
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
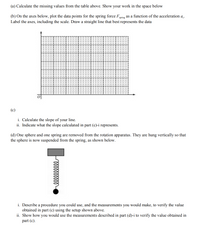
Transcribed Image Text:(a) Calculate the missing values from the table above. Show
your
work in the space below
(b) On the axes below, plot the data points for the spring force F
Label the axes, including the scale. Draw a straight line that best represents the data
as a function of the acceleration a..
spring
(c)
i. Calculate the slope of your line.
ii. Indicate what the slope calculated in part (c)-i represents.
(d) One sphere and one spring are removed from the rotation apparatus. They are hung vertically so that
the sphere is now suspended from the spring, as shown below.
i. Describe a procedure you could use, and the measurements you would make, to verify the value
obtained in part (c) using the setup shown above.
ii. Show how you would use the measurements described in part (d)-i to verify the value obtained in
part (c).
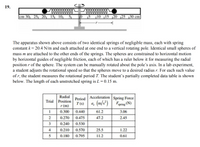
Transcribed Image Text:19.
cm 30, 25, 20, 15, 10, 5,
„10 ,15 |20 125 ,30 cm
The apparatus shown above consists of two identical springs of negligible mass, each with spring
constant k = 20.4 N/m and each attached at one end to a vertical rotating pole. Identical small spheres of
mass m are attached to the other ends of the springs. The spheres are constrained to horizontal motion
by horizontal guides of negligible friction, each of which has a ruler below it for measuring the radial
position r of the sphere. The system can be manually rotated about the pole's axis. In a lab experiment,
a student adjusts the rotational speed so that the spheres move to a desired radius r. For each such value
of r, the student measures the rotational period T. The student’'s partially completed data table is shown
below. The length of each unstretched spring is L = 0.15 m.
Radial
Acceleration Spring Force
Period
Trial
Position
T (s)
a. (m/s²)
Fspring (N)
r (m)
1
0.300
0.440
61.2
3.06
2
0.270
0.475
47.2
2.45
0.240
0.530
4
0.210
0.570
25.5
1.22
0.180
0.795
11.2
0.61
5.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Frictional torque causes a disk to decelerate from an angular speed of 4.10 rad/s at t = 0 to 1.30 rad/s at t = 4.70 s. The equation describing the angular speed of the wheel during this time interval is given by d? dt = ω0e−bt, where b and ω0 are constants. (a) What are the values of b and ω0 during this time interval? b = s−1 ω0 = rad/s (b) What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the disk at t = 4.70 s? rad/s2(c) How many revolutions does the disk make during the interval t = 0 to t = 4.70 s? revarrow_forwardA turntable (disk) of radius r = 27.0 cm and rotational inertia 0.440 kg · m2 rotates with an angular speed of 2.98 rad/s around a frictionless, vertical axle. A wad of clay of mass m = 0.242 kg drops onto and sticks to the edge of the turntable. What is the new angular speed of the turntable? (A) _______ rad/sarrow_forwardA potter's wheel having a radius 0.48 m and a moment of inertia of 10.5 kg · m2 is rotating freely at 50 rev/min. The potter can stop the wheel in 4.0 s by pressing a wet rag against the rim and exerting a radially inward force of 69 N. Find the effective coefficient of kinetic friction between the wheel and the wet rag.arrow_forward
- A uniform rod is set up so that it can rotate about an axis at perpendicular to one of its ends. The length and mass of the rod are 0.765 m and 1.27 kg respectively. A force of constant magnitude ?F acts on the rod at the end opposite the rotation axis. The direction of the force is perpendicular to both the rod's length and the rotation axis. Calculate the value of ?F that will accelerate the rod from rest to an angular speed of 6.21 rad/s in 9.91 sarrow_forwardA string is wrapped around a disk of mass m = 2.2 kg and radius R = 0.08 m. Starting from rest, you pull the string with a constant force F = 9 N along a nearly frictionless surface. At the instant when the center of the disk has moved a distance x = 0.12 m, your hand has moved a distance of d = 0.27 m. m d (a) At this instant, what is the speed of the center of mass of the disk? Vcm = m/s (b) At this instant, how much rotational kinetic energy does the disk have relative to its center of mass? Krot = Additional Materials M eBookarrow_forwardA grindstone in the shape of a solid disk (mass M = 50.0 kg) and radius R = 0.200 m (moment of Inertia | = 1/2 MR^2) is rotating at 90.0 rad/s. You press a metal box against the rim with a force F = 180 N and the grindstone comes to rest in 10.0 s. There is a friction force between the grindstone and the box. Find the magnitude of the friction.arrow_forward
- A potter's wheel having a radius 0.51 m and a moment of inertia of 14.9 kg · m2 is rotating freely at 50 rev/min. The potter can stop the wheel in 7.0 s by pressing a wet rag against the rim and exerting a radially inward force of 74 N. Find the effective coefficient of kinetic friction between the wheel and the wet rag.arrow_forwardA 250 g piece of kryptonite is attached to a 90 cm long masless string to form a pendulum. At its highest point (Point A) the string makes an angle of 55 degrees with the vertical. Its lowest point is Point B and Point C is where the string makes an angle of 35 degrees with respect to the vertical. Find the tension in the string and angular acceleration of the rock at (a) Point A, (b) Point B and (c) Point C. (a) Draw a free body diagran of the kryptonite, including all relevant angles and axes at Point A, Point B, and Point C. (Three total FBD) (b) Find the angular speed, angular acceleration and tension in the string at Point A. (c) Find the angular speed, angular acceleration, centripetal force and tension in the string at Point B. (d) Find the angular speed, angular acceleration, centripetal force and tension in the string at Point C.arrow_forwardA block of m = 2.00 kg hangs from a string that passes over a pulley with a moment of inertia / (to be determined) and a radius R = 0.44 m. The system of block and pulley is released from rest when the block is 5.00 m above the floor. It takes t = 1.17 s for the block to reach the floor. As the block accelerates downward, the pulley undergoes a counterclockwise angular acceleration. Using Newton's Laws (for linear and rotational motion), determine the moment of inertia I of the pulley. (Consider the linear acceleration of the block (from kinematics), the tension in the string, and the torque on the pulley. Careful with (+/-) directions} O 0.166 kg m² O 0.144 kg m² O 0.132 kg m2 O 0.173 kg m2 O 0.149 kg m2 30 F3 888 F4 esc F5 F6 #3 $ & 8arrow_forward
- An object (with mass m = 6.20 kg) is attached to the free end of a massless string wrapped around a reel of radius R = 0.550 m and mass M = 4.00 kg. The reel is a solid disk, free to rotate in a vertical plane about the horizontal axis passing through its center, as shown in the figure. The suspended object is released from rest 3.50 m above the floor. Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration (in m/s2) of the object. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.Note: I=1/2 MR^2arrow_forward= - = 6. A mass M₁ 10 kg resting on a horizontal frictionless surface is attached to a M₂ = 7 kg weight by a light wire that passes over a frictionless pulley. See figure. The pulley has the shape of a uniform disk of mass M3 4 kg and radius R 0.3 m. After the system is released, find (a) the tension in the wire on both sides of the pulley, (b) the acceleration of M₁, and (c) the horizontal and vertical forces that the axle exerts on the pulley. M1 M 3 M2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON