
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
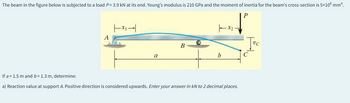
Transcribed Image Text:The beam in the figure below is subjected to a load P= 3.9 kN at its end. Young's modulus is 210 GPa and the moment of inertia for the beam's cross-section is 5×106 mm².
P
A
|×-|
a
B
1x₂.
b
If a 1.5 m and b= 1.3 m, determine:
a) Reaction value at support A. Positive direction is considered upwards. Enter your answer in kN to 2 decimal places.
Jvc
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5. The rigid beam is supported by a pin at C and a steel wire AB (Esteel = 200 GPa). a) If the wire has a diameter of 10mm, determine how much it stretches when a distributed load of w = 3kN/m acts on the beam (The material remains in the elastic region). b) Can we develop a visual measurement method (e.g. with help from a high-resolution camera) to determine the amount of an unknown load of w based on the length of CB? (assuming the load w is unknown). Briefly explain. A Gurb TH W 4 m 30° Barrow_forwardFrom the same problem could you please help me answer D, E and Farrow_forwardCantilever beam has fixed support at the point A as shown in Fig. 4. Determine the component of the support reaction at that point (A). 6 kN }30° 30° 1.5 m 4 kN 1.5 m -1.5 m- Fig. 4arrow_forward
- Consider the beam shown in (Figure 1). Suppose that w = 880 N/m . Determine the y component of reaction at A using scalar notation. Determine the x and y components of reaction at B using scalar notation.arrow_forwardThe beam in the figure below is subjected to a load P = 3.5 kN at its end. Young’s modulus is 210 GPa and the moment of inertia for the beam’s cross-section is 5×106 mm4. If a = 1.5 m and b = 0.6 m, determine: a) Reaction value at support A. Positive direction is considered upwards. b) moment equation M(x1) in the segment AB, where x1 changes from 0 at support A to a at support B. Enter the equation in terms of variables P, a, band x1. c) moment equation M(x2) in the segment BC, where x2 changes from 0 at point C to b at support B. Enter the equation in terms of variables P, a, band x2. d) the value of the constant of integration C1 e) the value of the constant of integration C2 f) the value of the constant of integration C3 g) the value of the constant of integration C4 h) the value of displacement at point C i) the position of maximum displacement in the segment AB j) the value of maximum displacement in the segment ABarrow_forwardConsider the pictured bar with axial loads of PB = 50 kip and Pc = 68.5 kip, and the indicated material properties. A = 5 in² E = 12 × 103 ksi Oy = = 35 ksi for this material B C PB PC PB РС 18 in 24 in 36 in 0.01 in a)For the chosen values of PB and Pc, determine the reaction at D b)Given PB = 50 kip, what value of Pc will produce yielding of the bar? kip kiparrow_forward
- Need help please, round answers to 3 sig figsarrow_forwardA D В C__0 L L· For the following beam, a) Use the method of superposition to determine the reactions at the supports B and C. (El is constant) b) Find the rotation at D. L=1.25mm W=2.5kN/marrow_forwarda) A steel 4 X 4X 0.25-inch square tube (moment of inertia I = 8.215 inª) is used as a simply supported beam. A 100-pound weight is dropped from a height of 24 inches onto the beam at mid- span. Find the maximum stress in the beam. Use E = 29 X 106 psi. 8 ft k = 200 lb/in 100 lb 8 ft b) Instead of fixed supports, the beam is supported by springs at both ends. Find the maximum stress in the beam when the 100-pound weight is dropped from a height of 24 inches (same beam properties as in part a). 24 in 100 lb 8 ft 24 in 8 ft k = 200 lb/inarrow_forward
- Problem For the beam shown in Figure A. Find the reaction at support B (RB) B. Find the reaction at support D (RD)arrow_forwardI tried this problem but I still don't get what I'm missing. Can you help me figure out what I'm missing here?arrow_forwardThe beam shown in Figure Q.2 consists of a W610 x 140 structural steel wide-flange shape [E =200 GPa; /= 1120 × 106 mm²]. If w = 62 kN/m and P= 123 kN, determine: AV, V 1.5 m B W 3.5 m P 2.5 m D Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY