
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Fill out Table 1 above by writing “+” if the compound is soluble/miscible in the solvent.
Otherwise, write “-“.
Determine the solubility group of the compound based on the results in Table 1.

Transcribed Image Text:Table 1. Results of the solubility tests for C4H6O2.
SOLUBILITY TEST
distilled water
Litmus paper test (indicate
if acidic, basic, or neutral)
10% NaOH
10% NaHCO3
OBSERVATIONS
clear, colorless solution
Blue litmus paper turned red
Clear, colorless solution
rapid production of bubbles; clear,
colorless solution
+/-
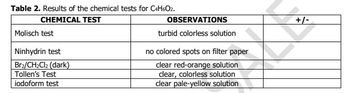
Transcribed Image Text:Table 2. Results of the chemical tests for C4H6O2.
CHEMICAL TEST
Molisch test
Ninhydrin test
Brz/CH₂Cl2 (dark)
Tollen's Test
iodoform test
OBSERVATIONS
turbid colorless solution
no colored spots on filter paper
clear red-orange solution
clear, colorless solution
clear pale-yellow solution
+/-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What trend in solubility can you infer for the alkaline earth metals as it relates to the position on the periodic table? In other words, do the alkaline earth metal cations become more soluble or less soluble as you move down the family? Rank from Most to Least Soluble.arrow_forwardThe solubility of a gas in a solvent changes when pressure is applied. Click on the image to explore this activity, which illustrates the relationship between the pressure (P) and the solubility (S) of a gas. In this activity, you can see a sealed container of water and Ny gas. Click on the Run button to see the relative changes in the solubility of N₂ gas in water as the pressure of the N₂ gas is increased and decreased. The values of the pressure and the solubility of gas are tabulated adjacent to the Run and Reset buttons in the activity Part A Click on the Run button in the activity. Watch how the solubility of a gas changes as pressure is increased and then decreased during the run Which of the following statements correctly explain the relationship between the solubility of a gas and its pressure? Check all that apply. View Available Hint(s) MacBook Air Show all Xarrow_forwardGive an example of a compound whose solubility can be calculated from each of the following expressions. Write the chemical formula for the compound and its name. A) Ksp = S2 B) Ksp = 4S3 C) Ksp = 27S4 D) Ksp = 108S5arrow_forward
- My professor said the answer choice was A.) please explain why in detail. Which of the following solutes, dissolved in 1.0Kg of water, creates a solution that boils at the highest temperature? A.) 0.010 mol H2SO4 B.) 0.010 mol HF C.) 0.010 mol HCL D.) 0.010 mol HCLO4 E.) 0.010 mol H3PO4arrow_forward3. Why does adding a salt solution cause soap to precipitate?arrow_forwardPlease give me answers in 5min I will give you like surearrow_forward
- . Consider the two molecules shown here. 1-butanol (1)- 7.3g/100ml and butyric acid (2)- miscible The solubilities of each in water is given. What is “solubility”? What does the solubility value given for (1) here mean? Please explain, based on their structures, why the solubility of (2) is greater than the solubility of (1) in water. For a complete answer, you should start with the types of IMFs involved in the different parts of the dissolving process. You should also use the kind of reasoning from class regarding the contributions…arrow_forwardPlease explain how to rate molar solubility and how to calculate solubility from given Ksp.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY