
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
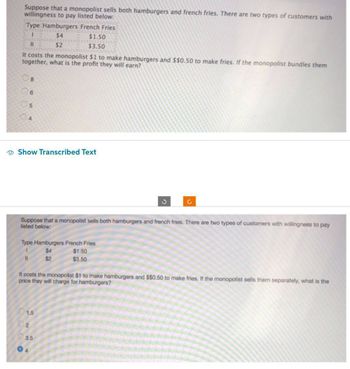
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that a monopolist sells both hamburgers and french fries. There are two types of customers with
willingness to pay listed below:
Type Hamburgers French Fries
1
$4
11
$2
It costs the monopolist $1 to make hamburgers and $$0.50 to make fries. If the monopolist bundles them
together, what is the profit they will earn?
8
5
Show Transcribed Text
11
Type Hamburgers French Fries
$4
$2
$1.50
$3.50
Suppose that a monopolist sells both hamburgers and french fries. There are two types of customers with willingness to pay
listed below:
1.5
02
3.5
04
$1.50
$3.50
3
It costs the monopolist $1 to make hamburgers and $$0.50 to make fries. If the monopolist sells them separately, what is the
price they will charge for hamburgers?
C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following table refers to information about a monopolist. The demand and total cost schedules for the monopolist are presented. Quantity 1 2 34 5 6 7 ܒܢ Calculate the marginal revenue from selling the 4th unit of output. Express your answer without units (e.g., if your answer is "$400", write "400" in the answer box). Type your answer... W 3 LU E a $ 4 R ddelddeelala www 000 6 Sº % Price $30 $28 $26 $24 $22 $20 $18 5 T 6 MacBook Pro Y & 7 A U * 00 8 1 Total cost $10 $20 $30 $40 $50 $60 $70 W 9 P O O T aarrow_forward6. The following graph shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves for a single-price monopolist that produces a drug that helps relieve arthritis pain.arrow_forwardNote:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
- The following table shows the maximum amount five potential car buyers are willing to pay for each level of sales. Suppose that the cars are being sold by a car dealer operating as a monopoly (perhaps because there are no other car dealers in the market). Maximum Amount He or She Would Pay for the Car Buyer 1 $40,000 Buyer 2 $35,000 Buyer 3 $30,000 Buyer 4 $25,000 Buyer 5 $20,000 a) If the price of the car is $30,000, the revenue will be $............thousand.b) If the marginal cost of each car is $20,000. The monopolistic car dealer will want to sell 3 cars and the price will be $................. thousand.c) In a perfectly competitive market, the number of cars sold would be 5 cars. Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardsolve all this Question compulsury. .......arrow_forward1. Refer to the figure below when the firm is a monopolist. Price P MC L K J ATC D T W Quaxtity \MR a) If the monopolist maximizes profit, how many units will it produce? b) What price will the monopolist charge? c) What area measure the monopolist's profit? d) What level of output would be socially efficient? 2. A Monopolist is facing a demand schedule that is shown in the following table. Quantity Total Revenue Average Revenue Marginal Revenue Price $35 $32 1 2 3 $29 14 $26 15 $23 $20 $17 $14 6 7 18 19 $11 10 $8 a) Fill out the rest of the table. b) Assume this monopolist's marginal cost is constant at $11. What quantity of output (Q) will it produce and what price (P) will it charge? ------arrow_forward
- Suppose a monopolist sells a product to faculty members and students on the campus. If the firm sets a single price, the monopolist produces 5000 units and sell them at the price of $3 per unit. At this price, the price elasticity of demand for faculty member is -2.5. And the price elasticity of demand for students is -1.5. The monopolist is considering whether she should set different prices for the faculty members and students and asks for your advice. The monopolist is thinking about charging faculty members a 10% higher price. The quantity demanded by the faculty members would fall by %. The monopolist is thinking about charging students a 10% higher price. The quantity demanded by the students would fall by %. Who should the monopolist charge more? mention faculty and students and how mucharrow_forwardI need help with #33 pleasearrow_forward2. A monopolist produces its output in two factories, whose cost curves are given by C1 (q1) = 10q and C2 (q2) demand for the firm's product is given by P = 700 – 5Q where Q is the total quantity sold by the monopolist. (a) On a diagram, illustrate the monopolist's decision about how much to produce at each factory and overall and the price to charge. Briefly explain your diagram. (b) Numerically calculate the monopolist's optimal choices for qı, q2, Q, and P. (c) Suppose that labor costs increase in Factory 1 but not in Factory 2. How should the firm change (i.e. raise, lower, or leave unchanged) each of the values you found in (b)? Your answer should be qualitative, not quantitative. 10q3 where q1 and q2 are the amounts produced at each factory. The diagram might be useful but is not necessary.arrow_forward
- MC ATC P2 P3 P4 MR Q, Q2 Quantity In the figure above, if the monopolist maximizes profit, how many units of output will be sold and at what price? Quantity = Q2, Price = P1 Quantity = Q1, Price = P3 Quantity = Q1, Price = P4 Quantity = Q2, Price = P2 Quantity = Q1, Price = P1 Pricearrow_forwardThe figure on the right shows the demand schedule for a product produced by a single-price monopolist. Price ($) 10 987654 Quantity demanded A. 9; 10; -1 B. 40; 45; 5 C. 36; 41; 5 D. 5; 4; 1 E. 15; 15; 0 4 567892 10 Using the graph on the right, suppose this single-price monopolist is initially selling 4 units at $10 each and then reduces the price of the product to $9. By making this change, the firm is giving up revenue of Its and gaining revenue of marginal revenue is therefore (All figures are dollars.) Price ($) 141 13- 12- 11- 10- 9- 6- 5- 4- 3- 2- 1- -N 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Quantity Q Qarrow_forwardChapter 9 - Monopoly OPEN Suppose the following are true for a monopolist market: P = 450 - 16Q MR = 450-32Q MC = 55+ 37Q ATC=55+ 18.5Q What is the profit maximizing Price and Quantity? Q* = P = S How much profit did the monopolist earn? Profit = S O E a hp * aarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education