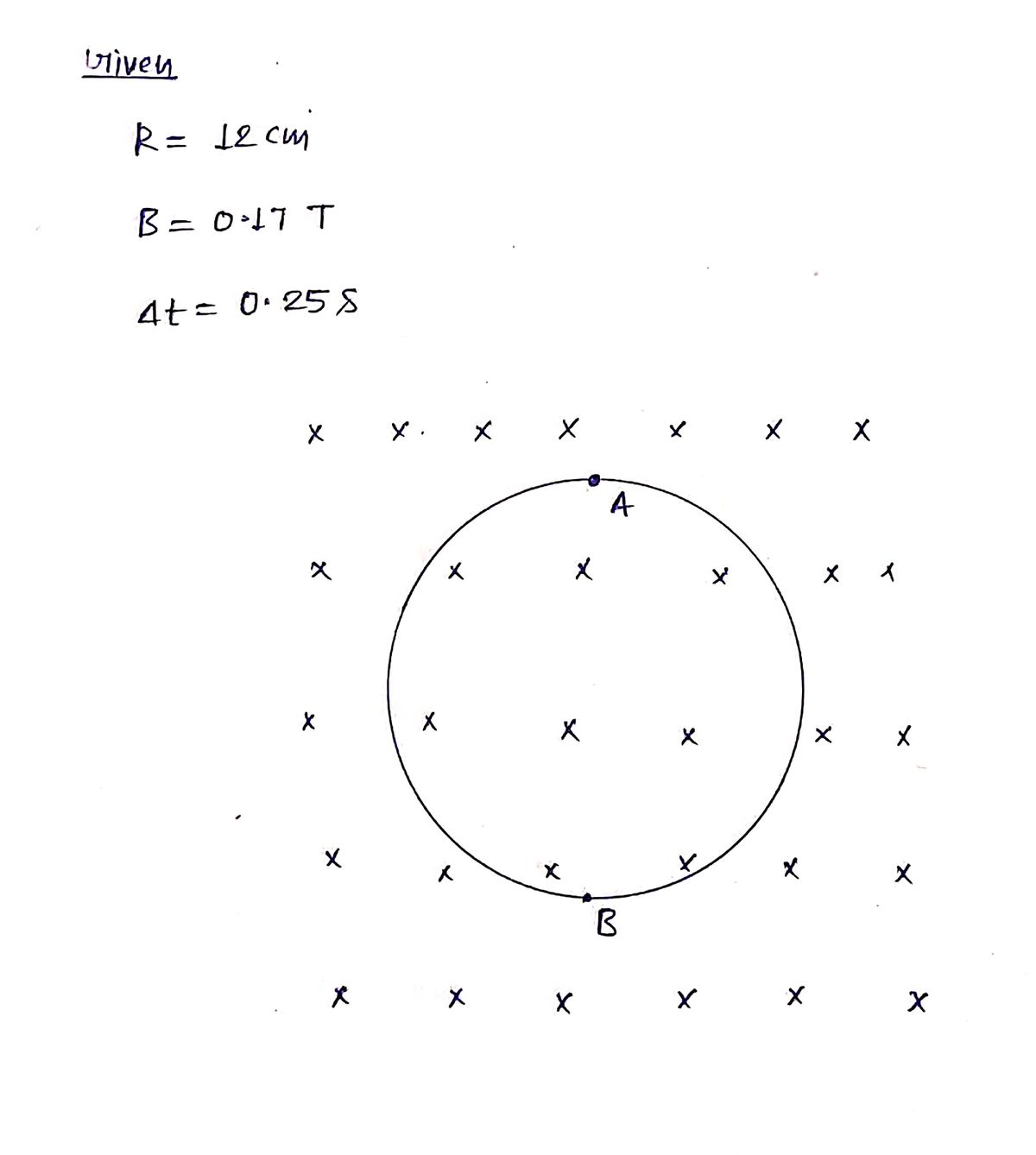
The flexible loop in the figure below has a radius of 12 cm and is in a magnetic field of strength 0.17 T. The loop is grasped at points A and B and stretched until its area is nearly zero. If it takes 0.25 s to close the loop, what is the magnitude of the average induced emf (in mV) in it during this time?
|E| = ________ mV
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows a circular loop situated in a uniform magnetic field. Green crosses represent the direction of the magnetic field, pointing into the plane of the loop. The loop is labeled at two points, A and B, which are the points where the loop is grasped to be closed. The arrows indicate the direction of manipulation.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A large power plant generates electricity at 12.0 kV. Its old transformer once converted the voltage to 360 kV. The secondary coil of this transformer is being replaced so that its output can be 770 kV for more efficient cross-country transmission on upgraded transmission lines.Randomized Variables V1 = 360 kVV2 = 770 kV a) What is the ratio of turns in the new secondary to the number of turns in the old secondary? b) What is the ratio of new current output to the old current output for the same power input to the transformer? c) If the upgraded transmission lines have the same resistance as the original ones, what is the ratio of new line power loss to the old?arrow_forwardThe flexible loop in the figure below has a radius of 10 cm and is in a magnetic field of strength 0.18 T. The loop is grasped at points A and B and stretched until its area is nearly zero. If it takes 0.17 s to close the loop, what is the magnitude of the average induced emf (in mV) in it during this time? |E| = X x X x x x X X X x mV XOAX Α X XB X В X X x x * X x x Oarrow_forwardA 2.00 cm diameter, 14.0 cm long solenoid has 60.0 turns and has a 1.00 cm diameter loop inside it. The loop has a resistance of 0.400 Ω. What is the current in the loop at 0.00600 s? The the maximum and the minimum current in the graph have the same magnitude which is 3.60 A.arrow_forward
- A loop of wire has a self-inductance of 5.5 mH. You pass a current of 9.0 Amps though the loop, and then drop the current to 0 at a contastant rate over 3.5 seconds. What is the EMF generated?arrow_forwardThe figure shows an LR circuit with L = 0.15 H, R = 25 Ω, and Vo = 36 V. The switch is initially open. Eight milliseconds (t = 8 ms) after the switch is closed, what is the current in the circuit and the potential difference between points a and b, Vab ?arrow_forwardIn the figure, R = 11.0 Ω, C = 6.82 μF, and L = 54.0 mH, and the ideal battery has emf = 32.0 V. The switch is kept in position a for a long time and then thrown to position b. What are the (a) frequency and (b) current amplitude of the resulting oscillations?arrow_forward
- Your physics professor is doing a demo to demonstrate Faraday’s law. He usesa 5m long wire of 10 Ohms total resistance, and he shapes it as a perfect square.Your professor places the loop in a plane perpendicular to a 2 Tesla uniformmagnetic field pointing from above into the plane of the loop. Then yourprofessor re-shaped the wire in five seconds from a square into a perfect circle.The new loop remains in the same plane.a. What is the magnitude of the average induced emf in the wire during thistime?b. Find the direction, and average magnitude of the current in the loopduring the deformation? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardW L X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X XX XXXX B 18 X X X X X X X X LB At t=0, a rectangular coil of resistance R = 2 ohms and dimensions w = 3 cm and L = 8 cm enters a region of constant magnetic field B = 1.6 T directed into the screen as shown. The length of the region containing the magnetic field is LB = 15 cm. The coil is observed to move at constant velocity v = 5 cm/s. What is the force required at time t = 0.8 sec to maintain this velocity? F(0.8 sec) = N Submitarrow_forwardTHANK YOUarrow_forward
- Problem 1. The wire is moving to the left with a linear velocity of 10 m/s as shown. Determine the magnitude and direction of the emf induced in the wire. Include a brief explanation. X X 45° Xv = 10 m/s 1=0.25 m X, X B= 02 T, into the page XE Xarrow_forwardA circular loop with a radius of 0.21 m is rotated by 90.0° over 0.210 s in a uniform magnetic field with B = 1.40 T. The plane of the loop is initially perpendicular to the field and is parallel to the field after the rotation. (a) What is the average induced emf in the loop? V(b) If the rotation is then reversed, what is the average induced emf in the loop? Varrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON