
Basic Clinical Laboratory Techniques 6E
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781133893943
Author: ESTRIDGE
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Based on the attached image, if we are using the Holliday junction model of recombination, where exactly would be the positions where DNA is cut? Would it be to the right because of branch migration?
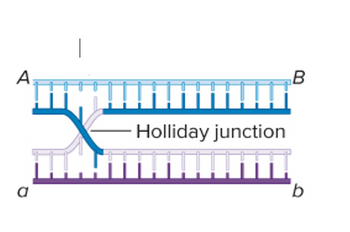
Transcribed Image Text:The image illustrates a Holliday junction, a critical intermediate structure in genetic recombination. This structure involves two double-stranded DNA molecules that are exchanging strands.
- **DNA Strands:** There are two DNA molecules labeled 'A' to 'B' and 'a' to 'b'. The strands are depicted in different shades to distinguish between the two original DNA molecules and their exchanged sections.
- **Cross-over Point:** The center of the diagram shows where the strands cross, forming the Holliday junction. At this junction, one strand from each DNA molecule has swapped partners, creating a cross-shaped structure.
- **Significance:** The Holliday junction is crucial for the repair of damaged DNA and the correct segregation of chromosomes during meiosis.
Understanding the dynamics and resolution of the Holliday junction is fundamental in the study of genetics and molecular biology.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Holliday Model
The Holliday model for recombination was proposed by Robin Holliday in 1964. According to this model, in each strand of the two strands of a DNA molecule, a single-strand break occurs at the same point in both strands. At this break point, the strands of the DNA migrate towards each other further leading to the formation of heteroduplex and as a result, causing the exchange of genes (due to the exchange of base pairs) between both DNA strands leading to recombination.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How many kilobases of the DNA strand below will code for the protein product?arrow_forwardState the properties of the WatsonCrick model of DNA in the following categories: a. number of polynucleotide chains b. polarity (running in same direction or opposite directions) c. bases on interior or exterior of molecule d. sugar/phosphate on interior or exterior of molecule e. which bases pair with which f. right- or left-handed helixarrow_forwardWhat are the base-pairing rules for DNA? a. A-G, T-C c. A-T, G-C b. A-C, T-G d. A-A, G-G, C-C, T-Tarrow_forward
- A chromosomes structure can be altered by _______. a. deletions b. duplications c. translocations d. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhat percentage of the DNA in the genome actually corresponds to genes? How much is actually protein-coding exons? What makes up the rest?arrow_forwardWhat is the purpose and benefit of the polymerase chain reaction?arrow_forward
- A geneticist discovers that a girl with Down syndrome has a Robertsonian translocation involving chromosomes 14 and 21. If she has an older brother who is phenotypically normal, what are the chances that he is a translocation carrier?arrow_forwardDNA contains many hydrogen bonds. Are hydrogen bonds stronger or weaker than covalent bonds? What are the consequences of this difference in strength?arrow_forwardHow many nucleotides does the human genome contain?arrow_forward
- Which of the following best describes the process of DNA sequencing? a. DNA is separated on a gel, and the different bands are labeled with fluorescent nucleotides and scanned with a laser. b. A laser is used to fluorescently label the nucleotides present within the DNA, the DNA is run on a gel, and then the DNA is broken into fragments. c. Nucleotides are scanned with a laser and incorporated into the DNA that has been separated on a gel, and then the DNA is amplified with PCR. d. Fragments of DNA are produced in a reaction that labels them with any of four different fluorescent dyes, and the fragments then are run on a gel and scanned with a laser. e. DNA is broken down into its constituent nucleotides, and the nucleotides are then run on a gel and purified with a laser.arrow_forwardFigure 9.10 You isolate a cell strain in which the joining together of Okazaki fragments is impaired and suspect that a mutation has occurred in an enzyme found at the replication fork. Which enzyme is most likely to be mutated?arrow_forwardTranscribe and translate the following DNA sequence (nontemplate strand): 5’-ATGGCCGGTTATTAAGCA-3’arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning


Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning