
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
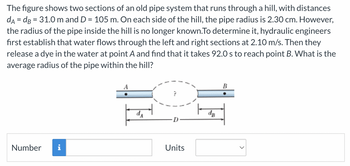
Transcribed Image Text:The figure shows two sections of an old pipe system that runs through a hill, with distances
dA = dB = 31.0 m and D = 105 m. On each side of the hill, the pipe radius is 2.30 cm. However,
the radius of the pipe inside the hill is no longer known.To determine it, hydraulic engineers
first establish that water flows through the left and right sections at 2.10 m/s. Then they
release a dye in the water at point A and find that it takes 92.0 s to reach point B. What is the
average radius of the pipe within the hill?
Number i
Units
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 0 Jorge wishes to observe the progress of his vacuum pump in evacuating a tall bell jar for the purpose of demonstrating that sound waves do not travel in a vacuum. So, Jorge places a mercury barometer inside the bell jar and follows the height of the mercury column as the pump chugs away. The density of mercury is 1.36 × 104 kg/m³ and the standard atmospheric pressure is 1.01 × 105 Pa. The acceleration g due to gravity is 9.81 m/s². When he observes a height of 7.89 mm of mercury, what fraction of atmospheric pressure, expressed as a percentage P, has Jorge achieved in his bell jar? P = %arrow_forwardHow do you solve this?arrow_forwardWater moves through a constricted pipe in steady, ideal flow. At the lower point, the pressure is P, = 1.75 x 104 Pa and the pipe diameter is 6.00 cm. At another point y = 0.250 m higher, the pressure is P2= 1.20 x 104 Pa and the inner pipe diameter is 3.00 cm. Find the speed of flow (a) in the lower section and (b) in the upper section. (c) Find the volume flow rate through the pipe. %3D P2arrow_forward
- Water moves through a constricted pipe in steady, ideal flow. At the lower point shown in the figure below, the pressure is 1.85 x 105 Pa and the pipe radius is 2.70 cm. At the higher point located at y = 2.50 m, the pressure is 1.27 x 105 Pa and the pipe radius is 1.30 cm. P₂ 66°F Clear P₁ (a) Find the speed of flow in the lower section. 14 X Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 100%. m/s (b) Find the speed of flow in the upper section. 35.6 X Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 100%. m/s (c) Find the volume flow rate through the pipe. 0.010 m³/s Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 100%. m Submit Answer * 2 # Search % 3 5 6 hp + 144 & 7 8 9 回 10:45 PM 4/12/2024 PRE pri scarrow_forwardThe lower section of a constricted pipe has a diameter of 8 cm. The upper section of the pipe, located 0.1 m above the lower section, has a diameter of 3 cm. The pressure at the lower section is 2.1 ×× 104 Pa, while the pressure in the upper section is 1 ×× 104 Pa. Assuming water moves through the pipe in a steady flow, calculate the speed (in m s-1) of the flow in the lower section. The density of water is 1000 kg m-3.arrow_forwardSolvearrow_forward
- Suppose it takes you 2 minutes and 13 seconds to swim 8 lengths of a 25.0 meter swimming pool (out and back 4 times, ending up where you started). What is your average velocity during this time interval? What is your average speed during this time interval? options: 0 m/s 3.0 m/s 1.5 m/sarrow_forwardQ.2. When an oblique shock strikes a solid wall, it reflects as a shock of sufficient strength to cause the exit flow M3 to be parallel to the wall, as in the figure. For airflow with M1 = 2.5 and p1 = 100 kPa, compute M3, p3 and the angle Ø. M2 M, = 2.5 M3 40°arrow_forward1. (a) Derive an alternative set of SI units for pressure that is equivalent to N/m ². (b) The figure below shows the displacement s versus time t graph for an object moving along a straight line. s (m) 3 A 10 4 N 15 (i) Discuss the motion of the object. (ii) Estimate the displacement of the object in 10 s. (iii) Sketch the velocity versus time graph for the motion of the object. (b) The figure below shows the displacement s versus time t graph for an object moving along a straight line. 2 A 10 s (m) -1 -2 15 t(s) (i) Discuss the motion of the object. (ii) Estimate the displacement of the object in 10 s. (iii) Sketch the velocity versus time graph for the motion of the object.arrow_forward
- A solid metal sphere of volume 0.722 m³ is lowered to a depth in the ocean where the water pressure is equal to 4.02 x 107 N/m². What is the change in the volume of the sphere? The atmospheric pressure is 1.013 × 105 Pa and the bulk modulus of the metal from which the sphere is made is 1.27 x 10¹⁰ N/m². Answer in units of m³. Your response... Previous Responses X #1.0.00228 PALETTEarrow_forwardA firefighter mounts the nozzle of his fire hose a distance 32.1 m away from the edge of a burning building so that it sprays from ground level at a 45° angle above the horizontal. After quenching a hotspot at a height of 9.33 m, the firefighter adjusts the nozzle diameter so that the water hits the building at a height of 17.5 m. By what factor was the nozzle diameter changed? Assume that the flow rate of water through the hose stays the same, and treat the water as an ideal fluid. factor by which the hose diameter changed:arrow_forwardThe density of water is 1.00 × 10³ kg/m³, and the density of mercury is 1.36 × 10¹ kg/m³. Calculate the absolute pressure på at the bottom of a 0.250-m tall graduated cylinder that is one-fourth full of mercury and three-fourths full of water. Pb = Paarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON