
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
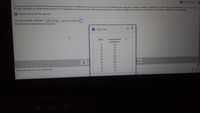
Transcribed Image Text:EQuestion Help
The ages (in years) of 10 men and their systolic blood pressures (in millimeters of mercury) are shown in the attached data table with a sample correlation coefficient r of 0.899. Remove the data entry for the man who is
50 years old and has a systolic blood pressure of 200 millimeters of mercury from the data set and find the new correlation coefficient. Describe how this affects the correlation coefficient r. Use technology
E Click the icon to view the data set.
The new correlation coefficient r gets stronger, going from 0.899 to
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Data Table
Age, x
Systolic blood
pressure, y
16
109
26
121
38
141
46
131
50
200
65
182
69
198
More
32
129
56
175
Enter your answer in the answer box
119
23
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following graph plots data for tax per gallon and internal miles.Carefully explain what the graph is about, and what it captures. What are the limitations of the correlation and what can a researcher do toovercome these?arrow_forwardQuestion Help The ages (in years) of 10 men and their systolic blood pressures (in millimeters of mercury) are shown in the attached data table with a sample correlation coefficient r of 0.910. Remove the data entry for the man who is 51 years old and has a systolic blood pressure of 200 millimeters of mercury from the data set and find the new correlation coefficient. Describe how this affects the correlation coefficient r. Use technology. Click the icon to view the data set. The new correlation coefficient r going from 0.910 to Data Table (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Age, x Systolic blood pressure, y 110 16 121 26 39 144 130 45 200 51 183 63 Loc 69 199 Bro 130 32 175 58 24 118 Print Done Enter your answer in the answer box. AdChoices PAGCS DEC O étv 13 MacBook Pro DD DII F6 F9 F2 F10 F12 F3 F8 F11 F5 F7 F1 F4 %23 $4 4 & 5. 9. 6. 8 0 utitamarrow_forwardC learn.vccs.edu/courses/474823/assignments/9794759 Identify if the following correlation. Describe if it is strong, weak, or no correlation. Then determine if the relationship is positive, negative, or neither. Explain your answer. O ● OHO ● ● ● ● O acer Provide your answer in the box below.arrow_forward
- If the Correlation Coefficient (r) between two variable was calculated to be 0.7898, what percent (%) of the variation of the dependent variable is due to the variation of the independent variable? Group of answer choices 103.1% 33.1% 62.4% 94.0%arrow_forwardSolve and explain please. Thanksarrow_forwardThe heights and weights of a set of students were recorded on a scatter graph. Describe the correlation depicted below: Select- strong, moderate, weak and Select- positive, negativearrow_forward
- I need correlation coefficient ,test statistic , p value & conclusion pls help I need in an hourarrow_forwarduse the sample data to construct a scatterplot. Use the first variable for the x-axis. Based on the scatterplot, what do you conclude about a linear correlation? FORECAST AND ACTUAL TEMPERATURES The table lists actual high temperatures and the high temperatures that were previously forecasted for these same days. The table includes data for ten different days near the author’s home. What does the result suggest about the accuracy of five-day predicted high temperatures?arrow_forwardUse a graphing calculator to find the equation of the line of best fit for the data in the table below. Find the value of the correlation coefficient r. Then predict the number of movie tickets sold in 2014.arrow_forward
- Please use the values from the given r values and assign the accurate value to the plots A,B,C, or D.arrow_forwardPLEASE SHOW AN EXPLANATION FOR EACH PARTarrow_forwardGiven the scatter plot shown, determine if the correlation is positive, negative, or if there is no relative correlation. Correlation for this scatter plot: Select an answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman