
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
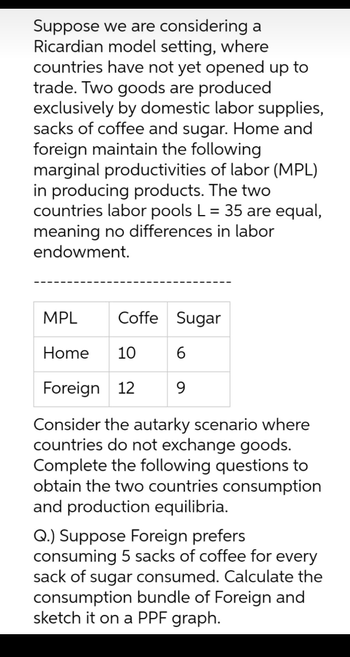
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose we are considering a
Ricardian model setting, where
countries have not yet opened up to
trade. Two goods are produced
exclusively by domestic labor supplies,
sacks of coffee and sugar. Home and
foreign maintain the following
marginal productivities of labor (MPL)
in producing products. The two
countries labor pools L = 35 are equal,
meaning no differences in labor
endowment.
Coffe Sugar
6
9
MPL
Home 10
Foreign 12
Consider the autarky scenario where
countries do not exchange goods.
Complete the following questions to
obtain the two countries consumption
and production equilibria.
Q.) Suppose Foreign prefers
consuming 5 sacks of coffee for every
sack of sugar consumed. Calculate the
consumption bundle of Foreign and
sketch it on a PPF graph.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 8 d e and f Please help solve 8 d e and farrow_forwardIn the Pure Specific Factors model with two sectors, Cars (C) and Wheat (W), Capital (K) is specific to C and Land (A) is specific to W. The government imposes a tariff on the imports of W then owners of A benefit. Why is this so ?arrow_forwardConsider the Specific Factors model with two countries, Home and Foreign, with two goods, cars (c) and pharmaceutical drugs (d), and three factors, capital K, skilled labour S, and unskilled labour L. The production functions are given by F.(Ke, Le) = K. Lễ and Fa(Ka, Sa) = K}S}. That is, skilled labour is specific to pharmaceutical drugs, and unskilled labour to cars. Suppose that the countries' factor endowments are KH = 2 = KF, L# and LF = 3/2, and SH = 1 and SF = 1 1/2, so that the total labour force is 2 in both countries. The price of capital is denoted by r, the price of skilled and unskilled labour by w, and w. Denote the goods' prices by pc and pd, and normalise pd 1 for simplicity. The demand for cars and drugs in country j = H, F is given by x and r: 1Yi 2Yi and x 3 ре || 3 pi where Y' denotes aggregate income in country j. (c) Compute the autarky equilibrium in Foreign and show that p > p. Compare equilibrium prices in Home and in Foreign and explain.arrow_forward
- Two planets, Endor and Kamino, both produce two goods, blasters and radio devices. The below graphs show the PPF curves of each planet before specialization. Initially, each planet produces 50,000 radio devices and 5,000 blasters. In total, 100,000 radios and 10,000 blasters are produced. Which planet has a comparative advantage in producing radios and which planet has a comparative advantage in producing blasters? If each planet was to fully specialize in producing one good, how many radios in total would be produced and how many blasters in total would be produced? Suppose that the two planets trade 5,000 blasters for 90,000 radios. Graph and label the new points on each planet’s PPF using the graphs above. What is the outcome of specialization and trade for each planet?arrow_forwardWhen a country has a comparative advantage in the production of a good, it means that it can produce this good at a lower opportunity cost than its trading partner. Then the country will specialize in the production of this good and trade it for other goods. The following graphs show the production possibilities frontiers (PPFs) for Glacier and Rainier. Both countries produce corn and basil, each initially (i.e., before specialization and trade) producing 18 million pounds of corn and 9 million pounds of basil, as indicated by the grey stars marked with the letter A. BASIL (Millions of pounds) 48 42 36 30 24 18 12 6 0 0 PPF 6 Glacier A 12 18 24 30 36 CORN (Millions of pounds) 42 48 ? BASIL (Millions of pounds) 48 42 36 30 24 18 12 6 0 0 PPF I + 6 Rainier 12 18 24 30 36 CORN (Millions of pounds) I 42 48 (?) Glacier has a comparative advantage in the production of while Rainier has a comparative advantage in the production of Suppose that Glacier and Rainier specialize in the production…arrow_forwardGains and Losses from Trade in the Specific-Factors Model - End of Chapter Problem Home produces two goods, computers and wheat, for which capital is specific to computers, land is specific to wheat, and labor is mobile between the two industries. Home has 100 workers and 100 units of capital but only 10 units of land. a. Suppose that when Home opens up to international trade, the price of computers rises. In the accompanying diagram, shift the appropriate curve to show this change, holding the price of wheat constant. b. The increase in the price of computers causes the Wage amount of labor used in wheat production a given quantity of labor 0 W The amount of labor used in computer production the change in the wage. L --> LLL" curve to shift vertically by PMPLC P_MPL W W <-C .... while the The vertical shift of the P MPL curve atarrow_forward
- Assume that two countries Alpha and Beta use a variety of inputs in their production Alpha exports excavating equipment and imports solar cells. Assume furthermore no economies of scale. Select the correct statement from the ones below: Even though there is trade, Alpha has a lower opportunity cost for excavating If the countries did not trade, Alpha would have a lower opportunity cost for excavating Neither country can consume at a point outside its production possibility frontier. Alpha avoids producing solar cells while B avoids producing no excavatingarrow_forwardWhen a country specializes in the production of a good, this means that it can produce this good at a lower opportunity cost than its trading partner. Because of this comparative advantage, both countries benefit when they specialize and trade with each other. The following graphs show the production possibilities frontiers (PPFS) for Maldonia and Lamponia. Both countries produce lemons and sugar, each initially (i.e., before specialization and trade) producing 24 million pounds of lemons and 12 million pounds of sugar, as indicated by the grey stars marked with the letter A. (? (?) Maldonia Lamponia 64 64 56 56 48 PPF 48 40 40 32 32 24 24 PPF 16 16 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 16 24 32 40 48 56 64 LEMONS (Millions of pounds) LEMONS (Millions of pounds) Maldonia has a comparative advantage in the production of production of while Lamponia has a comparative advantage in the . Suppose that Maldonia and Lamponia specialize in the production of the goods in which each has a comparative advantage.…arrow_forwardAnswer the next question(s) on the basis of the following information. Assume that by devoting all its resources to the production of X, nation Alpha can produce 40 units of X. By devoting all its resources to Y, Alpha can produce 60Y. Comparable figures for nation Beta are 60X and 40Y. Refer to the above information. The terms of trade will be at or within the 1X=1¹/2Y to 1X = ²/3Y range. Select one: True Falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education