
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
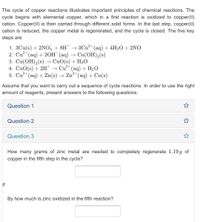
Transcribed Image Text:The cycle of copper reactions illustrates important principles of chemical reactions. The
cycle begins with elemental copper, which in a first reaction is oxidized to copper(II)
cation. Copper(II) is then carried through different solid forms. In the last step, copper(II)
cation is reduced, the copper metal is regenerated, and the cycle is closed. The five key
steps are
1. 3Cu(s) + 2NO, + 8H* → 3Cu²* (aq) + 4H2O+ 2NO
2. Cu (aq) + 20Н (аq) —> Сu(ОН),(s)
3. Cu(OH),(s) –→ CuO(s) + H2O
4. CuO(s) + 2H → Cu²* (aq) + H2O
5. Cu* (aq) + Zn(s) → Zn²*(aq) + Cu(s)
2+
2+
2+
cycle reactions.
amount of reagents, present answers to the following questions.
Assume that you wa
carry out a sequence
ord
use the right
Question 1
Question 2
Question 3
How many grams of zinc metal are needed to completely regenerate 1.19 g of
copper in the fifth step in the cycle?
By how much is zinc oxidized in the fifth reaction?
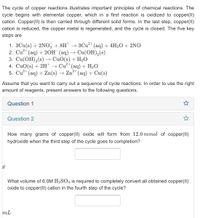
Transcribed Image Text:The cycle of copper reactions illustrates important principles of chemical reactions. The
cycle begins with elemental copper, which in a first reaction is oxidized to copper(II)
cation. Copper(I) is then carried through different solid forms. In the last step, copper(II)
cation is reduced, the copper metal is regenerated, and the cycle is closed. The five key
steps are
1. 3Cu(s) + 2NO3 + 8H* → 3Cu²+ (aq) + 4H2O+ 2NO
2. Cu?* (aq) + 20H (aq) → Cu(OH),(s)
3. Cu(OH),(s) → CuO(s) + H2O
4. CuO(s) + 2H → Cu²* (aq) + H2O
5. Cu** (aq) + Zn(s) → Zn²+(aq) + Cu(s)
2+
Assume that you want to carry out a sequence of cycle reactions. In order to use the right
amount of reagents, present answers to the following questions.
Question 1
Question 2
How many grams of copper(II) oxide will form from 12.0 mmol of copper(II)
hydroxide when the third step of the cycle goes to completion?
What volume of 6.0M H2SO4 is required to completely convert all obtained copper(II)
oxide to copper(II) cation in the fourth step of the cycle?
mL
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using enthalpies of formation, calculate AHrxn for the reaction: C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) → 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(()arrow_forwardCalculate the ΔG^O (in kJ/mol) for the following reaction at 25.0℃.3Co^+2(aq)+2Al(s)→3Co(s)+2Al^+3(aq)arrow_forwardDirect dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene to styrene is carried out in the vapor phase with steam over a catalyst consisting primarily of iron oxide. The reaction is endothermic, and can be accomplished either adiabatically or isothermally. Both methods are used in practice. The major reaction is the reversible, endothermic conversion of ethylbenzene to styrene and hydrogen: C6H3CH₂CH CoHsCHCH₂ + H₂ AH= 124.9 kJ/mol Competing thermal reactions degrade ethylbenzene to benzene C6H3CH₂CH3C6H6+ C₂H4 AH 101.8 kJ/mol Styrene also reacts catalytically to toluene: CH3CH₂CH3 + H2 CH3CH3 + CH4 AH=64.5 kJ/mol The reactions take place at 620°C. The costs are as shown in Table 1. The production rate of styrene is 200 mol/h. Chemical name Formula Cost (S/kmol) Ethylbenzene C6H5CH₂CH3 57.1 Styrene C.HSCHCH₂ 75.9 Benzene C6H6 32.8 Toluene C6H5CH3 25.8 Hydrogen H₂ 1.2 (as fuel) Methane CH4 4.0 (as fuel) Ethylene C₂H4 6.7 (as fuel) Correlation for the product selectivity and distribution are given as…arrow_forward
- Ethanol can be produced by the direct hydration of ethylene with H¿PO4 at 300°C and 6.8 MPa according to the reaction: CH2=CH2 + H2O → C>H;OH The following side reaction also occurs during the process: CH2 CH2 + H20 → C2H‚O + H2 The yield of ethanol is 92% and the single-pass conversion is 13%. The molar ratio of ethylene to water in the feed to the reactor is 1:0.6. Unreacted ethylene is separated from the reactor effluent and recirculated. a) How much ethylene and water are required to produce 100 kmol of ethanol? b) How much ethylene is recycled for the production rate?arrow_forwardQuestion 13.6. The CO/H2 gas mixture is fed to a reactor at a ratio of ¹1/2 and heated under pressure to 650 K in the presence of a suitable catalyst. In order for this industrial reaction to be economically feasible, the equilibrium conversion value must be at least 30%. It can be assumed that the gas mixture exhibits ideal gas behavior in equilibrium. CO (g) + 2H₂(g) → CH3OH (g) In a reactor where the maximum working pressure value is 200 atm, the reaction in question whether it can be achieved in a way that meets the desired conditions. determine. If any problem arises in this regard, the equilibrium condition Possible improvements (if any) in order to meet the requirements put it forward. Use the average heat capacity ((CD)H) approach in your calculations.arrow_forwardQ1. The combustion of acetylene, C₂H2, is done by the following reaction 2C₂H2 (g) +502 (g) 4CO2 (g) + 2H₂O(g) If 75.0 g of C₂H₂ is treated with 75.0g of O2, a) The Limiting reactant is b) The theoretical yield of CO₂ is c) The mass of excess reagent which is left unreacted at the end of the reaction isarrow_forward
- Determine the equilibrium conversion for the isomerization reaction of methylcyclopentane (CH3C-H9) to cyclohexane (C6H₁2) at 298°K. Gibbs energies of formation are given at 298°K as: Agot,CH3C5H9 = 31.72 [kJ/mol] and Ag f,c6H12 = 26.89 [kJ/mol]arrow_forwardExamine the reaction equation below. "Heat" being present on the reactant side of an equation indicates what? "Heat" + 2NH3 N2 + 3H2arrow_forwardIn the combustion of hydrogen, the following reactions involving radicals are fast in both the forward and reverse directions. Use the assumption of partial equilibrium to derive algebraic expressions for the molar concentrations of the three radical species, O, H, and OH, in terms of the kinetic rate coefficients and the molar concentrations of reactant and product species, H2, O2, and H2O.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The