
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please provide the correct answer for the wrong questions. To be honest, I have just followed the solutions as attached. Please provide the correct answer.

Transcribed Image Text:15. (a) The distance between qi and qz is
(x, –x,)* +(y; -y.)° =/(-0.020 m–0.035 m) +(0.015 m–0.005 m) =0.056 m.
The magnitude of the force exerted by q, on q, is
E.zt 199.1 (8.99×10ʻN-m³/C°) (3.0×10°C) (4.0×10“C)
(0.056 m)
= 35 N.
(b) The vector F, is directed toward qi and makes an angle 0 with the +x axis, where
972
CHAPTER 2I
1.5 cm-0.5 cm
0= tan 2-y
=tan
-10.3°-10°.
-2.0 cm-3.5 cm,
(c) Let the third charge be located at (x3, y3), a distance r from q2. We note that q1, q2, and
q3 must be collinear; otherwise, an equilibrium position for any one of them would be
impossible to find. Furthermore, we cannot place q3 on the same side of q2 where we also
find q1, since in that region both forces (exerted on q2 by q3 and q1) would be in the same
direction (since q2 is attracted to both of them). Thus, in terms of the angle found in part
(a), we have x; = x2 -r cose and y; = y2 –r sin@ (which means y3 > y2 since 0 is negative).
The magnitude of force exerted on q2 by q3 is F,=k|4:4,/r, which must equal that of
the force exerted on it by q; (found in part (a)). Therefore,
= k
= 0.0645 m = 6.45 cm.
Consequently, x3 =x2 -r cos0=-2.0 cm – (6.45 cm) cos(-10°) =-8.4 cm,
(d) and y; = y2 -r sine= 1.5 cm – (6.45 cm) sin(-10°) = 2.7 cm.
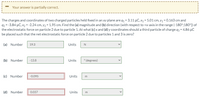
Transcribed Image Text:Your answer is partially correct.
The charges and coordinates of two charged particles held fixed in an xy plane are q1 = 3.11 µC, x1 = 5.01 cm, y1 = 0.163 cm and
92 = -3.84 µC, x2 = -2.24 cm, y2 = 1.95 cm. Find the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (with respect to +x-axis in the range (-180°;180°) of
the electrostatic force on particle 2 due to particle 1. At what (c) x and (d) y coordinates should a third particle of charge q3 = 4.86 µC
be placed such that the net electrostatic force on particle 2 due to particles 1 and 3 is zero?
(a) Number
19.3
Units
N
(b) Number
-13.8
Units
* (degrees)
(c) Number
-0.095
Units
(d) Number
0.037
Units
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The planet Jupiter has a mass of 1.9 × 1027 kg and a radius of 72,000 km. The Earth, meanwhile, has a mass of 6.0 × 1024 kg and a radius of 6,400 km. What is the volume of Jupiter in m3?arrow_forwardI am flying from Kansas City to Denver. My flight leaves Kansas City at 4:30 pm. I land in Denver at 4:25 pm on the same day. Denver and Kansas city are 320 miles apart. How is this possible?arrow_forwardThe surface of a lake has an area of 15.5 km². What is the area of the lake in m²? 1.55 × 108 m² 1.55 x 106m² 1.55 × 105 m² 1.55 × 104 m² 1.55 × 107 m²arrow_forward
- I am unsure if I should determine how many miles equal a kilometer or how many miles per hour equal kilometers per hour. A car travels with an average speed of 35 MPH. What is this speed in km/h?arrow_forwardplease answer question and just send me the paper solutions asap dont type the answer please and find everything that is asked please and the angle using cos and tan if need please do not leave that and answer will the directions please solve question asap please faster i just have 15 mins please faaster and only use the given formula please dont forget the angle please and in the let statement don't use something that is out of question please Round it to least sig dig at the end please 16ab the angle is 60degree The cart mass on the top is 0.80kg and the mass at the bottom cart is 2.0kg friction is 0.14arrow_forwardthe average density of an atom is approximately 103 kg/m3. The nucleus of an atom has a radius about 10-5 times that of the entire atom, and contains nearly all the mass of the atom. What is the approximate density, in kilograms per cubic meter, of a nucleus?arrow_forward
- In 1999, NASA lost the Mars Climate Orbiter because one group of engineers used metric units in their calculations while another group used English units. Consequently, the orbiter descended too far into the Martian atmosphere and burned up. Suppose that the orbiter was to have established orbit at 157 km and that one group of engineers specified this distance as 1.57 x 10³ m. Suppose further that a second group of engineers programmed the orbiter to go to 1.57 x 10³ ft. The $125 million Mars Climate Orbiter was lost in the Martian atmosphere in 1999 because two groups of engineers failed to communicate with each other about What was the difference in kilometers between the two altitudes? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Value Submit HA Provide Feedback Part B Complete previous part(s) Units Request Answer ?arrow_forwardYou are driving 52 mi/h and take your eyes off the road for "just a second" (exactly one second). What distance (in feet) do you travel in this time?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON