
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
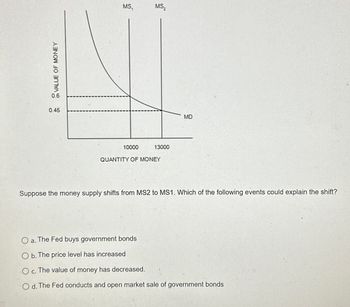
Transcribed Image Text:VALUE OF MONEY
0.45
10000
MSA
MS
13000
QUANTITY OF MONEY
MD
Suppose the money supply shifts from MS2 to MS1. Which of the following events could explain the shift?
○ a. The Fed buys government bonds
Ob. The price level has increased
Oc. The value of money has decreased.
C.
Od. The Fed conducts and open market sale of government bonds
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Interest rates fall as the supply of money increases because a.businesses want to borrow more when the money supply increases. b. Aggregate demand increases. c. The demand curve for money slopes down. d. The demand curve for money shifts to the right.arrow_forwardAttempts 2. The theory of liquidity preference and the downward-sloping aggregate-demand curve The following graph shows the money market in a hypothetical economy. Assume that the central bank fixes the quantity of money supplied. Suppose the price level increases from 90 to 105. Shift the appropriate curve on the graph to show the impact of an increase in the overall price level on the market for money. ? INTEREST RATE (Percent) Average/4 18 15 1-3°C Cloudy Money Supply Money Demand Money Demand 1 Money Supply T Q Search 2016 W acerarrow_forwardWhen the Fed fights inflation, ... A. a decrease in the supply of loanable funds raises the long-term interest rate and increases investment B. a decrease in the federal funds rate decreases aggregate demand C. an open market purchase increases the federal funds rate OD. a decrease in bank reserves decreases the quantity of money demandedarrow_forward
- All else equal, suppose the interest rate rise from 3% to 3.5%. What will happen in the supply of money? a. Shifts to the right. b. Shifts to the left. c. An upward movement along the supply curve. d. An downward movement along the supply curve. e. The supply will remain unchanged.arrow_forward16 A change in-----------leads to a change in-----------as well. a) the money supply indirectly; investment b) the interest rate; government purchases c) the money supply; government purchases d) consumption expenditures; the money supplyarrow_forwardPlease solve whole question will give like.arrow_forward
- N @ # $ % & 2 3 4 5 6 7 8arrow_forwardA. Discuss, with the help of diagrams, Friedman’s argument concerning the short and long-run effects of an increase in the money supply. B. Now discuss how his argument can be extended to study short and long-run effects of changes in the growth rate of a growing money supply. Both parts please.arrow_forwardHow does an increase in price level affect the money market? a. Money demand increases b. Money supply decreases c. Money demand decreases d. Money supply increasesarrow_forward
- When the Fed sells government securities (bonds), the money supply will ______ . a. first increase and then decrease b. first decrease and then increase c. increase d. decreasearrow_forwardWhen the Fed sells securities in the open market, the monetary base _______ and the interest rate _______. A. decreases; falls B. increases; rises C. decreases; rises D. increases; fallsarrow_forwardMoney neutrality is the idea that a. any policy can have intended and unintended consequences b. in the long-run, markets will clear and return the economy to equilibrium regardless of what happens to the money supply. c. there are two types of variables, nominal and real, and only nominal variables are affected by the money supply. d. nominal and real interest rates are unrelated. During the middle of the 20th century, income inequality in developed economies generally fell. The reason for this was a. average incomes didn't rise but welfare systems redistributed income. b. that returns to assets held by high income earners fell steadily. c. incomes overall rose but taxation systems were slowly made more and more progressive. d. a rise in average income with incomes of the bottom deciles rising faster than the top.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education