
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
![### Transcription for Educational Website
#### b. Analysis of Bonferroni Results
The Bonferroni results inform us that:
- **There is a significant difference between the No Treatment and Fertilizer groups.**
- **There is a significant difference between the No Treatment and Irrigation groups.**
- **There is a significant difference between the No Treatment and Fertilizer and Irrigation groups.**
#### c. Bonferroni Test Procedure
Using the Bonferroni test with a 0.10 significance level, we determine if there's a significant difference between the mean amount of the irrigation treatment group and the group treated with both fertilizer and irrigation.
##### Steps for Analysis:
1. **Test Statistic:**
- [Input the calculated value, rounded to two decimal places as needed.]
2. **P-value:**
- [Input the calculated value, rounded to three decimal places as needed.]
##### Result Interpretation:
- **Option A:** Reject \( H_0 \). There is insufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the irrigation treatment group and the group treated with both fertilizer and irrigation yield the same mean poplar weight.
- **Option B:** Fail to reject \( H_0 \). There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the irrigation treatment group and the group treated with both fertilizer and irrigation yield the same mean poplar weight.
- **Option C:** Fail to reject \( H_0 \). There is insufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the irrigation treatment group and the group treated with both fertilizer and irrigation yield the same mean poplar weight.
- **Option D:** Reject \( H_0 \). There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the irrigation treatment group and the group treated with both fertilizer and irrigation yield the same mean poplar weight.
**Note:** Please fill in the test statistic and P-value where indicated for a complete analysis.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/6d1239aa-d77b-4fd4-9256-17d7501a8b6d/84407399-8627-4b8c-82d6-4fa96bda0b57/8zhfqlf_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:### Transcription for Educational Website
#### b. Analysis of Bonferroni Results
The Bonferroni results inform us that:
- **There is a significant difference between the No Treatment and Fertilizer groups.**
- **There is a significant difference between the No Treatment and Irrigation groups.**
- **There is a significant difference between the No Treatment and Fertilizer and Irrigation groups.**
#### c. Bonferroni Test Procedure
Using the Bonferroni test with a 0.10 significance level, we determine if there's a significant difference between the mean amount of the irrigation treatment group and the group treated with both fertilizer and irrigation.
##### Steps for Analysis:
1. **Test Statistic:**
- [Input the calculated value, rounded to two decimal places as needed.]
2. **P-value:**
- [Input the calculated value, rounded to three decimal places as needed.]
##### Result Interpretation:
- **Option A:** Reject \( H_0 \). There is insufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the irrigation treatment group and the group treated with both fertilizer and irrigation yield the same mean poplar weight.
- **Option B:** Fail to reject \( H_0 \). There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the irrigation treatment group and the group treated with both fertilizer and irrigation yield the same mean poplar weight.
- **Option C:** Fail to reject \( H_0 \). There is insufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the irrigation treatment group and the group treated with both fertilizer and irrigation yield the same mean poplar weight.
- **Option D:** Reject \( H_0 \). There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the irrigation treatment group and the group treated with both fertilizer and irrigation yield the same mean poplar weight.
**Note:** Please fill in the test statistic and P-value where indicated for a complete analysis.
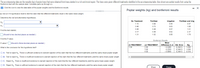
Transcribed Image Text:# Educational Resource: Analyzing Poplar Weight Data with Bonferroni Tests
## Overview
This example explores the effect of different treatments on the mean weight of poplar trees. Poplar weights were measured in kilograms (kg) from trees subjected to different treatments in a rich and moist environment. The aim is to test the hypothesis that these treatments do not result in significantly different mean weights.
### Hypothesis Testing
We use a significance level of 0.10 for this test.
#### Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- **Null Hypothesis (H₀):** The treatments result in the same mean poplar weight.
- **Alternative Hypothesis (H₁):** The treatments result in different mean poplar weights.
#### Tasks
1. **Find the Test Statistic:**
- Calculation involves determining the variance among the treatment groups.
- Results should be rounded to two decimal places.
2. **Find the P-value:**
- Calculation of the probability to observe the outcomes given that the null hypothesis is true.
- Results should be rounded to three decimal places.
### Bonferroni Results
The table details the mean differences between treatments alongside their statistical significance.
#### Poplar Weights (kg)
There are four categories:
- **No Treatment:** Weights range from 0.17 kg to 1.31 kg.
- **Fertilizer:** Weights range from 0.49 kg to 1.02 kg.
- **Irrigation:** Weights range from 0.06 kg to 0.88 kg.
- **Fertilizer and Irrigation:** Weights range from 0.87 kg to 1.76 kg.
#### Statistical Comparisons
- **Mean Difference (I-J):** Reflects the difference in mean weights between treatments I and J.
- **Std. Error:** The standard error of the difference.
- **Sig.:** Significance level determining if the difference is statistically meaningful.
### Conclusions
Based on the significance:
- **A.** Fail to reject H₀: There's enough evidence to reject the claim that all treatments yield the same result.
- **B.** Fail to reject H₀: There's insufficient evidence to reject this claim.
- **C.** Reject H₀: There's insufficient evidence to support the claim that treatments yield the same weight.
- **D.** Reject H₀: There's sufficient evidence to support rejection of the
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Claim: : P = 0.23; a 0.10; Sample Statistics : P = 0.17₁ n = 100 A.) Find the 2- test static. Select the Correct Choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to Complete Your choice. 2 = ( Round to two decimal places as needed) 0 3.) What is the result of the test Reject or fail to reject? ?arrow_forwardJ In-shop othesis test for the difference between two population proportions 02562 2600368.qx3zqy7 Jump to level 1 The manager of a coffee shop is trying to determine if drive-through customers buy fewer items than customers who come into the shop. The manager randomly samples both populations and calculates the proportion of customers in each that buy three or more items. The results of the data collected are shown below. What are the population parameters? Y Pick Drive-through Successes 27 Successes What is the level of significance? Ex: 0.12 Observations 76 Observations 41 119 0.345 p-hat_1 0.355 p-hat_2 What is the null hypothesis Ho? Pick Confidence Level 0.1429 What is the alternative hypothesis Ha? Pick p-value Should Ho be rejected or does Ho fail to be rejected? Pick What conclusion can be drawn from the data? Pick evidence exists to support the claim that drive-through customers buy fewer items than in-shop customers. 2 p Warrow_forwardNote:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman