
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The diagram shows a subsidy on wheat production given by the Canadian government to wheat producers. Which area represents the gain in
A: PLGB
B: ACFP
C:ACHK
D: PFGB
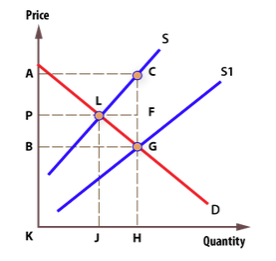
Transcribed Image Text:Price
A
P
B
K
J
H
F
G
S1
D
Quantity
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find the consumer surplus and producer surplus. Demand p= 100-0.00006x Supply p= 90+0.00004xarrow_forwardMove the point, E, in the accompanying graph to reflect equilibrium in the competitive market for corn and answer the following questions. Market for Corn 10 Calculate consumer surplus (CS). CS = s 1250 Calculate producer surplus (PS). PS = $ 4 6 3 4 5 10 Quantity (thousands of bushels) Price (S/bushel) coarrow_forwardthe demand and supply curves for a product are given as: 2q-15p=-120 q+2p = 35 Find the consumer surplus at the equilibrium Find the producer surplus at the equilibrium. Note: don't use chat gpt.arrow_forward
- Rent control is common in some cities, particularly in the United States. You will have noticed some of the consequences in movies or TV shows, usually police stories, set in the high-rise areas of New York City, for example. Suppose you have been given the following information about the market for rental housing in Winona: Quantity Demanded Rent (dollars per month) $500 550 600 650 700 750 800 20,000 15,000 10,000 5,000 2,500 1,500 1,000 a) What is the equilibrium rent? b) What is the equilibrium quantity of rented housing? Quantity Supplied 10,000 10,000 10,000 10,000 10,000 10,000 10,000 Now suppose that a rent ceiling of $700 is imposed in the housing market for Winona. c) What is the quantity of housing demanded? d) What is the quantity of housing supplied? e) Is there excess demand for or excess supply of housing with the imposition of a rent ceiling? Explain what is happening in the market for rental housing market in Winona.arrow_forwardng.cengage.com CENGAGE MINDTAP Chapter 08 Homework First, use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the equilibrium price and quantity of electric scooters in the absence of a tax. Then use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade the area representing total consumer surplus (CS) at the equilibrium price. Next, use the purple point (diamond symbol) to shade the area representing total producer surplus (PS) at the equilibrium price. PRICE (Dollars per scooter) 300 270 Demand 240 210 180 150 120 90 Supply 60 30 Before Tax 0 0 140 280 420 560 700 840 980 QUANTITY (Scooters) 1120 1260 1400 Equilibrium A Consumer Surplus Producer Surplus Suppose the government imposes an excise tax on electric scooters. The black line on the following graph shows the tax wedge created by a tax of $120 per scooter. First, use the tan quadrilateral (dash symbols) to shade the area representing tax revenue. Next, use the green point (triangle symbol) to shade the area representing total consumer surplus…arrow_forwardIn 2020 the UK government introduced a sales tax on all products bought online from overseas. Please note this is not a tariff – it is a tax. The tax will be 2% of the value of the products sold in the UK. This tax is collected from online sellers such as Amazon or ebay. Source: BBC (2019). See link: https://www.bbc.com/news/business-50656106 Consider the market for online products. The initial market equilibrium is at 10 million products sold per year at an average price of $500 each. Then, the UK government imposes a tax on the market, collected from sellers (for example Amazon and ebay). The tax is 2% per item (each item has an average price of $500). Show the effect of this on the market for online products. Show the effect on consumers of online products, on the online sellers and on the government. Does the UK economy gain or lose as a result of the tax? Explain why. Use a diagram to support your answer.arrow_forward
- The following diagram represents the market for paperback books. Which area represents producer surplus? Price per book 30 (dollars) с B O A A X 15 15 None of the above. 30 Thousands of books per weekarrow_forwardGraphically, producer surplus is the area from the market price ($120) down to the supply curve and over to the equilibrium quantity of 120.arrow_forwardIn a perfectly competitive market for cheese with downward sloping demand and upward sloping supply, the equilibrium price is $12 per kilo. If the government imposes a price ceiling of $10, we can conclude that the government policy will: Select one: a. reduce the number of units sold only if demand is elastic b. decrease producer surplus and decrease total surplus c. reduce the number of units sold only if demand is inelastic d. decrease producer surplus but increase total surplus e. increase producer surplus but decrease total surplusarrow_forward
- Please explainarrow_forwardUse the graph below to answer the following questions: a) what is the level of producer surplus if the market clearing price is $6? b) calculate the change in producer surplus if price increases from $6 to $8. c) what is the elasticity of supply in the $6-$8 price range?arrow_forwardFor years the government has subsidized higher education through grants; consider the demand and supply for college credit hours at a local private liberal arts collegeQD = 6,000 – 300PQS = 700P – 500 where P is the price, in hundreds of dollars, and Q is the number of credit hours per semester. Suppose the government subsidizes credit hours at a rate of $120 per hour. Calculate changes in consumer surplus. What is the size of the deadweight loss?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education