
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Using the data collected in Table 1 fill in the blanks of Table 2
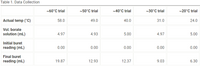
Transcribed Image Text:Table 1. Data Collection
~60°C trial
~50°C trial
~40°C trial
~30°C trial
~20°C trial
Actual temp (°C)
58.0
49.0
40.0
31.0
24.0
Vol. borate
solution (mL)
4.97
4.93
5.00
4.97
5.00
Initial buret
reading (mL)
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
Final buret
reading (mL)
19.87
12.93
12.37
9.03
6.30
![Table 2. Calculations
~60°C trial
~50°C trial
~40°C trial
~30°C trial
~20°C trial
Vol. of HCI used
(mL)
19.87
12.93
12.37
9.03
6.30
Moles of HCI
used (mol)
9.94
6.47
6.19
4.52
3.15
Moles of borate
present (mol)
[Borate] (M)
Ksp
In(Ksp)
1/T (K-1)](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/108a0acc-c86a-4fb9-81b6-4d3403f04067/bc3c55ae-ea6e-43a6-a27c-2467eb4ea72b/673fu5kjs_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:Table 2. Calculations
~60°C trial
~50°C trial
~40°C trial
~30°C trial
~20°C trial
Vol. of HCI used
(mL)
19.87
12.93
12.37
9.03
6.30
Moles of HCI
used (mol)
9.94
6.47
6.19
4.52
3.15
Moles of borate
present (mol)
[Borate] (M)
Ksp
In(Ksp)
1/T (K-1)
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
In the given experiment the titration of borate with hydrochloric acid is being carried out at different temperatures. From the give data we are required to calculate the number of moles of borate titrated, concentration of borate at different temperature solubility product and the inverse of temperature.
Note: The number of moles of solution given are taken as millimoles instead of moles as it seems inappropriate to have 9.94 moles of in just of solution.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the number of each type of atom in each of the following formulas. Part C NaCN Express your answers as integers. Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. NNa, NC, NN = Submit Part D 17 ΑΣΦ Request Answer Submit Ba(HCO3)2 Express your answers as integers. Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. NBа, NH, NC, No = ΨΕ ΑΣΦ ? Request Answer ?arrow_forwardAlumimnum foil dimensions Length (cm)14.45 cm Width (cm)11.41 cm Mass of aluminum foil (g) 8.593 g What is the volume of the aluminum foil (cm^3)? What is the thickness of the aluminum foil (cm)?arrow_forwardE Copy of Fall 2020 Fina X hHp8TPKsYapxmOBQpq19sYHEQfKQudwLFoPO2ojmMGw/edit d-ons Help Last edit was seconds ago BIUA c 田回。三=== 三ニ三▼E 三E X Arial 14.5 2 3 4 6 A student needs to identify an unknown substance found in the lab based on its physical properties. The substance has a mass of 130.5 g and a volume of 36.73 ml and tarnishes when it comes in contact with water. (AKS 2b, DOK2). Density e/cm3) 0.42 0.95 0.36 3.71 0.30 1.12 0.20 0.69 Name Cherry Alloy Cuppric Alloy Elastica Aloy Galvanized Alloy Holy Alloy Marblic Alloy Porous Alloy Silica Dioxica Alloy Stuper Alloy Trisphereica Alloy Vulcan Alloy Zink Alloy 0.62 246 1.88 3.55 Question options: A.The unknown substance is Cherry Alloy. The student was able to use the reactivity to solve the problem-because tarnishing is a physical property of the Cherry Alloy. B. The unknown substance is Vulcan Alloy. The student was able to use density to solve the problem because density is a physical property of Vulcan Alloy. C.The unknown…arrow_forward
- Calculate the mass of tetraborane (B4H₁0) that contains a million (1.00 x 10°) boron atoms. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol if necessary, and round it to 3 significant digits. x10 X 5 ?arrow_forwardComplete the following table by either identifying the electron configuration, the symbol of the neutral (no charge) a number of valence electrons, and/or the normal valence (common number of bonds) in the spaces provided. Form electron configuration answers like this: 1s22s22p4, for example (i.e. no spaces and no superscript notations). A able is provided below: Electron Configuration 1s²2s²2p63s23p³ 1s²2s²2p² Neutral Atom Symbol N Si No. of Valence Electrons 5 Normal Valer number of ba hparrow_forwardThe density of mercury is 13.6 g/cm³. What is the mass of 6.50 cm³ of mercury? 2.38 g 18.9 g 88.4 g O 0.478 g O 1.10 x 10² garrow_forward
- Which statement is FALSE? O A pure substance can be varied by changing the proportion of pure substances making it up A mixture can be separated into 2 or more substances by physical or mechanical means A pure substance had properties that are constant, no matter where you find it A pure substance has constant chemical composition A mixture's composition can be varied by changing the proportion of pure substances making it uparrow_forwardPercentage Abundance. The element rubidium consists of two isotopes, one having an isotopic mass of 84.912 and the other having an isotopic mass of 86.920. Determine the percentage abundance of the lighter isotope. Record the answer to the correct number of significant figures. Show the numerical set-ups. Include units and the correct number of significant figures in the set-up.arrow_forwardA piece of copper has a volume of 560 L what is mass of sample in grams. For the problem it gives me 1cm^3Cu = 9g CU 9.5 x 10^21 atoms Cu= 1 Cu 1KG =1000g 1cm^3 =1mL 1L=1000cm^3 It basically wants me to write out the conversions correctly i just dont know which ones to use. Thank you so much for the help I really appreciate it.arrow_forward
- The element rubidium consists of two isotopes, one having an isotopic mass of 84.912 and the other having an isotopic mass of 86.920. Determine the percentage abundance of the lighter isotope. Record your answer, to the correct number of significant figures, in the box below; do not include the units of your final answer. Then show your numerical set-up(s) in the next question.arrow_forwardYou have a sample of each of the following five metals, with the mass and density of each sample given. Which sample has the smallest volume? Aluminum, mass 139 g, d=2.7 g/cm3 Copper mas 225 g d=8.92 Iron mass 235g d=7.86 Magnesium mass 105 g d=1.74 Silver mass 215 g d=10.5arrow_forwardThe following prompt will be used to answer the first six questions. An experiment was performed to separate the components of a binary mixture composed of sucrose (sugar) and sand. The following data was collected in lab during the experiment. Mass of original binary mixture: 20.100 ± 0.001 g Mass of initial filter paper: 21.206 ± 0.001 g Mass of filter paper and isolated sand: 25.226 ± 0.001 g 9b Given the data and information in the prompt, what is the calculated absolute error on the percent of sugar in the mixture? Enter the absolute error you calculated in the box below. You do not need to include the % symbol with your answer.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY