
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
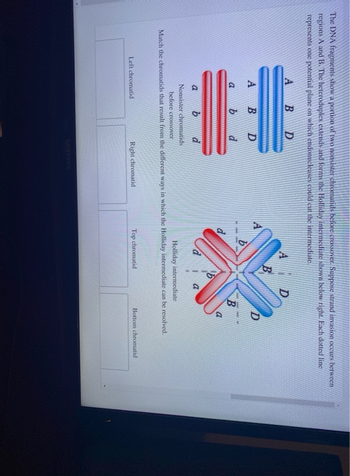
Transcribed Image Text:The DNA fragments show a portion of two nonsister chromatids before crossover. Suppose strand invasion occurs between
regions A and B. The heteroduplex extends and forms the Holliday intermediate shown below right. Each dotted line
represents one potential plane on which endonucleases could cut the intermediate.
DEDE
Left chromatid
A
Right chromatid
b
A
B
D
Nonsister chromatids
before crossover
Holliday intermediate
Match the chromatids that result from the different ways in which the Holliday intermediate can be resolved.
Top chromatid
B
D
Bottom chromatid
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The recombination process below occurs when two recombination occurs between two different alleles, but only only one of the alleles is perpetuated in the final product. This process is called [x]?arrow_forwarda) Fluorescent probes such as DAPI are often used tostudy cells that are in the different phases of cell cycle.DAPI is a fluorescent stain that binds to DNA. The graphshows the variation in fluorescence intensity of humanskin cells that were sorted by FACs into 2 populationsbased on the amount of fluorescence.Which phase(s) of the cell cycle are population A in?Population B? Why did you pick those phases?arrow_forwardBased on the attached image, if we are using the Holliday junction model of recombination, where exactly would be the positions where DNA is cut? Would it be to the right because of branch migration?arrow_forward
- Crossing over occurs frequently during prophase 1 Play 0:12 / 1:43 1x CC 目: A tetrad is made up of Multiple Choice two homologous chromosomes, each consisting of two chromatids ) four nonhomologous chromatids four nonhomologous chromosomes four homologous pairs of chromosomes MacBook Air 20 F3 000 F2 F4 F5 F6 F7arrow_forwardThere are two different pathways for repairing double-strand breaks in the DNA. In which type of cell is homology-directed repair least likely to be able to repair the damage? Choose one. A haploid cell A diploid cell in G1 phase of the cell cycle A diploid cell in G2 phase of the cell cycle All three the same.arrow_forwardThe plant Haplopappus gracilis has a 2n of 4. A diploid cellculture was established and, at premitotic S phase, aradioactive nucleotide was added and was incorporatedinto newly synthesized DNA. The cells were then removed from the radioactivity, washed, and allowed to proceed through mitosis. Radioactive chromosomes or chromatids can be detected by placing photographic emulsionon the cells; radioactive chromosomes or chromatids appeared covered with spots of silver from the emulsion.(The chromosomes “take their own photograph.”) Drawthe chromosomes at prophase and telophase of the firstand second mitotic divisions after the radioactive treatment. If they are radioactive, show it in your diagram. Ifthere are several possibilities, show them, too.arrow_forward
- You are studying the M-cyclin. You treat mitotic cells with an inhibitor of the proteasome and find that M-cyclin is no longer degraded and that this prolongs mitosis. You also find that in the presence of the inhibitor, M-cyclin is now running slower/larger in a Western than you have previously observed. In 1-2 sentences, explain why this might be happening. Edit View Insert Format Tools Table 12pt Paragraph B IU Αν S A C I AT²✓ #tv A MacBook Air X : Garrow_forwardExplain why telomerase required in dividing cells but not required in cells that do not dividearrow_forwardExplain two ways that a chromosomal rearrangement can cause a position effect.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education