
Principles of Accounting Volume 1
19th Edition
ISBN: 9781947172685
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax College
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
None
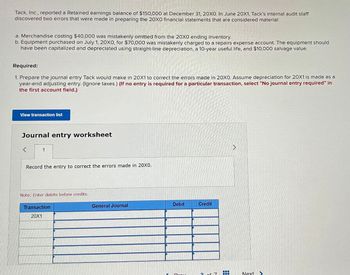
Transcribed Image Text:Tack, Inc., reported a Retained earnings balance of $150,000 at December 31, 20X0. In June 20X1, Tack's internal audit staff
discovered two errors that were made in preparing the 20X0 financial statements that are considered material:
a. Merchandise costing $40,000 was mistakenly omitted from the 20X0 ending inventory.
b. Equipment purchased on July 1, 20X0, for $70,000 was mistakenly charged to a repairs expense account. The equipment should
have been capitalized and depreciated using straight-line depreciation, a 10-year useful life, and $10,000 salvage value.
Required:
1. Prepare the journal entry Tack would make in 20X1 to correct the errors made in 20XO. Assume depreciation for 20X1 is made as a
year-end adjusting entry. (Ignore taxes.) (If no entry is required for a particular transaction, select "No journal entry required" in
the first account field.)
View transaction list
Journal entry worksheet
<
1
Record the entry to correct the errors made in 20X0.
Note: Enter debits before credits.
Transaction
20X1
General Journal
Debit
Credit
Next>
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose that an audit of Prime Sports Gear encountered the following two errors: a. Inventory totaling 4,500 should have been written off as worthless at the end of the year. Year-end inventory should be only 195,600. Net income is reduced to 117,110. b. Checks totaling 20,000 for some of the salaries payable at year-end had in fact been written and mailed out on December 31, 2013. Thus, both the cash account and the salaries payable account are overstated at year-end. Correct both errors on the worksheet. Save your completed file as CASHFLOW4. Print the worksheet when done. What impact did each of these adjustments have on cash flow for 2013?arrow_forwardIf Wakowski Companys ending inventory was actually $86,000 but was adjusted at year end to a balance of $68,000 in error, what would be the impact on the presentation of the balance sheet and income statement for the year that the error occurred, if any?arrow_forwardShetland Company reported net income on the year-end financial statements of $125,000. However, errors in inventory were discovered after the reports were issued. If inventory was understated by $15,000, how much net income did the company actually earn?arrow_forward
- Tack, Inc., reported a Retained earnings balance of $150,000 at December 31, 20X0. In June 20X1, Tack's internal audit staff discovered two errors that were made in preparing the 20X0 financial statements that are considered material: a. Merchandise costing $40,000 was mistakenly omitted from the 20X0 ending inventory. b. Equipment purchased on July 1, 20X0, for $70,000 was mistakenly charged to a repairs expense account. The equipment should have been capitalized and depreciated using straight-line depreciation, a 10-year useful life, and $10,000 salvage value. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entry Tack would make in 20X1 to correct the errors made in 20X0. Assume depreciation for 20X1 is made as a year-end adjusting entry. (Ignore taxes.) (If no entry is required for a particular transaction, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) View transaction list Journal entry worksheetarrow_forwardCandle Co. performs an inventory court at year - end. The company records a ending balance of $56,000 for inventory on its balance sheet. During the following year, the accountant discovers that the ending inventory was miscounted, causing ending inventory to be overstated by $2, 500. a. What is the effect of the misstatement on the income statement? b. Besides ending inventory, what was the effect of the error on the balance sheet?arrow_forwardAt the beginning of the year Candle Co. has an inventory balance of $32,000. The company has net income for the year of $56,000. Later, the accountant discovers an error that caused the beginning invenotory to be understated by $6,000. a. Assuming no other changes, what is the correct net income for the year? b. If the error was discovered after year-end, what was the effect of the error on the balance sheet? Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
- E6-2 Farley Bains, an auditor with Nolls CPAS, is performing a review of Ryder Company's Inventory account. Ryder did not have a good year, and top management is under pressure to boost reported income. According to its records, the inventory balance at year-end was $740,000. However, the following information was not considered when determining that amount. 1. Included in the company's count were goods with a cost of $228,000 that the is holding on consignment. The goods belong to Nader Corporation. 2. The physical count did not include goods purchased by Ryder with a cost of $40,000 that were shipped FOB shipping point on December 28 and did not arrive at Ryder's warehouse until January 3. 3. Included in the Inventory account was $17,000 of office supplies that were stored in the warehouse and were to be used by the company's supervisors and managers dur- ing the coming year. 4. The company received an order on December 29 that was boxed and was sitting on the loading dock awaiting…arrow_forwardFarley Bains, an auditor with Nolls CPAs, is performing a review of Ryder Company’s Inventory account. Ryder Company did not have a good year, and top management is under pressure to boost reported income. According to its records, the inventory balance at year-end was $740,000. However, the following information was not considered when determining that amount. Included in the company’s count were goods with a cost of $228,000 that the company is holding on consignment. The goods belong to Nader Corporation. The physical count did not include goods purchased by Ryder Company with a cost of $40,000 that were shipped FOB shipping point on December 28 and did not arrive at Ryder Company’s warehouse until January 3. Included in the Inventory account was $17,000 of office supplies that were stored in the warehouse and were to be used by the company’s supervisors and managers during the coming year. The company received an order on December 29 that was boxed and was sitting on the…arrow_forwardFarley Bains, an auditor with Nolls CPAs, is performing a review of Teal Mountain Inc.’s Inventory account. Teal Mountain Inc. did not have a good year, and top management is under pressure to boost reported income. According to its records, the inventory balance at year-end was $808,200. However, the following information was not considered when determining that amount. Ending inventory-as reported $enter a dollar amount 1. Included in the company’s count were goods with a cost of $224,170 that the company is holding on consignment. The goods belong to Nader Corporation. enter a dollar amount 2. The physical count did not include goods purchased by Teal Mountain Inc.with a cost of $38,530 that were shipped FOB shipping point on December 28 and did not arrive at Teal Mountain Inc.’s warehouse until January 3. enter a dollar amount 3. Included in the Inventory account was $18,300 of office supplies that were stored in the…arrow_forward
- A company overstated its ending inventory in Year 1 by $77,000. The error was not discovered until Year 3. No errors were made in Year 2. After finding the error in Year 3, management provides restated balance sheets for Year 1 and Year 2 by reducing the reported ending inventory in both Year 1 and Year 2 by $77,000. Which of the following statements is correct for Year 2? Multiple Choice No adjustments to the amounts reported for inventory or retained earnings are needed in Year 2. The amount reported for inventory in Year 2 needs to be increased by $77,000, and the amount reported for retained earnings in Year 2 needs to be decreased by $77,000.arrow_forwardLindy Company's auditor discovered two errors. No errors were corrected during 2017. The errors are described as follows: (1.) Merchandise costing $4,200 was sold to a customer for $9,200 on December 31, 2017, but it was recorded as a sale on January 2, 2018. The merchandise was properly excluded from the 2017 ending inventory. Assume the periodic inventory system is used. (2.) A machine with a five-year life was purchased on January 1, 2017. The machine cost $22,000 and has no expected salvage value. No depreciation was taken in 2017 or 2018. Assume the straight-line method for depreciation. Required:Prepare appropriate journal entries (assume the 2018 books have not been closed). Ignore income taxes.arrow_forwardThe following are independent errors made by a company that uses a periodic inventory system: Failure to record a purchase of $10,000 inventory on credit; however, inventory was properly counted at the end of the period. Assume the error was discovered prior to any payment for the purchase. Expensed the purchase of a machine of $50,000. The machine has a 10 year useful life with no salvage value. Failure to accrue wages of $8,000. Wages had not been paid at the time the error was discovered. Failure to record an allowance for uncollectibles of $25,000. The error was discovered prior to the accrual for bad debt in the following year. Included collections in advance of $100,000 as revenue. Included payments of $12,000 advance as expenses. Failure to accrue warranty costs of $14,000. Failure to record depreciation expense of $6,000 on assets purchased during the year. Required: Prepare the correcting journal entries if the company discovers each error in the year after it is made.…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach to Conducting a Q...AccountingISBN:9781305080577Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach to Conducting a Q...AccountingISBN:9781305080577Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:South-Western College Pub  Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course L...AccountingISBN:9781337619455Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course L...AccountingISBN:9781337619455Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172685
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College

Excel Applications for Accounting Principles
Accounting
ISBN:9781111581565
Author:Gaylord N. Smith
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach to Conducting a Q...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305080577
Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. Rittenberg
Publisher:South-Western College Pub

Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course L...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619455
Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. Rittenberg
Publisher:Cengage Learning