
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
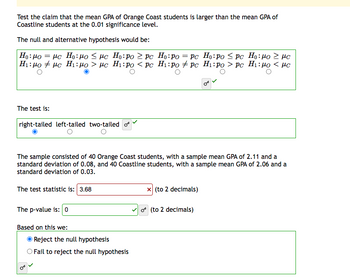
Transcribed Image Text:Test the claim that the mean GPA of Orange Coast students is larger than the mean GPA of
Coastline students at the 0.01 significance level.
The null and alternative hypothesis would be:
=
Ho: Po
με Ho:μο < με Ho:po >pc
H:μο # με H:μο > με Hi:po < pc
The test is:
right-tailed left-tailed two-tailed of
The sample consisted of 40 Orange Coast students, with a sample mean GPA of 2.11 and a
standard deviation of 0.08, and 40 Coastline students, with a sample mean GPA of 2.06 and a
standard deviation of 0.03.
The test statistic is: 3.68
The p-value is: 0
Based on this we:
Ho:po = pc Ho:po Spc Ho:μο 2 με
Hi:po + pc Hi:po > pc Hı:mo < με
Reject the null hypothesis
Fail to reject the null hypothesis
x (to 2 decimals)
o(to 2 decimals)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Test the claim that the mean GPA of Orange Coast students is significantly different than the mean GPA of Coastline students at the 0.1 significance level.The null and alternative hypothesis would be: H0:pO≤pCH0:pO≤pCH1:pO>pCH1:pO>pC H0:pO=pCH0:pO=pCH1:pO≠pCH1:pO≠pC H0:pO≥pCH0:pO≥pCH1:pO<pCH1:pO<pC H0:μO=μCH0:μO=μCH1:μO≠μCH1:μO≠μC H0:μO≥μCH0:μO≥μCH1:μO<μCH1:μO<μC H0:μO≤μCH0:μO≤μCH1:μO>μCH1:μO>μC The test is: left-tailed right-tailed two-tailed The sample consisted of 80 Orange Coast students, with a sample mean GPA of 2.73 and a standard deviation of 0.08, and 80 Coastline students, with a sample mean GPA of 2.68 and a standard deviation of 0.05.The test statistic is: (to 2 decimals)The p-value is: (to 2 decimals)Based on this we: Reject the null hypothesis Fail to reject the null hypothesisarrow_forwardTest the claim that the proportion of men who own cats is smaller than the proportion of women who own cats at the .005 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Ho: PM = PF Ho: MM = F Ho: PM = PF H₁ PM PF H₁: μM μF H₁ PM > PF O O The test is: left-tailed two-tailed O O Based on a sample of 80 men, 25% owned cats Based on a sample of 20 women, 35% owned cats The test statistic is: The p-value is: right-tailed O Based on this we: O Reject the null hypothesis O Fail to reject the null hypothesis Ho: PM = MF H₁: MM > MF (to 2 decimals) (to 2 decimals) Ho: MM = F Ho:PM = PF H₁: MM < MF H₁:PM < PF O Oarrow_forwardTest the claim that the mean GPA of night students is smaller than 2.8 at the .05 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: = 2.8 Ho:p= 0.7 Ho:μ = 2.8 : Ho p= 0.7 Ho:μ = 2.8 Ho: p = 0.7 Ho:μ = H₁:p 2.8 H₁:p 0.7 H₁:μ 0.7 H₁:μ ‡ 2.8 The test is: right-tailed two-tailed left-tailed Based on a sample of 50 people, the sample mean GPA was 2.75 with a standard deviation of 0.02 The test statistic is: (to 2 decimals) The critical value is: (to 2 decimals) Based on this we: Reject the null hypothesis Fail to reject the null hypothesisarrow_forward
- Test the claim that the mean GPA of night students is significantly different than 2.3 at the 0.05 significance level.The null and alternative hypothesis would be: H0:μ=2.3H0:μ=2.3H1:μ>2.3H1:μ>2.3 H0:p=0.575H0:p=0.575H1:p>0.575H1:p>0.575 H0:μ=2.3H0:μ=2.3H1:μ<2.3H1:μ<2.3 H0:p=0.575H0:p=0.575H1:p≠0.575H1:p≠0.575 H0:μ=2.3H0:μ=2.3H1:μ≠2.3H1:μ≠2.3 H0:p=0.575H0:p=0.575H1:p<0.575H1:p<0.575 The test is: two-tailed left-tailed right-tailed Based on a sample of 80 people, the sample mean GPA was 2.27 with a standard deviation of 0.02The test statistic is: (to 2 decimals)The positive critical value is: (to 2 decimals)Based on this we: Fail to reject the null hypothesis Reject the null hypothesisarrow_forwardIarrow_forwardTest the claim that the mean GPA of night students is significantly different than 2.2 at the 0.01 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Ho: p = 0.55 H₁: p > 0.55 Ho : μ = 2.2 H₁ : µ 2.2 Ho:|=2.2 H₁: μ2.2 O Ho: p = 0.55 H₁: p0.55 O Ho: p = 0.55 H₁: p < 0.55 Based on a sample of 80 people, the sample mean GPA was 2.22 with a standard deviation of 0.06 The test statistic is decimals) The positive critical value is Based on this we (to 3 decimals) reject the null hypothesis fail to reject the null hypothesis (to 3arrow_forward
- Test the claim that the mean GPA of night students is larger than 2.3 at the .025 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Но : р — 2.3 Но:н — 2.3 Но:р %3D 0.575 Но: д —— 2.3 Но:р %3D 0.575 Но:р 3 0.575 H:р + 2.3 Hi:p 2.3 Н:р#0.575 H:р> 0.575 The test is: left-tailed right-tailed two-tailed Based on a sample of 65 people, the sample mean GPA was 2.34 with a standard deviation of 0.06 The test statistic is: (to 2 decimals) The critical value is: (to 2 decimals) Based on this we: O Fail to reject the null hypothesis O Reject the null hypothesisarrow_forwardIs there an association between hair color and body type? The table below shows the results of a researcher's observations of randomly selected people. Frequencies of Hair Colors for Various Body Types Blonde Brunette Red Head Short and Slender 73 90 43 Short and Pudgy 110 108 70 Tall and Slender 53 99 70 Tall and Heavy 60 106 78 What can be concluded at the αα = 0.05 significance level? What is the correct statistical test to use? Independence Goodness-of-Fit Paired t-test Homogeneity What are the null and alternative hypotheses?H0:H0: The distribution of hair color is not the same for each body type. Hair color and body type are dependent. The distribution of hair color is the same for each body type. Hair color and body type are independent. H1:H1: The distribution of hair color is the same for each body type. The distribution of hair color is not the same for each body type. Hair color and body type are independent. Hair color and body type are…arrow_forwardTest the claim that the proportion of people who own cats is significantly different than 40% at the 0.2 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Ho:p 0.4 Ho: u 2 0.4 Ho:p = 0.4 Ho: p = 0.4 Ho:u 0.4 H1:p 0.4 The test is: two-tailed left-tailed right-tailed Based on a sample of 700 people, 34% owned cats The p-value is: (to 2 decimals) Based on this we: O Fail to reject the null hypothesis O Reject the null hypothesis Question Help: DVideo M hparrow_forward
- Test the claim that the proportion of men who own cats is significantly different than 30% at the 0.01 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Ho:p = 0.3 Ho:p = 0.3 Ho:u = 0.3 Ho:µ = 0.3 Ho:p = 0.3 Ho:u = 0.3 H1:p # 0.3 H1:p > 0.3 H1:4 > 0.3 H1:µ < 0.3 H1:p < 0.3 H1:u + 0.3 The test is: left-tailed two-tailed right-tailed Based on a sample of 50 people, 22% owned cats The test statistic is: (to 2 decimals) The positive critical value is: (to 2 decimals) Based on this we: O Fail to reject the null hypothesis Reject the null hypothesisarrow_forwardTest the claim that the proportion of men who own cats is significantly different than the proportion of women who own cats at the 0.02 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Но: HF Ho: UM = µF Ho:PM — pF Ho:рм PF Ho: им — MF Ho:; PF Нi: рм > иF Hi: рм # pF Hi:рм рF Hi: рм < pF Hi:рм # pғ The test is: right-tailed two-tailed left-tailed Based on a sample of 80 men, 25% owned cats Based on a sample of 40 women, 50% owned cats The test statistic is: (to 2 decimals) The p-value is: (to 2 decimals) Based on this we: O Reject the null hypothesis O Fail to reject the null hypothesisarrow_forwardTest the claim that the mean GPA of night students is significantly different than 2.5 at the 0.1 significance level. The null and alternative hypothesis would be: Ho: µ 2 2.5 Ho:p 0.625 Ho:p= 0.625 Ho: µ 0.625 H1:p 2.5 H:µ + 2.5 The test is: left-tailed two-tailed right-tailed Based on a sample of 60 people, the sample mean GPA was 2.47 with a standard deviation of 0.07 The test statistic is: (to 2 decimals) The p-value is: (to 2 decimals) Based on this we: O Reject the null hypothesis O Fail to reject the null hypothesisarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman