
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013924
Author: Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
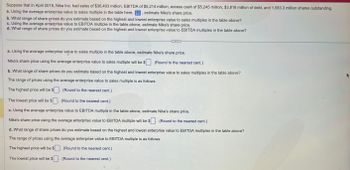
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that in April 2019, Nike Inc. had sales of $36,403 million, EBITDA of $5,214 million, excess cash of $5,245 million, $3,818 million of debt, and 1,583.3 million shares outstanding.
a. Using the average enterprise value to sales multiple in the table here,, estimate Nike's share price.
b. What range of share prices do you estimate based on the highest and lowest enterprise value to sales multiples in the table above?
c. Using the average enterprise value to EBITDA multiple in the table above, estimate Nike's share price.
d. What range of share prices do you estimate based on the highest and lowest enterprise value to EBITDA multiples in the table above?
a. Using the average enterprise value to sales multiple in the table above, estimate Nike's share price.
Nike's share price using the average enterprise value to sales multiple will be $
(Round to the nearest cent.)
b. What range of share prices do you estimate based on the highest and lowest enterprise value to sales multiples in the table above?
The range of prices using the average enterprise value to sales multiple is as follows:
The highest price will be $
(Round to the nearest cent.)
The lowest price will be $
(Round to the nearest cent.)
c. Using the average enterprise value to EBITDA multiple in the table above, estimate Nike's share price.
Nike's share price using the average enterprise value to EBITDA multiple will be $
(Round to the nearest cent.)
d. What range of share prices do you estimate based on the highest and lowest enterprise value to EBITDA multiples in the table above?
The range of prices using the average enterprise value to EBITDA multiple is as follows:
The highest price will be $
(Round to the nearest cent.)
The lowest price will be $
(Round to the nearest cent.)
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that in
a. Using the average enterprise value to sales multiple in the table here,, estimate Nike's share price.
5. What range of share prices do you estimate based on the highest and lowest enterprise value to sales multiples in the table above?
c. Using the average enterprise value to EBITDA multiple in the table above, estimate Nike's share price.
d. What range of share prices do you estimate based on the highest and lowest enterprise value to EBITDA multiples in the table above?
a. Us
Nike'
b. W
The r
The H
The I
c. Us
Nike'
d. WI
The r
The H
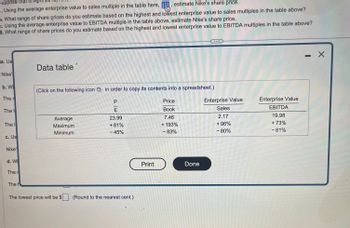
Data table
(Click on the following icon in order to copy its contents into a spreadsheet.)
Average
Maximum
Minimum
The lowest price will be $
PE
23.99
+81%
-45%
(Round to the nearest cent.)
Y
Print
Price
Book
7.46
+ 193%
- 83%
Done
Enterprise Value
Sales
2.17
+ 96%
- 80%
--------------ZA
Enterprise Value
EBITDA
19.98
+ 73%
- 81%
- X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose that in April 2019, Nike Inc. had sales of $36,367 million, EBITDA of $5,229 million, excess cash of $5,238 million, $3,804 million of debt, and 1,583.2 million shares outstanding. a. Using the average enterprise value to sales multiple in the table here,, estimate Nike's share price. b. What range of share prices do you estimate based on the highest and lowest enterprise value to sales multiples in the table above? c. Using the average enterprise value to EBITDA multiple in the table above, estimate Nike's share price. d. What range of share prices do you estimate based on the highest and lowest enterprise value to EBITDA multiples in the table above? Data table (Click on the following icon in order to copy its contents into a spreadsheet.) Average Maximum Minimum P 23.99 +81% - 45% Print Price Book 7.46 + 193% - 83% Done Enterprise Value Sales 2.17 + 96% - 80% Enterprise Value EBITDA 19.98 + 73% - 81% Xarrow_forwardYou are given financial statements and a Dupont analysis for Tesco and Ahold. What do you conclude about the two companies’ performances based on these numbers?arrow_forwardTNT Corporation's stock is currently selling at $36 per share. TNT reported total revenues of $5.26 billion over the past year, has a book value of equity of $2.9 billion, and has 296 million shares outstanding. Based on comparable firms, the appropriate P/S and P/B for TNT are 2.85 and 4.75, respectively. A. What is the stock's approximate intrinsic value based on the P/S multiplier? B. What is the stock's approximate intrinsic value based on the P/B multiplier?arrow_forward
- Estimating Share Value Using the DCF ModelAssume following are forecasts of Abercrombie & Fitch's sales, net operating profit after tax (NOPAT), and net operating assets (NOA) as of January 29, 2011. Reported Horizon Period (In millions) 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 Terminal Period Sales $ 3,750 $ 4,500 $ 5,400 $ 6,480 $ 7,776 $ 7,853 NOPAT 464 539 654 794 982 960 NOA 1,320 1,602 1,933 2,332 2,791 2,802 Answer the following requirements assuming a discount rate (WACC) of 13.3%, a terminal period growth rate of 1%, common shares outstanding of 86.2 million, and net nonoperating obligations (NNO) of $(261) million (negative NNO reflects net nonoperating assets such as investments rather than net obligations).(a) Estimate the value of a share of Abercrombie & Fitch common stock using the discounted cash flow (DCF) model as of January 29, 2011. Rounding instructions: Round answers to the nearest whole number unless noted otherwise. Use your rounded answers for…arrow_forward(Market value analysis) The balance sheet for Larry Underwood Motors shows a book value of stockholders' equity (book value per share x total shares outstanding) of $1,314,000. Furthermore, the firm's income statement for the year just ended has a net income of $578,000, which is $0.264 per share of common stock outstanding. The price-earnings ratio for firms similar to Underwood Motors is 21.81. a. What price would you expect Underwood Motors shares to sell for? b. What is the book value per share for Underwood's shares? a. What price would you expect Underwood Motors shares to sell for? The market price per share is $ (Round to the nearest cent.) C...arrow_forwardQ20arrow_forward
- ABC's Net Income this year was $20,650,000 and there were 19.5 million shares outstanding. If the firm's Price/Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio) is 18.7 then what is the firm's share price? Group of answer choicesarrow_forwardThe following information relates to three companies in the same industry Latest Earnings Dividends Company market price per share per share A $ 35 $11 $0 B $40 $5 $4 C $ 90 $10 $6 Required: Explain and calculate the price -earnings and dividend yield ratios. On the basis of only the foregoing information, which company represents the most attractive investment opportunity to you? Explain.arrow_forwardSanedrin Company has an earnings per share (EPS) of $4.50, a value per share of $45 and a market value of $38. Calculate the price/earnings ratio (P/E).arrow_forward
- 6arrow_forward2. If RTM's stock is currently trading at AED 24 and RTM has 25 million shares outstanding, shareholder equity of 100 million and cash of 5 million, What is the RTM's market-to-book ratio, the market capitalization and the enterprise value.arrow_forwardAs of the end of 2020, Microsoft had an annual net income of $51.3 Billion and total assets of $301.3 Billion. Microsoft's total book value of equity as of the end of 2020 was $118.3 Billon. Finally, Microsoft currently has 7.56 billion shares outstanding, and is priced at $243 a share. What is Microsoft's leverage, also known as its equity mulitplier (EM) (remember to use market value of equity)? 7.56 5.42 6.10 8.11arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education