
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
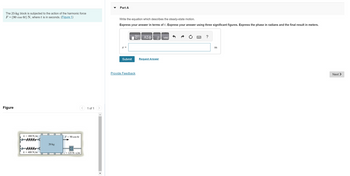
Transcribed Image Text:The 20-kg block is subjected to the action of the harmonic force
F = (90 cos 6t) N, where t is in seconds. (Figure 1)
Figure
k= 400 N/m
k = 400 N/m
O
20 kg
F= 90 cos 6t
125 N.s/m
1 of 1
Part A
Write the equation which describes the steady-state motion.
Express your answer in terms of t. Express your answer using three significant figures. Express the phase in radians and the final result in meters.
x =
Submit
17 ΑΣΦ
Provide Feedback
↓↑
Request Answer
vec
?
m
Next >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4. A spring with stiffness constant k = 2000 N/m attached to a platform launched a mass of 2kg vertically in the air to some maximum height (measured from the equilibrium point of the spring). The spring was compressed by 0.3 meters before launch. Due to internal friction of the spring, 10 Joules of energy was lost as the spring expanded. How fast was the mass travelling when it was at half of its maximum height? You must use g= 10m/s? for this problem or you will actually find it much more difficult to calculate. Hint: First solve the problem of finding what the maximum height is and then solve the problem of finding the speed at half of that height.arrow_forwardDamian’s car weighs 2000kg. The spring has a natural unstretched length of 2m and a spring constant of k = 80000N/m. Hooke's law can be written as T = kd. Where T is the tension force in newtons, k is the spring constant and d is the length in metres. Let x(t) be the position of the front of Damian’s car and let y(t) be the position of the back of Eva’s 4WD. We will assume that the position of Eva’s car is a known function of time. Q1 a) Create a sketch of the positions of the vehicles similar to the one given and add the positions x and y. b) What is the extension of the spring in terms of x(t) and y(t)? Be careful to take into account that the unstretched length of the spring is 2m.arrow_forwardA used battery was brought to the workshop and the technician noticed that it had 1 litre of distilled water in it but was fully discharged. The specs sheet for this type of battery states that it is fully charged when the change in distilled water to the change in charge equals to the difference between twice the amount of charge and the actual amount of distilled water existing in the battery For the used battery, derive the differential equation and state the initial condition for the range x= 0(0.2)1.0, then obtain a numerical solution for this equation using Euler’s method.arrow_forward
- 1. The mechanical system shown in Figure 1 is initially at rest. The displacement x of mass m is measured from the rest position. With m = 10 kg, b = 20 N-s/m, and k = 500 N/m, the system is set into motion at t=0 by an impulsive force whose strength is 20 N. Obtain the initial velocity *(0,) of the mass due to the impulsive force.arrow_forwardI need help on this problem.arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution .....arrow_forward
- Q4. A two-degree-of-freedom model consisting of two masses connected in series by two springs is shown in the figure below. The physical parameters have the values m, = 8 kg, m, = 2 kg, k, = 20 N/m, and k2 = 30 N/m. X1 X2 m1 m2 k1 k2 (A) Write down the equation of motion for mass m, (B) Write down the equation of motion for mass m, Calculate the first (larger) natural frequency of the system (D) Calculate the second (smaller) natural frequency of the systemarrow_forwardA 20 kg weight is attached to a spring with constant k = 320 kg/m and subjected to an external force F(t) = 1200 cos(2t). The weight begins at rest in its equilibrium position. Find its displacement for t> 0, with y(t) measured positive upwards. y(t) =arrow_forwardFBD: The mass of a pendulum is connected to a spring with a spring constant Kas shown in the figure. The spring stays vertical all the time with the help of a massless follower. The vertical distance between the fixed point O and the path of the massless follower is 2L. Use Newton's second law and find the equation of motion of the system in terms of 0. 762 mgbi Img 2L L bil Nig K 777777 P EMO = Jaz ->0₂ ?arrow_forward
- An object attached to the end of a vertical helical spring bounces with a frequency of 2.1 Hz. If the spring constant is 5.9 N/m, what is the mass of the object?arrow_forwardshow each step for answerarrow_forwardA force of F = 50 N is applied to the rope that causes the angle 0₁ = 60 degrees to keep the system at equilibrium. The N spring constant is k = 100 m B a 0₁ с a b с Variable Value 2 m 2 m 2 m F b Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. cc i❀O BY NC SA 2013 Michael Swanbomarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY