
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The figure below is a system consisting of two masses MA = 1.82 kg and MB = 3.6 kg, whose distance from the pore axis is R₁ = R₂ = 15 cm, while the angular positions are 0₁ = 30° and 0 = 150° . Determine the weight and position of the balancing mass placed on planes C and D if the distance from the axis RC = RD = 15 cm.
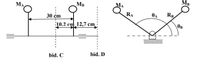
Transcribed Image Text:MB
MB
MA
RA
RB
30 cm
OB
10.2 сm 12,7 сm
bid. D
bid. C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The plant in the picture has mass of 29 kg, and is hanging at a distance of 1.4 meters from the wall. The horizontal rod has mass of 6.2 kg. Assume that its weight is evenly distributed, therefore it can be treated as a single force at the center of mass. The rod is 2 meters long, and there is a cable at a 23° angle supporting it at the end. Center of mass of rod from the point = 2/2=1m Using the wall as the axis of rotation, find the magnitude of the downward torque, from both the weight of the rod and the weight of the plant. t=458.64Nm a.The downward torque is balanced by the upward torque from the force of tension. Find the magnitude of the force of tension. T=?N b.F is the contact force between the rod and the wall. Using the other horizontal force in the problem, find the horizontal component of F (the normal force) that must be present for the rod to be at equilibrium. Fx=?N c.There is a vertical force from a component of the tension, but this is not enough to balance the…arrow_forwardThe position of the head and neck and the forces acting on the head are shown in the figure. The center of gravity of the head of mass m=9 kg is located at point C. The joint reaction force of F J = 150 N, which makes an angle of α = 30° with the vertical from the point B, is acting on the skull by the neck extensor muscles. The center of the atlantooccipital joint is located at point B. For this flexion position of the head, the neck muscle force FM, which makes an angle of γ with the horizontal from the point A , is effective . (Take the gravitational acceleration g as 9.81 m/s 2. ) Accordingly; a) Calculate the angle γ of the muscle force F M with the horizontal. b) Calculate the muscle strength F M. (Write your result in N units.)arrow_forwardThree identical 8.60-kg masses are hung by three identical springs, as shown in the figure. (Figure 1) Each spring has a force constant of 5.90 kN/m and was 11.0 cm long before any masses were attached to it. Make a free-body diagram for the top mass. Draw the vectors starting at the black dot at the center of the top mass.arrow_forward
- Don't skip the steps/explanationarrow_forward18 B 77 L-2 -L- A -x- Persons A and B are standing on a board of uniform linear density that is balanced on two supports, as shown in the figure. What is the maximum distance x from the right end of the board at which person A can stand without tipping the board? Treat persons A and B as point masses. The mass of person B is 1.75 times that of person A, and the mass of the board is 0.359 times that of person A. Give your answer in terms of L, the length of the board.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY