
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
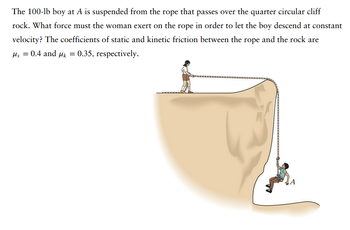
Transcribed Image Text:The 100-lb boy at A is suspended from the rope that passes over the quarter circular cliff
rock. What force must the woman exert on the rope in order to let the boy descend at constant
velocity? The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the rope and the rock are
Ms = 0.4 and μk = 0.35, respectively.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 130-lb crate is being transported by a 175-lb hand- truck cart along the frictionless floor. The coefficients of friction between the cart and the box are μ = 0.20 and Mk = 0.15. If a force P = 45 lb is applied as shown, P determine the smallest ratio d/b for which the box will tip before it slides. Neglect the mass of the wheels of the cart. Show the complete and clear solutions including the necessary diagrams (i.e., FBD and the KD diagrams).arrow_forwardAssume that a driver (car modeled as a point mass) is negotiating a circular turn with a radius of 160 ft. The car and driver have a mass of 3800 lb and the coefficient of friction between the car and road is µ1 = 0.85. What is the maximum constant speed for which the car can travel at the given radius? r= 160 ftarrow_forwardThe block has a mass of 140 kg and rests on a surface for which the coefficients of static and kinetic friction are Hs = 0.5 and uj. = 0.4, respectively. (Figure 1) Part A If a force F = (60t2 ) N, where t is in seconds, is applied to the cable, determine the power developed by the force when t = 5 s. Hint: First determine the time needed for the force to cause motion. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. µA ? P = Value Units Figure 1 of 1 Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forward
- Block A has a mass of 10 kg and bloc B has a mass of 2 Kg and are kept at rest. The 2 blocs are comected by a cord passing by a wheel at the top of the incline. The surface of the incline has a friction coefficient -0.12. The angle of the incline is 0= 30°. A is at 6 meters above the incline floor. After being released from rest, the bloc A will move down. Determine the total energy of the bloc A after it has moved down the incline by 4 meters.. Calculate its velocity. 6 m Barrow_forwardThe 498-N force is applied to the 89-kg block, which is stationary before the force is applied. Determine the magnitude and direction of the friction force F exerted by the horizontal surface on the block. The force is positive if to the right, negative if to the left. H₂ = 0.66 Hk = 0.52 36° P = 498 Narrow_forwardTwo blocks A and B have a weight of 11 lb and 6 lb , respectively. They are resting on the incline for which the coefficients of static friction are μA = 0.16 and μB = 0.23. Determine the angle θ which will cause motion of one of the blocks. What is the friction force under each of the blocks when this occurs? The spring has a stiffness of k = 2 lb/ft and is originally unstretched. Determine the smallest angle θ which will cause motion of one of the blocks. Determine is the friction force under the block A at this angle. Determine is the friction force under the block B at this angle.arrow_forward
- The 2-kg spool S fits loosely on the inclined rod for which the coefficient of static friction is μ = 0.28. (a) If the spool is located 0.25 m from A, determine the maximum constant speed the spool can have so that it does not slip up the rod. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardPlease give a detailed solution asap. Handwritten answer,no gpt.arrow_forwardBlock A has a mass of 26 kg and block B has a mass of 43 kg. The two blocks are stacked on the ramp with an incline of 0 = 33°. Determine the largest horizontal force F that can be applied to block B without either block moving for each of the following two cases: a.) The friction coefficient for the contact between blocks A and B is Ha1 = 0.62 and the friction coefficient for the contact between block A and the ramp is H2 = 0.26. b.) The friction coefficient for the contact between blocks A and B is Ha1 = 0.62 and the friction coefficient for the contact between block A and the ramp is H2 = 0.65. F В A Part a) The limiting slip condition occurs at the contact betveen A and the ramp ♥ N The maximum force before either block A or B slips is Part b) The limiting slip condition occurs at the contact between A and B N. The maximum force before either block A or B slips isarrow_forward
- The coefficient of friction between all surfaces is us = 0.4 and μK = 0.3. The mass of A is 11 kg and the mass of B is 36 kg. Assume the pulley is mass less and frictionless. Determine the smallest force P required to keep the system moving. P A A Barrow_forwardThe force Pis applied to the 52-kg block when it is at rest. Determine the magnitude and direction of the friction force exerted by the surface on the block if (a) P = 0, (b) P = 184 N, and (c) P = 245 N. (d) What value of P is required to initiate motion up the incline? The static and kinetic coefficients of friction between the block and the incline are ug = 0.20 and µ = 0.16, respectively. The friction force is positive if up the incline, negative if down the incline. 52 kg 21° H, = 0.20 H = 0.16 13 Answers: (a) F= i N (b) F = i N (c) F= i N (d) P= i Narrow_forwardNEED ASAParrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY