
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
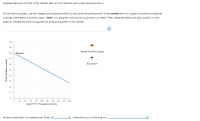
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose there are 10 firms in this market, each of which has the cost curves previously shown.
On the following graph, use the orange points (square symbol) to plot points along the portion of the market short-run supply curve that corresponds
to prices where there is positive output. (Note: You are given more points to plot than you need.) Then, place the black point (plus symbol) on the
graph to indicate the short-run equilibrium price and quantity in this market.
100
90
Market Short-Run Supply
80
Demand
70
60
Equilibrium
50
40
30
20
10
50
100
150 200 250 300 350 400
450
500
QUANTITY (Thousands of shirts)
At the current short-run market price, firms will.
in the short run. In the long run,
PRICE (Dollan per shirt)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The supply curves for the only two firms in a competitive industry are given by: S₁: P = 2Q1 S2: P = 2 + Q2, where Q1 is the output of firm 1 and Q2 is the output of firm 2. These two supply curves are shown in the graph below. Draw the market supply curve for this industry. Instructions: Use the tool provided to plot 4 price-quantity combinations for prices $0, $2, $4 and $6. Price Market Supply 7 S₁ S2 की 6 5 + 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 4 Quantity сл 5 10 6 7 80 Tools line toolarrow_forwardIn competitive markets, there are many small firms with each firm unable to influence the market price. Suppose company ABX operates in the wheat market. The company produces and markets wheats at a Price = $20 per container. The firm’s total costs are given as: TC = 50 +2Q + 3Q2 What level of output should the firm produce? Hint: Set P = MC and solve for Q. Use a graph to show your answers as wellarrow_forwardThe following diagram shows the market demand for steel. Use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 20 firms in the market. (Hint: You can disregard the portion of the supply curve that corresponds to prices where there is no output since this is the industry supply curve.) Next, use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 40 firms. Finally, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 60 firms. PRICE (Dollars per ton) 80 72 Supply (20 firms) 64 58 Demand 48 Supply (40 firms) 40 32 2 24 16 8 ° 0 120 240 360 480 600 720 840 960 1080 1200 QUANTITY OF OUTPUT (Thousands of tons) Supply (60 firms) ? If there were 60 firms in this market, the short-run equilibrium price of steel would be $ Therefore, in the long run, firms would Because you know that perfectly competitive firms earn be $ per ton. At that price, firms in this industry…arrow_forward
- Suppose a typical (representative) corn farm has a short run production technology which results in the outcome of U-shaped Average Variable Cost (AVC), Average Total Cost (ATC), and Marginal Cost (MC). Further, suppose this firm sells its product in a market where the price of the good is determined by the interaction of market Demand and Supply. Because an individual firm is very small compared to the rest of the market, we treat the market price as the price given to the firm, and the individual firm cannot impact that price. assume we are in the Short Run for this firm. In graphing, put $ on the vertical axis and lower-case q (firm output) on the horizontal axis. Start with the AFC0, AVC0, ATC0, and MC0 curves . show shifts in any of the cost curves, reflecting the higher cost of land (keeping in mind that this higher cost is independent of how much or how little corn is actually produced) and labeling the changed cost curves with a subscript 1. On the graph with $ on the…arrow_forwardThe following graph plots the market demand curve for ruthenium. Use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the initial short-run industry supply curve when there are 10 firms in the market. (Hint: You can disregard the portion of the supply curve that corresponds to prices where there is no output since this is the industry supply curve.) Next, use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 20 firms. Finally, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 30 firms. PRICE (Dollars per pound) 80 72 64 03 58 Supply (10 firms) 48 Demand Supply (20 firms) 40 32 24 16 8 0 0 120 240 350 480 600 720 840 960 1080 1200 QUANTITY (Thousands of pounds) Supply (30 firms) ? If there were 20 firms in this market, the short-run equilibrium price of ruthenium would be $ would Therefore, in the long run, firms would per pound. At that price, firms in this industry the ruthenium market. Because you…arrow_forwardFarmer Johnson producers Eggs in a perfectly competitive egg market. The short run cost curves are displayed below. $4.00 MC $3.50 ATC AVC $3.00 $2.50 $2.00 $1.50 $1.00 $0.50 $0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 Dozens of Eggs Price of Eggsarrow_forward
- 7. Short-run supply and long-run equilibrium Consider the perfectly competitive market for steel. Assume that, regardless of how many firms are in the industry, every firm in the industry is identical and faces the marginal cost (MC), average total cost (ATC), and average variable cost (AVC) curves shown on the following graph. COSTS (Dollars per ton) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 ATC 30 20 10 + MC AVC 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY OF OUTPUT (Thousands of tons) The following diagram shows the market demand for steel. ⑦? Use the orange points (square symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 20 firms in the market. (Hint: You can disregard the portion of the supply curve that corresponds to prices where there is no output since this is the industry supply curve.) Next, use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the short-run industry supply curve when there are 30 firms. Finally, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the short-run industry…arrow_forwardLong Run Equilibrium Consider a perfect competitive market with n identical firms. The cost functions of an individual firm are: The market demand is given by TC=q³ - 4q² + 74q MC=3q² - 8q+74. P= 120-Q a) In the above space draw two graphs one for the market and one for the firm to show the long run equilibrium b) In the long run, each firm will produce q.. i.e. the firm is operating at its minimum c) The long run equilibrium price must be P=. d) Thus the total amount purchased will be Q= e) This means there is enough room for n=. f) No more entry will take place because.. g) Show all equilibrium values on your graph ..firms Because. because..arrow_forwardShow what happens in the short run on both graphs when a new medical study shows soybeans to be highly carcinogenic. On the market graph, you will shift a curve or curves. On the firm's graph, use Price 2 to draw a new price line for the firm. On both graphs, indicate the new equilibrium point with point B. Now, show the changes that get both graphs back to long‑run equilibrium. Use shift(s) for the market and Price 3 for the firm. Indicate the new long‑run equilibrium with point C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education