
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
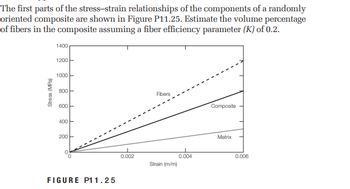
Transcribed Image Text:The first parts of the stress-strain relationships of the components of a randomly
oriented composite are shown in Figure P11.25. Estimate the volume percentage
of fibers in the composite assuming a fiber efficiency parameter (K) of 0.2.
Stress (MPa)
1400
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
I
T
FIGURE P11.25
0.002
Fibers
Strain (m/m)
0.004
Composite
Matrix
0.006
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Figure 3 shows a cross-sectional shape of a composite beam. (a) Determine the moment of inertia with respect to y-axis. (b) Determine the radius of gyration of the composite body (ky). 5 mm 15 mm 10 15 15 10 mm mm mm mm Figure 3 5 mm 15 mm 5 mm 50 mm 15 mm Xarrow_forwardpls show me a solution.arrow_forwardFor a continuous and oriented fiber-reinforced composite, the moduli of elasticity in the longitudinal and transverse directions are 19.7 and 3.66 GPa (2.8x10 and 5.3x 105 psi), respectively. If the volume fraction of fibers is 0.42, determine the moduli of elasticity of fiber and matrix phases. Em- E₁= i GPa GPaarrow_forward
- Question 2 Calculate the bending stress at the bottom edge of the following composite beam subject to a bending moment of M= 1500 Nm. The lower section is made from steel (E = 200 GPa) and the upper section is made from aluminium (E = 70 GPa). All dimensions are in mm. 100 YA 100 Z 10 >arrow_forwardASAParrow_forwardA composite sample of carbon reinforced epoxy has dimensions of in 20 in x 20 in x 0.135 in and mass of 3 lb. The carbon fibres have a modulus of elasticity of 80(106) lb/in2 and a density of 0.15 lb/in3. The epoxy matrix has modulus of elasticity of 0.90(106) lb/in2 and a density of 0.05 lb/in3. Assume there are no voids in the sample, calculate the volume fraction of: (i) The carbon fibres (ii) The epoxy matrix in the sample.arrow_forward
- The composite shaft shown consists of a solid brass segment (1) and a solid aluminum segment (2) that are connected at flange B and securely attached to rigid walls at A and C. Brass segment (1) has a diameter of 18 mm, a length of L₁ 235 mm, and a shear modulus of 39 GPa. Aluminum segment (2) has a diameter of 24 mm, a length of L₂ = 165 mm, and a shear modulus of 28 GPa. If a concentrated torque of 270 N-m is applied to flange B, determine (a) the maximum shear stress magnitudes in segments (1) and (2). (b) the rotation angle of flange B relative to support A. N 235 mm (1) B 165 mm Partial Ans: Max shear stress in Member 1 is 55.7 MPa 270 N-m (2)arrow_forward= 12 mm. The The following figure depicts an aluminum I beam of height h = 0.25 m, width b = 0.2 m, flange thickness ta = 16 mm, and web thickness tw beam is reinforced by two layers of unidirectional composite material of thickness to = 5 mm. The section is subjected to an axial force N₁ = 500 kN. The Young's moduli for the aluminum and unidirectional composite are Ea 73 GPa and Ec 140 GPa, respectively. = (a) Compute the axial stiffness for this structure. (b) Compute the maximum axial stress in both the aluminum and composite layers. CS Scanned with CamScanner 1₁ I h t₂ I b poarrow_forwardA composite beam made of steel and bronze has the cross section shown. The cross-sectional dimensions are b1 = 0.5 in, b2 = 1.5 in., and d = 1.0 in. The elastic modulus of the steel is E1 = 30,000 ksi, and its allowable bending stress is 24 ksi. The elastic modulus of the bronze is E, = 15,000 ksi, and its allowable bending stress is 16 ksi. Calculate the magnitude of the allowable bending moment that can be applied about the z centroidal axis. y Bronze (2) Steel (1) bị b2 Answer: M = i Ib-in. Save for Later Attempts: 0 of 1 used Submit Answerarrow_forward
- A fiber-reinforced polymer composite under isostrain condition consists of 35% fibers and 45% polymer by volume. The moduli of elasticity of the fibers and the polymer are 260 GPa and 3.4 GPa, respectively, and the Poisson’s ratios of the fibers and the polymer are 0.25 and 0.41, respectively. Calculate the following:a. modulus of elasticity of the composite.b. percentage of load carried by the fibersc. Poisson’s ratio of the compositearrow_forwardCalculate the modulus of elasticity of fiberglass under isostrain condition if the fiberglass consists of 70% E-glass fibers and 30% epoxy by volume. Also, calculate the percentage of load carried by the glass fibers. The moduli of elasticity of the glass fibers and the epoxy are 70.5 and 6.9 GPa, respectively. If a longitudinal stress of 60 MPa is applied on the composite with a cross-sectional area ofm300 mm2, what is the load carried by each of the fiber and the matrix phases? What is the strain sustained by each of the fiber and the matrix phases?arrow_forward4arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning