Question
A book starts at rest. If Fa=20.0 N, the mass of the book is 3.00 kg, θ=30º and d = 6.2 m, determine the speed of the book at the end of the displacement. Use g = 10 Kg/m. Hint: Determine the net force (applied force net gravity) in the direction of displacement and then multiply by the displacement. Use the work energy theorem to get speed.
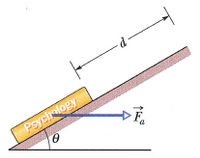
Transcribed Image Text:Psychelogy
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The figure shows a block of mass 10 Kg. Determine what work will be done by the force F that will lift said block with constant speed to a height of 18 m. µ = 0.3 a. 2931 J b. 4870 J c. 61 J d. 37 J e. 1262 Jarrow_forward. A box with a mass of 3.00 kg is pushed a distance of 2.0 m by a horizontal force of 12.0 N across a frictionless table. Determine the work done by: a) the applied force b) the normal force c) the force of gravity d) the net force on the blockarrow_forwardA mechanic pushes a 3850 kg car from rest to a speed of v, doing 5083 J of work in the process. Find the speed v. Neglect friction between car and road. Answer in units of m/s.arrow_forward
- With a starting velocity of 2 m/s to the right, you drag a 30.0 kg box for 4 meters. Your force is 200.0 N and the box's final velocity is 1.15 m/s to the right. Friction does -840 J of work. What is the force of friction?arrow_forwardA lunch plate has a mass of 590g. It is pushed 90.0cm along a dining table by a constant force of F= 3.60N directed at an angle of 26.0 degrees below the horizontal, as shown in the picture below. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the plate and the table's surface is 0.440, figure out; a. the normal force exerted on the plate by the table. b. the work done by the applied force F. c. the work done by the force of kinetic friction. F 90 cmarrow_forwardThe figure here shows an overhead view of three horizontal forces acting on a cargo canister that was initially stationary but that now moves across a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes are F₁ = 2.60 N, F₂= 3.60 N, and F3 = 10.0 N, and the indicated angles are 02 = 49.0° and 93 = 30.0°. What is the net work done on the canister by the three forces during the first 3.90 m of displacement? 8₂ 03 Number i 11 Unit Jarrow_forward
- The figure here shows an overhead view of three horizontal forces acting on a cargo canister that was initially stationary but that now moves across a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes are F₁ = 2.80 N, F₂ = 3.60 N, and F3 = 10.0 N, and the indicated angles are 0₂ = 52.0° and 03 = 32.0 ˚. What is the net work done on the canister by the three forces during the first 4.00 m of displacement? 15 15 Number 03 F F3 Unitarrow_forwardThe figure below shows an overhead view of three horizontal forces acting on a cargo canister that was initially stationary but that now moves across a frictionless floor. The force magnitudes are F1 = 3.10 N, F2 = 4.10 N, and F3 = 20.0 N, and the indicated angles are 02 = 50.0° and 03 = 34.0°. What is the net work done on the canister by the three forces during the first 4.00 m of displacement? Additional Materialsarrow_forwardSuppose the ski patrol raises a rescue sled and victim, having a total mass of 85.0 kg, up a ? = 62.0° slope at constant speed, as shown in the figure. DO NOT USE THE ANGLE SHOWN IN THE FIGURE! USE THE ANGLE IN THE PROBLEM STATEMENT ABOVE. The coefficient of friction between the sled and the snow is 0.130. Calculate the normal force on the sled (in N). Calculate the work done (in J) by the force of friction as the sled moves 30.0 m up the hill. (Hint: Think about the direction of the friction force. Should it be different than the direction shown in the figure?). Calculate the work done (in J) by the tension force in the rope on the sled over this distance. Calculate the work done (in J) done by the force of gravity on the sled over this distance.arrow_forward
- The concepts in this problem are similar to those in Multiple-Concept Example 4, except that the force doing the work in this problem is the tension in the cable. A rescue helicopter lifts a 82.3-kg person straight up by means of a cable. The person has an upward acceleration of 0.668 m/s² and is lifted from rest through a distance of 9.10 m. (a) What is the tension in the cable? How much work is done by (b) the tension in the cable and (c) the person's weight? (d) Use the work-energy theorem and find the final speed of the person. t touarrow_forward1)A block with a mass of 44.0 kg is pushed with a horizontal force of 150 N. The block moves at a constant speed across a level, rough surface a distance of 6.65 m. Please draw and show your free body diagrams in your answers. This will also help you to solve the problem! (a)What is the work done (in J) by the 150 N force? (b)What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios