
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Note:-
- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism.
- Answer completely.
- You will get up vote for sure.
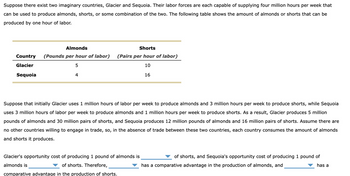
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose there exist two imaginary countries, Glacier and Sequoia. Their labor forces are each capable of supplying four million hours per week that
can be used to produce almonds, shorts, or some combination of the two. The following table shows the amount of almonds or shorts that can be
produced by one hour of labor.
Almonds
Country (Pounds per hour of labor)
Glacier
Sequoia
5
4
Shorts
(Pairs per hour of labor)
10
16
Suppose that initially Glacier uses 1 million hours of labor per week to produce almonds and 3 million hours per week to produce shorts, while Sequoia
uses 3 million hours of labor per week to produce almonds and 1 million hours per week to produce shorts. As a result, Glacier produces 5 million
pounds of almonds and 30 million pairs of shorts, and Sequoia produces 12 million pounds of almonds and 16 million pairs of shorts. Assume there are
no other countries willing to engage in trade, so, in the absence of trade between these two countries, each country consumes the amount of almonds
and shorts it produces.
Glacier's opportunity cost of producing 1 pound of almonds is
almonds is
of shorts. Therefore,
comparative advantage in the production of shorts.
of shorts, and Sequoia's opportunity cost of producing 1 pound of
has a comparative advantage in the production of almonds, and
has a
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How to aduittor detect kitingarrow_forwardThe goal of this activity is to help you better understand how the rational decision-making process applies in a realistic workplace scenario. First, hover over each term or phrase to read the description. Then, click and drag each term or phrase into the correct place in the rational decision-making process. Measuring performance Identify the problem or opportunity Consultants. Inclusive or exclusive Generate alternative. solutions Inclusive or exclusive Consultants Collecting data Evaluate alternatives and Implement and evaluate the solution chosen. select a solution Measuring performance Collecting data Reset 4arrow_forwardNote:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
- Could you please answer questions d and e.arrow_forwardNote:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardplease help Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for surearrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forwardNote:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardNote:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education