
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
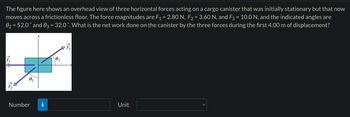
Transcribed Image Text:The figure here shows an overhead view of three horizontal forces acting on a cargo canister that was initially stationary but that now
moves across a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes are F₁ = 2.80 N, F₂ = 3.60 N, and F3 = 10.0 N, and the indicated angles are
0₂ = 52.0° and 03 = 32.0 ˚. What is the net work done on the canister by the three forces during the first 4.00 m of displacement?
15
15
Number
03
F
F3
Unit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 41 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Starting from rest, a 5.40-kg block slides 3.40 m down a rough 30.0° incline. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline is µ, = 0.436. (a) Determine the work done by the force of gravity. (b) Determine the work done by the friction force between block and incline. (c) Determine the work done by the normal force. (d) Qualitatively, how would the answers change if a shorter ramp at a steeper angle were used to span the same vertical height?arrow_forwardThe spring-flex exercise system consists of a spring with one end fixed and a handle on the other end. The idea is that you exercise your muscles by stretching the spring from its natural length, which is 38 cm. If a 170 Newton force is required to keep the spring stretched to a length of 52 cm, how much work is required to stretch it from 51 cm to 70 cm? Your answer must include the correct units. Work =arrow_forwardA block is displaced vertically by Ar = 2.5 m under the influence of three forces, F = 4.0 N, FR = 6.0 N, and F = 8.0 N as shown in the diagram. The angles 0c = 15°. There are no other forces acting on the block. What is the net work done by these three forces on the block? FB %3D %3D %3D 0c FA W = FArcos(0)arrow_forward
- The spring-flex exercise system consists of a spring with one end fixed and a handle on the other end. The idea is that you exercise your muscles by stretching the spring from its natural length, which is 48 cm. If a 200 Newton force is required to keep the spring stretched to a length of 66 cm, how much work is required to stretch it from 62 cm to 76 cm? Your answer must include the correct units. Work=arrow_forwardThe figure shows three forces applied to a trunk that moves leftward by 3.23 m over a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes are F1 = 4.70 N, F2 = 8.63 N, and F3 = 3.16 N, and the indicated angle is 0 = 60°. (a) During the displacement, what is the net work done on the trunk by the three applied forces, the gravitational force, and the normal force? (b) Is there a net transfer of energy to or from the trunk? (c) Does the kinetic energy of the trunk increase or decrease? (a) Number i Units (b) (c) >arrow_forwardThe figure here shows an overhead view of three horizontal forces acting on a cargo canister that was initially stationary but that now moves across a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes are F₁ = 2.60 N, F₂= 3.60 N, and F3 = 10.0 N, and the indicated angles are 02 = 49.0° and 93 = 30.0°. What is the net work done on the canister by the three forces during the first 3.90 m of displacement? 8₂ 03 Number i 11 Unit Jarrow_forward
- The figure below shows an overhead view of three horizontal forces acting on a cargo canister that was initially stationary but that now moves across a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes are F1 = 3.10 N, F2 = 4.10 N, and F3 = 20.0 N, and the indicated angles are 02 = 50.0° and 03 = 34.0°. What is the net work done on the canister by the three forces during the first 4.00 m of displacement? Additional Materialsarrow_forward2.55 N, and the indicated angle The figure shows three forces applied to a trunk that moves leftward by 3.28 m over a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes are F1 is e = 60°. (a) During the displacement, what is the net work done on the trunk by the three applied forces, the gravitational force, and the normal force? (b) Is there a net transfer of energy to or from the trunk? (c) Does the kinetic energy of the trunk increase or decrease? 5.03 N, F2 = 8.83 N, and F3 (a) Number Units (b) (c)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON