
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
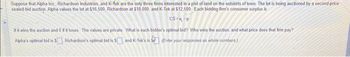
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that Alpha Inc, Richardson Industries, and K-Tek are the only three firms interested in a plot of land on the outskirts of town. The lot is being auctioned by a second-price
sealed-bid auction. Alpha values the lot at $16,500, Richardson at $18,000, and K-Tek at $12,500. Each bidding firm's consumer surplus is
CS=-P
if it wins the auction and 0 if it loses. The values are private. What is each bidder's optimal bid? Who wins the auction, and what price does that firm pay?
Alpha's optimal bid is $. Richardson's optimal bid is 5, and K-Tek's is
(Enter your responses as whole numbers)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose that the following prisoner's dilemma game (stage game) is played repeatedly and players discount future payoffs with the common discount factor δ <1. a) Carefully specify the strategy spaces for both players, draw the extensive form game and find a subgame perfect Nash equilibrium when the stage game is played twice, and both players observe the outcome of the first play.arrow_forwardAssume that we have an entry situation like that in the Judo Economics example. There is an incumbent firm (I) and a new entrant (E). Now we will look at the outcome if the entrant is at a disadvantage. The incumbent has constant marginal costs of production of $100, while marginal costs for the entrant are $120 per unit. There are 100 identical buyers who are willing to pay $200 for the incumbent’s product, but only $160 to buy from the entrant. Any consumer can buy from the incumbent, but only those targeted by the entrant can buy from the entrant. Those consumers targeted by the entrant can choose to buy from the incumbent or the entrant and will choose the lowest price (with the incumbent winning ties). At the first move of the game the entrant decides how many consumers (N) to target and sets a single price (P) to those targeted consumers. The incumbent then sets a single price for all 100 consumers, deciding to defend the market or accommodate the new entrant. Consumers then…arrow_forwardQ² 4 PROBLEM (4) Firm A and Firm B with identical total costs TCA (QA) related goods and competing in prices (Bertrand competition), with demands: QA = 510 - 2PA + pв and Qв= 510 - 2pв+ pa, respectively. = and TCB (QB) Q² 4 are producing (a) Calculate the Bertrand-Nash equilibrium prices. (b) Calculate the prices they charge when A is the leader and sets its price first, anticipating B's best response and taking it into account (like in Stackelberg competition). (c) Calculate the prices they charge when they collude, in order to maximize sum of their profits.arrow_forward
- Explain all option compulsary......you will not explain all option then I will give you down upvote...arrow_forwarda. Consider the game faced by the British and Dutch managers when both are given contracts that compensate them with (1)/(2) of 1% of revenue. The strategic form game is shown. Find the Nash equilibria. b. Now consider the game between the British and Dutch shareholders as to what kind of contracts to give their managers. Assume that they simultaneously choose between a contract that gives the manager 1% of profit and one that gives him (1)/(2) of 1% of revenue. Assume, as before, that the shareholders’ payoff is profit (and we ignore the trivial amount that they pay to their managers). After a pair of contracts is selected, the two contracts are revealed to both managers, and the managers then choose between supply levels of low, moderate, and high. Find all SPNE.arrow_forwardWhat is Revenue Equivalence Theorem for the standard auction types?arrow_forward
- #7arrow_forward2. Suppose the following prisoner's dilemma is played twice with the payoff for the entire game being the sum of the payoffs from the two stages. Assume no discounting. Find the subgame-perfect outcome. Player 1 A B Player 2 A B 6,6 8,2 2,8 4,4arrow_forwardGame Theory Question Consider the following normal form entry deterrence game between an incumbent monopolist and a potential entrant. Potential entrant Stay out 400,0 Enter PH 200,40 Incumbent PL 100,-10 150,0 a) Can you find any pure strategy Nash equilibrium/a in this game? b) Assume playing mixed strategies, find their best response functions and draw them in a diagram. c) Assume the incumbent firm can observe the opponent's choice before he decides and that the potential entrant knows this, will the potential entrant enter? d) Write down the sequential (extensive form) game and find the subgame perfect equilibrium. Explain the outcome. e) How many strategies does each player have?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education