
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
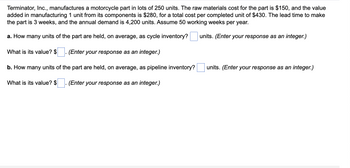
Transcribed Image Text:Terminator, Inc., manufactures a motorcycle part in lots of 250 units. The raw materials cost for the part is $150, and the value
added in manufacturing 1 unit from its components is $280, for a total cost per completed unit of $430. The lead time to make
the part is 3 weeks, and the annual demand is 4,200 units. Assume 50 working weeks per year.
a. How many units of the part are held, on average, as cycle inventory?
units. (Enter your response as an integer.)
(Enter your response as an integer.)
b. How many units of the part are held, on average, as pipeline inventory?
What is its value? $ (Enter your response as an integer.)
What is its value? $
units. (Enter your response as an integer.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Iguana, Inc., manufactures bamboo picture frames that sell for $25 each. Each frame requires 4 linear feet of bamboo, which costs $2.00 per foot. Each frame takes approximately 30 minutes to build, and the labor rate averages $12.00 per hour. Iguana has the following inventory policies: Ending finished goods inventory should be 40 percent of next month’s sales. Ending direct materials inventory should be 30 percent of next month’s production. Expected unit sales (frames) for the upcoming months follow: March 275 April 250 May 300 June 400 July 375 August 425 Variable manufacturing overhead is incurred at a rate of $0.30 per unit produced. Annual fixed manufacturing overhead is estimated to be $7,200 ($600 per month) for expected production of 4,000 units for the year. Selling and administrative expenses are estimated at $650 per month plus $0.60 per unit sold.Iguana, Inc., had $10,800 cash on hand on April 1. Of its sales, 80 percent is in cash. Of the…arrow_forwardGlobal GPS industries assembles its GPS systems with the following costs. Each or requires one computer system and 4 batteries. Computer systems cost $140 each, and Batteries are $2.50 each. Global is able to reliably obtain computers as needed and does not maintain them in inventory. However, batteries are stocked in inventory sufficient to produce 20% of the following month's expected production. Planned production is as follows: January February March April 24,000 systems 39,750 systems 23,850 systems 25,000 systems BB batter Compute No end/No Required: Prepare a direct material purchasing plan for January, February, and March based on the above facts.arrow_forwardSuppose a company has 1,000 units of a raw material part on hand. If 750 of these units are routed into production, should the company place an order to stock up on more of these parts? (Show calculations). Determine the economic order quantity (EOQ) for this part, assuming the following:The company plans to use 10,000 units during the coming year.The company orders this part in lots of 1,000 units, and each order placed carries a processing cost of $2.50.Each unit of inventory carries an annual holding cost of $6.40.arrow_forward
- Leeds Corp. produces product BR500. Shamokin expects to sell 10,000 units of BR500 and to have an ending finished inventory of 2,000 units. Currently, it has a beginning finished inventory of 800 units. Each unit of BR500 requires two labor operations, one labor hour of assembling and two labor hours of polishing. The direct labor rate for assembling is $10 per assembling hour and the direct labor rate for polishing is $12.50 per polishing hour. The expected number of hours of direct labor for BR500 for this period are O 8,800 hours of assembling; 17,600 hours of polishing O 11,200 hours of assembling: 22,400 hours of polishing 17,600 hours of assembling: 8,800 hours of polishing O 22,400 hours of assembling: 11,200 hours of polishingarrow_forwardA manufacturer has a production facility that requires 19,111 units of component JY21 per year. Following a long-term contract, the manufacturer purchases component JY21 from a supplier with a lead time of 6 days. The unit purchase cost is $12.8 per unit. The cost to place and process an order from the supplier is $113 per order. The unit inventory carrying cost per year is 20 percent of the unit purchase cost. The manufacturer operates 250 days a year. Assume EOQ model is appropriate. What is the optimal total annual inventory and purchase cost for the manufacturer? Use at least 4 decimal places.arrow_forwardCeder Company has compiled the following data for the upcoming year: Sales are expected to be 16,000 units at $52 each. Each unit requires 4 pounds of direct materials at $2.40 per pound. Each unit requires 2.1 hours of direct labor at $13 per hour. Manufacturing overhead is $4.90 per unit. Beginning direct materials inventory is $5,400. Ending direct materials inventory is $6,950. Selling and administrative costs totaled $138,720. Determine Ceder's budgeted cost of goods sold. Complete Ceder's budgeted income statement.arrow_forward
- Iguana, Inc., manufactures bamboo picture frames that sell for $25 each. Each frame requires 4 linear feet of bamboo, which costs $2.00 per foot. Each frame takes approximately 30 minutes to build, and the labor rate averages $12.00 per hour. Iguana has the following inventory policies: • Ending finished goods inventory should be 40 percent of next month's sales. • Ending raw materials inventory should be 30 percent of next month's production. Expected unit sales (frames) for the upcoming months follow: March April 275 250 May 300 June 400 July August 375 425 Variable manufacturing overhead is incurred at a rate of $0.30 per unit produced. Annual fixed manufacturing overhead is estimated to be $7,200 ($600 per month) for expected production of 4,000 units for the year. Selling and administrative expenses are estimated at $650 per month plus $0.60 per unit sold. Iguana, Inc., had $10,800 cash on hand on April 1. Of its sales, 80 percent is in cash. Of the credit sales, 50 percent is…arrow_forwardFaber Manufacturing, Inc., of St. Paul, Minnesota has an economic order quantity considering backordering of 763, a maximum backordering quantity in units of 480, annual holding cost/unit = $3.5; lead time = 1.4 month (the firm operates 12 months per year). If the firm's customers do not object to backordering and each unit backordered costs $ 4.5/year, then: What is the maximum inventory level?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education