
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
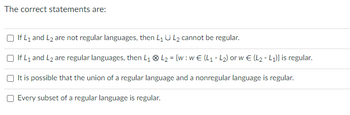
Transcribed Image Text:The correct statements are:
If L₁ and L2 are not regular languages, then L₁ U L₂ cannot be regular.
If L₁ and L₂ are regular languages, then L₁ L₂ = {w: w€ (L₁-L₂) or w€ (L₂-L₁)} is regular.
It is possible that the union of a regular language and a nonregular language is regular.
Every subset of a regular language is regular.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 38 The correct statements are: If If Σ □ If If Ø, then Σ* has a subset that is not regular. Ø, then Σ* has a subset that is not context free. Ø, then Σ* has a subset that is not in D. Ø, then Σ* has a subset that is not in SD.arrow_forwardLet LPrime = {I the number of strings accepted by M is prime}. Classify this language as either (i) decidable, (ii) recognizable but not decidable, or (iii) not recognizable. Prove your answer. You may give a high-level description of any TM programs used in your proof. ( You should not use Rice's theorem.)arrow_forwardState whether the following claim is true or false and prove your answer. Claim: For any (non-empty) alphabet Σ, there is no language L ⊆ Σ∗ which is both regular and inherently ambiguous.arrow_forward
- Let E be the alphabet {a,b}. E* – (e|E*b)aa(ɛ|b£*), where the hyphen denotes set difference and ɛ de- notes the empty string. (Hint: L consists of the strings over E in which no maximal substring consisting solely of a's is of length 2.) Draw a finite automa- ton that accepts L. Let L be the language described byarrow_forward1. Is the following language B regular or non-regular? B = {0% 0 | a,b ≥ 0 and a =b} 2. If your answer above is regular, please provide a Regular Expression that recognizes the language. If your answer is non-regular, please prove it by contradiction via Pumping Lemma for Regular Languages. The format and style of the proof using Pumping Lemma are supposed to follow those in the textbook.arrow_forward2. The function f is defined for non-negative integers a and b recursively as follows: f (а, b) 3D1 if a = 0 or b = 0 f (a - 1, b f (a f (а, а) 1) + 2a - 1 if a if a > b if a < b b b, b) + f (b, b) + f (b а, а) } Compute f (2, 3) by drawing a recursion tree showing all of the computation required and then use your tree to compute the answer.arrow_forward
- Let C(x. v) be x is enrolled in y, where the domain for x is the set of all students at a certain university and the domain for y is the set of all computer science classes being offered at the university. Match each English statement with its equivalent logical expression. ? v 1. No one is enrolled in both CS222 and CS252. A. -3x(C(x, CS222) ^ C(x, CS252)) B. C(Sarah, CS232) C. Ex(C(x, CS222) v C(x, CS252)) D. Vx3yC(x, y). E. 3yVxC(x, y) F. -Vx(C(x, CS222) A C(x, CS252)) G. VyC(Sarah, y) H. 3XVYC(x, y) 1. 3x(C(x, CS222) A C(x, CS252)) J. ByC(Sarah, y) v 2. Everyone is enrolled in some computer science classes, ? v 3. Sarah is enrolled in some computer science class. ? v 4. Someone is enrolled in all domputer science classes. v 5. Someone is enrolled in both CS222 and CS252. ? v 6. There is one class that is enrolled by all students.arrow_forwardConsider the language L of strings over the alphabet Σ = {a, b} which contain an equal number of a’s and b’s, and the set of b’s is consecutive in the string, e.g., ab, abba, aabb, abbbaa, aaabbbbbaa, etc. Note that ε ∈ L for completeness (0 number of a’s is equal to 0 number of b’s, which are also consecutive). Show that this language is context-free by giving a context-free grammar. Please make sure to test the answers onhttps://web.stanford.edu/class/archive/cs/cs103/cs103.1156/tools/cfg/arrow_forwardSuppose LS {a, b}* is defined as follows: A e L; for every x and y in L, the strings axb, bxa, and xy are in L. Show that L= AE B, the language of all strings x in {a, b}* satisfying na(x) = n¿(x).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education