
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
Ten laboratories were asked to determine the concentration of an analyte A in three standard test samples. Following are the results, in parts per million.
Determine if there is a significant difference between Sample 1, Sample 2, and Sample 3 at a significance level of α = 0.05.
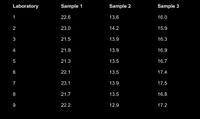
Transcribed Image Text:Laboratory
Sample 1
Sample 2
Sample 3
1
22.6
13.6
16.0
2
23.0
14.2
15.9
3
21.5
13.9
16.3
4
21.9
13.9
16.9
5
21.3
13.5
16.7
6
22.1
13.5
17.4
7
23.1
13.9
17.5
8
21.7
13.5
16.8
9
22.2
12.9
17.2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Four brands of lightbulbs are being considered for use in the final assembly area of the Ford F-150 truck plant in Dearborn, Michigan. The director of purchasing asked for samples of 100 from each manufacturer. The numbers of acceptable and unacceptable bulbs from each manufacturer are shown below. At the .05 significance level, is there a difference in the quality of the bulbs? (Round your answers to 3 decimal places.) H0: There is no relationship between quality and manufacturer. H1: There is a relationship. 1. Reject H0 if X2 >____ 2. X2 = ____ (Reject or Do Not Reject) H0. Ther (is a/is no) relationship between quality and manufacturer.arrow_forwardSix samples of each of four types of cereal grain grown in a certain region were analyzed to determine thiamin content, resulting in the following data (µg/g). Wheat 5.2 4.4 6.1 6.2 6.6 5.8 Barley 6.5 7.9 6.0 7.6 6.0 5.7 Maize 5.8 4.6 6.4 4.9 6.0 5.2 Oats 8.4 6.2 7.8 7.1 5.4 7.2 USE SALT Does this data suggest that at least two of the grains differ with respect to true average thiamin content? Use a level α = 0.05 test. State the appropriate hypotheses. | H₂: M₁ = H₂ = H3 = H4 H₂: all four μ's are unequal • Ho: M₁ = H₂ = H3 = H4 H₂: at least two μ's are unequal ⒸH₂² H₁ H₂ H3 H4 # H: all four μ's are equal O Ho: M₁ #M₂ #H3 H4 H₂: at least two μ's are equal Compute the test statistic value. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) f = What can be said about the P-value for the test? O P-value > 0.100 O 0.050 < P-value < 0.100 O 0.010 < P-value < 0.050 O 0.001 < P-value < 0.010 O P-value < 0.001 State the conclusion in the problem context. O Reject Ho. There is not significant evidence…arrow_forwardSamples were collected from two ponds in the Bahamas to compare salinity values (in parts per thousand). Several samples were drawn at each site. Pond 1: 37.03, 37.45, 36.75, 37.54, 37.71, 37.02, 37.32 Pond 2: 38.89, 39.05, 38.51, 38.53, 38.71 Use a 2% significance level to test the claim that the two ponds have the same mean salinity value. Assume that nothing is known about the population distribution of salinities. (a) Enter the rank values in the same order as in the original sample. The rank values for Pond 1 are: The rank values for Pond 2 are: (b) The test statistic is: . (c) The test critical value is: . (d) The conclusion isA. There is not sufficient evidence to indicate that the two ponds have different distributions of salinity values.B. There is sufficient evidence to indicate that the two ponds have different distributions of salinity values.arrow_forward
- It has been estimated that the 1991 G-car obtains a mean of 35 miles per gallon on the highway, and the company that manufactures the car claims that it exceeds the estimate in highway driving. To support its assertion, the company randomly selects 49 1991 G-cars and records the mileage obtained for each car over a driving course similar to that used to obtain the estimate. The following data resulted: x = 36.5 miles per gallon, s = 7 miles per gallon. %3D a. Find the observed significance level for testing Ho: u= 35 vs. Ha: u> 35. %3D b. For what value of significance level a, you will reject the null hypothesis.arrow_forwardPeriodically, the county Water Department tests the drinking water of homeowners for contaminants such as lead and copper. The lead and copper levels in water specimens collected in 1998 for a sample of 10 residents of a subdevelopement of the county are shown below. lead (μμg/L) copper (mg/L) 4.4 0.643 2.4 0.57 1.5 0.46 2.6 0.895 5.9 0.2 3.4 0.54 3.8 0.245 1.6 0.583 5.7 0.769 1.7 0.215 (a) Construct a 9999% confidence interval for the mean lead level in water specimans of the subdevelopment. ≤μ≤arrow_forwardListed below are the number of cricket chirps in 1 min and the corresponding temperatures in degrees Fahrenheit. Is there sufficient evidence to conclude that there is a relationship between the number of cricket chirps in 1 min and the temperature? Use a significance level of α=0.05. Chirps in 1 min 1171 1105 1185 852 1089 950 917 862 Temperature (°F) 78.4 88.2 91.5 86.3 90.2 79.3 83.8 84.4 Determine the null and alternative hypotheses for this test. Find the value of the correlation coefficient. rs=enter your response here (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Determine the critical value(s) of the correlation coefficient. enter your response here (Round to three decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman