
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the drum and brake bar are μS= 0.4 and μK= 0.3, respectively. If M= 50 N.m and P= 85 N. determine the horizontal and vertical components of reaction at the pin O (shown in Fig. 3). Neglect the weight and thickness of the brake. The drum has a mass of 25 kg.
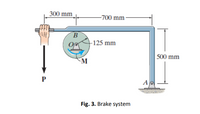
Transcribed Image Text:300 mm
-700 mm·
B
-125 mm
500 mm
M
P
A
Fig. 3. Brake system
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q3/ If the coefficients of friction between brake arm and cylinder Cis 0.3 and between cylinder C and the floor is 0.12, determine the minimum force P required to hold the cylinder from the rotation. Note that the weight of the cylinder Cis 1000 Ib and neglect the weight of the brake arm? 5-15 Higd 20" 10" 0" 1500-ibarrow_forwardCalculate the horizontal force P on the light 14° wedge necessary to initiate movement of the 54-kg cylinder. The coefficient of static friction for both pairs of contacting surfaces is 0.37. Also determine the friction force FB at point B. (Caution: Check carefully your assumption of where slipping occurs.) P Answers: P = FB i i 149 54 kg B N N Aarrow_forwardThe figure shows a bar in equilibrium position resting on the floor at point A and on the wall at point B. If the mass of the bar is m and the angle it makes with the floor is θ = π/6, find the magnitudes of the frictional and normal forces at points A and B.arrow_forward
- 5. Using the definition of the static friction and the first condition of equilibrium, show or prove that the coefficient of static friction in Table B is the ratio of the “rise” to the “run”. Note: Show the free body diagram. Please refer to my experimental Dataarrow_forwardPLLLSS ANSWER WITHIN AN HOUR The spool in the given figure weighs 25 N, and its center of gravity is located at the geometric center. The weight of block C is 50 N. The coefficients of static friction at the two points of contact are as shown. Determine the largest horizontal force P that can be applied without disturbing the equilibrium of the system.arrow_forwardThe uniform box shown in next figure, has a mass of 40 Kg. If the two forces T 60 N and F 30 N are applied on the box, determine if it remains in equilibrium. The coefficient of static friction (u) = 0.24 F=30N T=60N 30 40 Kgarrow_forward
- The crate shown is held against wedge B by a spring. The spring is 93.5% of its original uncompressed length 1 = 2.25 m, and the spring constant is given as k = 1650 N/m. The coefficient of static friction at all contacting surfaces is µ = 0.150. The mass of the crate is m = 24.0 kg. The angle is 0 = 10.0°. Neglect the mass of the wedge. Assume the crate only moves in the y direction and that wedge A cannot move. (Figure 1) Figure B A 1 of 1 L Part A - Determining the normal force exerted by the crate on the wedge Determine the normal force No that the crate exerts on the wedge when the system is at rest. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ► View Available Hint(s) Nc = Submit O P = Submit μA Value Part B - Finding the smallest horizontal force P to move the crate upward Units Determine the magnitude of the smallest horizontal force P that is necessary to begin moving the crate upward. Express your answer to three significant figures and…arrow_forwardThe beam AB has a negligible mass and thickness and is subjected to a triangular distributed loading. It is supported at one end by a pin and at the other end by a post having a mass of 50 kg and negligible thickness. Determine the two coefficients of static friction at B and at C so that when the magnitude of the applied force is increased to P = 150 N, the post slips at both B and C simultaneously. Take F = 940 N/m. (Figure 1) Figure -2 m 400 mm 300 mm Part A Determine the coefficient of static friction at B Express your answer using three significant figures. HB = Submit Part B HC = Submit ΕΠ ΑΣΦ VI Determine the coefficient of static friction at C. Express your answer using three significant figures. Provide Feedback ↓↑ vec • Request Answer Π|| ΑΣΦ ↓↑ Request Answer vec ? ?arrow_forwardCalculate the horizontal force P on the light 14° wedge necessary to initiate movement of the 58- kg cylinder. The coefficient of static friction for both pairs of contacting surfaces is 0.23. Also determine the friction force Fg at point B. (Caution: Check carefully your assumption of where slipping occurs.) 58 kg B P > 149 Answers: P = i FB = i Narrow_forward
- The horizontal force P = 90 N is applied to the upper block with the system initially stationary. The block masses are mA = 14.4 kg and mB = 5.1 kg. Use g = 9.81 ms-2. Determine the magnitude of the frictional force that block B exerts on block A. The coefficients of static friction are µ1 = 0.40 and µ2 = 0.50. The coefficients of kinetic friction are 75% of the respective static values. Give your answer in Newtons.arrow_forwardSolve the example pleasearrow_forwardThe high strength, square-threaded bolt that holds the three plates together has a nominal diameter of 1 in. The coefficient of friction is us = 0.36. The mean diameter of the thread is 0.94 in. The lead of the bolt is L = 0.160 in. Neglect friction between the nut and the washer. Determine the torque one must apply in in. Ib to the nut to induce a tension of 47,500 lb. (Enter the magnitude.) in. · Ib When that tension is achieved, determine the torque in in. · Ib required to loosen the bolt. (Enter the magnitude.) in. • Ibarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY