
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
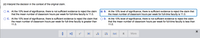
Transcribed Image Text:(d) Interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
A. At the 10% level of significance, there is not sufficient evidence to reject the claim
that the mean number of classroom hours per week for full-time faculty is 11.0.
B. At the 10% level of significance, there is sufficient evidence to reject the claim that
the mean number of classroom hours per week for full-time faculty is 11.0.
C. At the 10% level of significance, there is sufficient evidence to reject the claim that
the mean number of classroom hours per week for full-time faculty is greater than
11.0.
D. At the 10% level of significance, there is not sufficient evidence to reject the claim
that the mean number of classroom hours per week for full-time faculty is less than
11.0.
(1,1)
More

Transcribed Image Text:The dean of a university estimates that the mean number of classroom hours per week for full-time faculty is 11.0. As a member of the student council, you want to test this claim. A
random sample of the number of classroom hours for eight full-time faculty for one week is shown in the table below. At a = 0.10, can you reject the dean's claim? Complete parts (a)
through (d) below. Assume the population is normally distributed.
11.4
7.1
13.2
7.6
5.9
11.9
12.1
8.4 O
(a) Write the claim mathematically and identify H, and Ha.
Which of the following correctly states H, and H?
В. Но: иS11.0
Hạ: u> 11.0
E. Ho: µ>11.0
Ha: us11.0
A. Ho: µ<11.0
Hại u2 11.0
C. Ho: μ= 11.0
Ha: u#11.0
D. H μ#11.0
Hại u=11.0
O F. Ho: µ211.0
Ha: u<11.0
(b) Use technology to find the P-value.
P= 0.010 (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
(c) Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Which of the following is correct?
A. Fail to reject H, because the P-value is less than the significance level.
O B. Reject H, because the P-value is less than the significance level.
C. Reject H, because the P-value is greater than the significance level.
D. Fail to reject H, because the P-value is greater than the significance level.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The "Freshman 15" refers to the belief that college students gain 15 lb (or 6.8 kg) during their freshman year. Listed in the accompanying table are weights (kg) of randomly selected male college freshmen. The weights were measured in September and later in April. Use the listed paired sample data, and assume that the samples are simple random samples and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Complete parts (a) through (c). = 0 kg Ho: Ha H₁: Hd > 0 kg (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) Identify the test statistic. t = 2.82 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Identify the P-value. a. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that for the population of freshman male college students, the weights in September are less than the weights in the following April. In this example, is the mean value of the differences d for the population of all pairs of data, where each individual difference d is defined as the April weight minus the September…arrow_forwardThe mall has a set of data with employee age (X) and the corresponding number of annual on-the-job-accidents(Y). Analysis on the set finds that the regression equation is Y=100-3X. What is the likely number of accidents for someone aged 30? 97 100 10 none of the abovearrow_forward3. Can SAT scores predict college performance? Let x be a variable that represents SAT score of a computer science major, and let y be a variable that represents a student’s GPA upon graduation. A random sample of n =15 computer science majors provided their SAT scores and GPAs: x 1232 1070 1086 1287 1130 1048 1121 1095 1135 1208 1333 1160 1186 1243 1261 y 3.52 2.91 2.4 3.47 3.47 2.37 2.4 2.24 3.02 3.32 3.59 2.54 3.19 3.71 3.58 The scatter diagram for the SAT score and GPA is given below: (a) Find the sample correlation coefficient r. Truncate to two decimal places. What does the value tell you about the data? (b) Find the equation of the least squares line . Truncate to four decimal places. What does the slope mean? (c) Find the value of the coefficient of determination . Truncate to two decimal places. What does this number mean? (d) What is the predicted GPA if a computer science major got a…arrow_forward
- 2. This is a sample of 10 random seasons in the National Hockey League, Wayne Gretzky scored 50% more points than anyone who ever played professional hockey. He accomplished this amazing feat while playing in 280 fewer games than Gordie Howe, the previous record holder. Here are the number of games Gretzky played during each season. 45 70 73 73 74 78 79 80 80 82 e. What is the shape of the data?f. What is the best measure of center and spread to use for this data setarrow_forwardThe average fruit fly will lay 377 eggs into rotting fruit. A biologist wants to see if the average will be greater for flies that have a certain gene modified. The data below shows the number of eggs that were laid into rotting fruit by several fruit flies that had this gene modified. Assume that the distribution of the population is normal. 367, 374, 364, 388, 407, 369, 375, 362, 403, 383, 381, 391, 371 What can be concluded at the the αα = 0.10 level of significance level of significance? The test statistic = (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) The p-value = (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.)arrow_forwardJoan's Nursery specializes in custom-designed landscaping for residential areas. The estimated labor cost associated with a particular landscaping proposal is based on the number of plantings of trees, shrubs, and so on to be used for the project. For cost-estimating purposes, managers use two hours of labor time for the planting of a medium-sized tree. Actual times from a sample of 10 plantings during the past month follow (times in hours). B, C, and Darrow_forward
- Need crit value, the pictured question b, and rejection region.arrow_forwardThe accompanying data are x = advertising share and y = market share for a particular brand of soft drink during 10 randomly selected years. x 0.104 0.072 0.072 0.077 0.086 0.047 0.060 0.050 0.070 0.052 y 0.137 0.127 0.120 0.086 0.079 0.076 0.065 0.059 0.051 0.039 b)Calculate the equation of the estimated regression line. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) d)Calculate a point estimate of ?e. (Round your answer to five decimal places.)arrow_forwardA political newspaper, Politically Sound, is interested in the distances voters in Rising Falls County live from their nearest polling station. Politically Sound has hired you to estimate the population mean of all such distances for voters in this county. To estimate this population mean, you select a random sample of 17 Rising Falls County voters and record the distance (in km) each voter lives from their nearest polling station. Assume the population is approximately normally distributed. Based on your sample, follow the steps below to construct a 99% confidence interval for the population mean of all the distances voters in Rising Falls County live from their nearest polling station. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) (a) Click on "Take Sample" to see the results for your random sample. Take Sample Number of voters 17 Sample mean 4.757 Sample standard deviation 2.363 Enter the values of the sample size, the point estimate of the mean, the sample standard deviation, and the…arrow_forward
- 3. Can SAT scores predict college performance? Let x be a variable that represents SAT score of a computer science major, and let y be a variable that represents a student’s GPA upon graduation. A random sample of n =15 computer science majors provided their SAT scores and GPAs: x 1232 1070 1086 1287 1130 1048 1121 1095 1135 1208 1333 1160 1186 1243 1261 y 3.52 2.91 2.4 3.47 3.47 2.37 2.4 2.24 3.02 3.32 3.59 2.54 3.19 3.71 3.58 The scatter diagram for the SAT score and GPA is given below: (a) Find the sample correlation coefficient r. Truncate to two decimal places. What does the value tell you about the data? (b) Find the equation of the least squares line . Truncate to four decimal places. What does the slope mean? (c) Find the value of the coefficient of determination . Truncate to two decimal places. What does this number mean? (d) What is the predicted GPA if a computer science major got a…arrow_forwardA researcher collected how many grams of fat people on a specific diet consumed at breakfast and at lunch. The data for a sample of 8 people is shown in the table below. xx 11.3 8.2 7.2 3.6 2.3 2.5 2.7 0.4 yy 13.7 10.7 10.2 7.2 6.3 6.5 6.1 4.1 xx = grams of fat in breakfastyy = grams of fat in lunchThis data can be modeled by the equation ˆy=0.84x+4.07.y^=0.84x+4.07.Given this, how many grams of fat in lunch would be expected for a person who consumed 1.2 grams of fat at breakfast? Round to 1 decimal place.Answer =arrow_forwardPlease show complete solution Thank you!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman