
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Two blocks A and B have a weight of 11 lb and 6 lb , respectively. They are resting on the incline for which the coefficients of static friction are μA = 0.16 and μB = 0.23. Determine the angle θ which will cause motion of one of the blocks. What is the friction force under each of the blocks when this occurs? The spring has a stiffness of k = 2 lb/ft and is originally unstretched. Determine the smallest angle θ which will cause motion of one of the blocks. Determine is the friction force under the block A at this angle. Determine is the friction force under the block B at this angle.
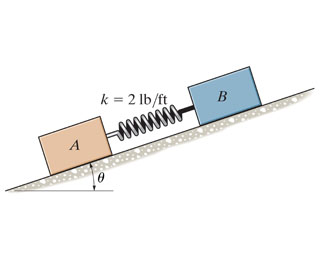
Transcribed Image Text:A
k = 2 lb/ft
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The horizontal force P = 90 N is applied to the upper block with the system initially stationary. The block masses are mA = 14.4 kg and mB = 5.1 kg. Use g = 9.81 ms-2. Determine the magnitude of the frictional force that block B exerts on block A. The coefficients of static friction are µ1 = 0.40 and µ2 = 0.50. The coefficients of kinetic friction are 75% of the respective static values. Give your answer in Newtons.arrow_forwardS If the coefficients of static friction at contact points A and B areμ = 0.21 andμ¹ = 0.24 respectively, determine the smallest force P that will cause the 179-kg spool to have impending motion. Supply your answer in Newtons. 400 mm 200 mm B P 150 mmarrow_forwardThe force P = 150 N is applied to the 50-kg crate, which is stationary before the force is applied. Take ? = 30 Coefficient of static friction ?? = 0.3 and coefficient of kinetic friction ?? = 0.25 Determine the magnitude of the normal force, which is acting on the box. Express your answer in N to three significant figures. Do not include the units.arrow_forward
- The 100-lb boy at A is suspended from the rope that passes over the quarter circular cliff rock. Determine if it is possible for the 185-lb woman to hoist him up; and if this is possible, what smallest force must she exert on the rope? The coefficient of static friction between the rope and the rock is μ = 0.2, and between the shoes of the woman and the ground μ' = 0.8.arrow_forwardThe 447-N force is applied to the 94-kg block, which is stationary before the force is applied. Determine the magnitude and direction of the friction force Fexerted by the horizontal surface on the block. The force is positive if to the right, negative if to the left. P = 447 N 33° = 0.60 H = = 0.46 Answer: F = i Narrow_forwardThe man pushes on the roller with force P through a handle that connects to the central axle of the roller. If the coefficient of static friction between the 49-lb roller and the floor is s = 0.22, determine the maximum force Pthat can be applied to the handle, so that roller rolls on the ground without slipping. Assume the roller to be a uniform cylinder. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper unit. Take g = 32.2 ft/s2. 1.5 ft 30° Your Answer: Answer unitsarrow_forward
- The man pushes on the roller with force P through a handle that connects to the central axle of the roller. If the coefficient of static friction between the 43-lb roller and the floor is g = 0.16, determine the maximum force P that can be applied to the handle, so that roller rolls on the ground without slipping. Assume the roller to be a uniform cylinder. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper unit. Take g = 32.2 ft/s². Your Answer: Answer 30° units 1.5 ftarrow_forwardBlocks A and B weigh 50 Ib and 30 lb, respectively. Using the coefficients of static friction indicated, determine the greatest weight of block E without causing motion.arrow_forwardDetermine the maximum and the minimum values of weight W which may be applied without causing the 25-kg block to slip. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is μs= 0.2, and between the rope and the drum D is μ′s= 0.3.arrow_forward
- The uniform rod has a mass of 13.09 kg and rests on the inside of the smooth ring at B and on the ground at A. If the rod is on the verge of slipping, determine the coefficient of static friction between the rod and the ground.arrow_forward5) The crate at a 10° incline has a mass of 350 kg and is subjected to a towing force P acting at a 20° angle with the horizontal. If the coefficient of static friction is µs = 0.5, determine the magnitude of P needed start impending motion. Given: M = 350 kg = 20 deg = 10 deg Us = 0.5 m g = 9.81arrow_forwardThe fork lift has a weight of 2,400 lb and a center of gravity at G. If the rear wheels are powered, whereas the front wheels are free to roll, determine the maximum number of 300-lb crates the fork lift can push forward. The coefficient of static friction between the wheels and the ground is μw = 0.4 and between the each crate and the ground μc = 0.35. 2.5 ft 1.25 ft -3.50 ft- XIXIXarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY