
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
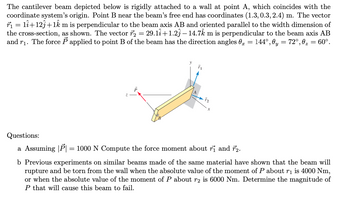
Transcribed Image Text:The cantilever beam depicted below is rigidly attached to a wall at point A, which coincides with the
coordinate system's origin. Point B near the beam's free end has coordinates (1.3, 0.3, 2.4) m. The vector
r₁ = 11+12ĵ+1km is perpendicular to the beam axis AB and oriented parallel to the width dimension of
the cross-section, as shown. The vector 7₂ = 29.1î+1.23 — 14.72 m is perpendicular to the beam axis AB
and r₁. The force P applied to point B of the beam has the direction angles 0 = 144°, 0y = 72°,0₂ = 60°.
fa
Questions:
a Assuming |P| = 1000 N Compute the force moment about ri and 72.
b Previous experiments on similar beams made of the same material have shown that the beam will
rupture and be torn from the wall when the absolute value of the moment of P about r₁ is 4000 Nm,
or when the absolute value of the moment of P about r2 is 6000 Nm. Determine the magnitude of
P that will cause this beam to fail.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given:
The coordinates of point A, A(0,0,0)
The coordinates of point B, B (1.3,0.3,2.4) m
The position vector, r₁ = I + 12j +k
The position vector, r₂ = 29.1i + 1.2j – 14.7k
The angle, θx = 144ᵒ
The angle, θy = 72ᵒ
The angle, θz = 60ᵒ
The magnitude of force, P = 1000 N
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The Cartesian vector form of the moment produced by force F, about point O is equal to. 1 ft -2 ft- 3 ft F = (-20i + 10j + 30k} lb 2 ft F2 = |-10i – 30j + 50k} Ib %3Darrow_forwardWhat is the norminal force, N in kilo Newtons(kN). What is the shear force, V in kilo Newtons (kN). Find the bending moment, M in kilo Newton metres (kNm).arrow_forward4) Determine the total moment caused by the forces Fp4 and Fca about the plate diagonal that goes through point B (the dashed line). Write your answer in cartesian vector notation. FCA= 500 lb 14 ft FRA = 350 Ib FDA= 400 lb 3 ft-> 3 ft 3 ft 2 t 6 ftarrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY