
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
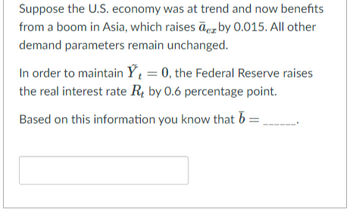
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose the U.S. economy was at trend and now benefits
from a boom in Asia, which raises de by 0.015. All other
demand parameters remain unchanged.
In order to maintain Y₁ = 0, the Federal Reserve raises
the real interest rate R by 0.6 percentage point.
Based on this information you know that b =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following functions for consumption and investment: C = 1,000 + (2/3)*(Y – T) and I = 1,200 – 100*r. Furthermore, Y = 8,000, G = 2500, T = 2,000. Compute private, public, and national savings for this economy, and find the equilibrium real interest rate (r). Assume that G declines by 500 units. How will it change your answers in part (a)? What happens to the national savings, given everything else, if the public decides to consume less out of their disposable income (assume that the propensity of consume falls by 10 percent)? Given your answer in part (c), what happens to investment and real interest rate? Answer all four.arrow_forwardJohn has the following utility function U(C₁, C2) = min{c₁ + ac2, C2}, where C₁ and c₂ are his consumption in periods 1 and 2, respectively and a is some positive constant. Suppose John has $100 income in period 1 and $105 income in period 2. Prices in both periods are $1. Question 2 Part al Suppose a = 2. If John can freely borrow and lend at 5% interest rate what would be his optimal consumption in both periods? 1 Question 2 Part a2 Suppose a = 2. Now, John can lend at 5% interest rate, but can't borrow at all. What would be his optimal consumption in both periods? Question 2 Part bl Suppose a 0.5. If John can freely borrow and lend at 5% interest rate what would be his optimal consumption in both periods? Question 2 Part b2 Suppose a 0.5. Now, John can lend at 5% interest rate, but can't borrow. What would be his optimal consumption in both periods?arrow_forwardSuppose the U.S. economy was at trend and now benefits from a boom in Asia, which raises āez by 0.015. All other demand parameters remain unchanged. In order to maintain Ý, = 0, the Federal Reserve raises the real interest rate R, by 0.6 percentage point. Based on this information you know that b =arrow_forward
- When interest rates increase, we expect the supply curve for large durable goods to shift upwards. True Falsearrow_forwardHello! please can you solve question B? Thanksarrow_forwardConsider a small macroeconomy located near the South Pacific Ocean where the current interest rate is 15 percent and the potential level of real GDP equal to $2.7 billion. Consumers spending behavior is described by the equation: C = 175 + 0.8DI, while firm's investment spending behavior is described by the equation: 1 = 60 +0.25Y-750r. Trade is allowed and currently, total exports is fixed at $150 million while total imports is described by the equation: IM = 320 + 0.1Y. The government's spending is fixed at $840 million and net taxes is described by the equation: T=50 +0.25Y. (Question 4 of 6) Consider that actual rate of unemployment is 5 percent and the current government implements a monetary policy to stabilize the current economic environment. Given the government's policy, what will be the new equilibrium level of GDP (in millions of dollars)? (report your answer at 2 decimal places)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education