
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
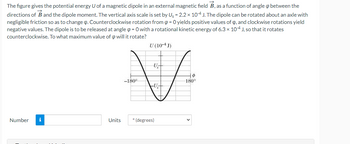
Transcribed Image Text:The figure gives the potential energy U of a magnetic dipole in an external magnetic field B, as a function of angle between the
directions of B and the dipole moment. The vertical axis scale is set by Us = 2.2 × 10-4 J. The dipole can be rotated about an axle with
negligible friction so as to change . Counterclockwise rotation from @= 0 yields positive values of Q, and clockwise rotations yield
negative values. The dipole is to be released at angle =0 with a rotational kinetic energy of 6.3 x 10-4 J, so that it rotates
counterclockwise. To what maximum value of 0 will it rotate?
U (10-4 J)
Number
i
Units
-180°
U₂
U₁
° (degrees)
0
180°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A small circular coil consisting of 19 turns of wire lies in a uniform magnetic field whose magnitude is 0.49 T such that the normal to the plane of the coil makes an angle of 60° with the direction of B. The radius of the coil is 4.0 cm, and it carries a current of 3.2 A. (a) What is the magnitude of the magnetic moment of the coil? A m2 (b) What is the magnitude of the torque exerted on the coil? N.marrow_forwardA particle with an unknown mass and charge moves with a constant speed of v = 2.2 x 106 m/s as it passes un-deflected through a pair of parallel plates as shown. The plates are separated by a distance of d = 5.0 x 10-3m, and a constant potential difference V is maintained between them. A uniform magnetic field of B = 1.20 T directed into the page exists between the plates and to the right of them as shown. After the particle passes into the region to the right of the plates where only the magnetic field exists, its trajectory is circular with radius r = 0.10 m. Determine the charge sign and charge/mass ratio of the particle, and the electric field direction and potential difference magnitude for plates.arrow_forwardA permanent magnet has a magnetic dipole moment of 0.160 A · m2. The magnet is in the presence of an external uniform magnetic field (provided by current-carrying coils) with a magnitude of 0.0800 T, which makes an angle of 29.0° with the orientation of the permanent magnet.(a)What is the magnitude of the torque (in N · m) on the permanent magnet? N.m (b)What is the potential energy (in J) of the system consisting of the permanent magnet and the magnetic field provided by the coils? Jarrow_forward
- Doubly-ionized particles with an atomic mass of 59.4 u are moving due N at a speed of 7.78 x 105 m/s when they enter a uniform magnetic field of strength, B = 35.5 mT. The ions, which are moving perpendicular to the field, follow a circular path of radius, r, and travel north a distance, h = 2.02 m, before leaving the field at an angle, 0, as shown in the figure. (a) What is the radius of the ions' circular path? m (b) At what angle do the ions leave the field? 0 = h 2arrow_forwardProblem 10: A magnetic needle with magnetic moment μ-0.065 Am2 is placed in a uniform magnetic field B0.65 T as shown in the figure. The angle between the direction of the magnetic moment and the direction of the magnetic field is θ 250 Randomized Variables μ= 0.065 Arn B- 0.65T θ 250 Δ Part (a) Express the potential energy U in terms oft, B, θ. | cos(p) sin(p) | cos(α) sin(a) cos(0) sin(0) ( HOMI 4 5 6 BACKSPACE CLEAR Submit Hint I give up! Hints: 1% deduction per hint. Hints remaining: 1 Feedback: 1% deduction per feedback. Part (b) Calculate the numerical value of U in J. Part (c) If θ can be changed, which value has the minimum potential energy? Part (d) If θ can be changed, which value has the maximum potential energy in degrees? Δ Part (e) Ignore the mass of the needle, express the work needed to change the angle from θ to α in terms oftı, B, θ, α Part (f) If α-1500, calculate the numerical value of the work in J.arrow_forwardA student makes a short electromagnet by winding 390 turns of wire around a wooden cylinder of diameter d = 4.1 cm. The coil is connected to a battery producing a current of 4.1A in the wire. (a) What is the magnitude of the magnetic dipole moment of this device? (b) At what axial distance z>> dwill the magnetic field have the magnitude 4.8 µT (approximately one-tenth that of Earth's magnetic field)? (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- The image below shows a mass spectrometer, an analytical instrument used to identify the various molecules in a sample by measuring their charge-to-mass ratio e/m. The sample is ionized, the positive ions are accelerated (starting from rest) through a potential difference ΔV, and they then enter a region of uniform magnetic field. The field bends the ions into circular trajectories, but after just half a circle they either strike the wall or pass through a small opening to a detector. As the accelerating voltage is slowly increased, different ions reach the detector and are measured. Typical design values are a magnetic field strength B = 0.627 T and a spacing between the entrance and exit holes d = 5.83 cm. a)What accelerating potential difference ΔV is required to detect N2+? b)What accelerating potential difference ΔV is required to detect O2+? c)What accelerating potential difference ΔV is required to detect CO+?arrow_forwardThe magnetic moment of the Earth is approximately 8.00 x 1022 A ⋅ m2. Imagine that the planetary magnetic field were caused by the complete magnetization of a huge iron deposit with density 7 900 kg/m3 and approximately 8.50 x 1028 iron atoms/m3. (a) How many unpaired electrons, each with a magnetic moment of 9.27 x 10-24 A ⋅ m2, would participate? (b) At two unpaired electrons per iron atom, how many kilograms of iron would be present in the deposit?arrow_forwardA circular coil of 205 turns has a radius of 1.84 cm. (a) Calculate the current that results in a magnetic dipole moment of magnitude 3.44 A-m2. (b) Find the maximum magnitude of the torque that the coil, carrying this current, can experience in a uniform 46.8 mT magnetic field. (a) Number Units (b) Number Unitsarrow_forward
- Suppose that the dipole moment associated with an iron atom of an iron bar is 2.8 x 1023 J/T. The bar is 5.2 cm long and has a cross-sectional area of 1.5 cm2. Two-thirds of the atoms have their dipole moment in one directions and remaining one-third have their dipole moment in the opposite direction. What torque (in N*m) must be exerted to hold this magnet perpendicular to an external field of 1.2 T? (The density of iron is 7.9 g/cm3 and its molar mass is 55.9 g/mol. Avogadro's number is 6.022*1023 atoms/mol.)arrow_forwardA magnetic dipole with a dipole moment of magnitude 0.016 J/T is released from rest in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 58 mT. The rotation of the dipole due to the magnetic force on it is unimpeded. When the dipole rotates through the orientation where its dipole moment is aligned with the magnetic field, its kinetic energy is 0.60 mJ. (a) What is the initial angle between the dipole moment and the magnetic field? _____________°(b) What is the angle between the dipole moment and the magnetic field when the dipole is next (momentarily) at rest? ______________°arrow_forwardA permanent magnet has a magnetic dipole moment of 0.160 A · m2. The magnet is in the presence of an external uniform magnetic field (provided by current-carrying coils) with a magnitude of 0.0800 T, which makes an angle of 17.0° with the orientation of the permanent magnet. (a)What is the magnitude of the torque (in N · m) on the permanent magnet? (b)What is the potential energy (in J) of the system consisting of the permanent magnet and the magnetic field provided by the coils?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON