
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
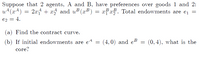
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that 2 agents, A and B, have preferences over goods 1 and 2:
u+(x4)
2x + x5 and u (x³) = xFx. Total endowments are ej =
B B Total endowments are e¡ =
e2 = 4,
(a) Find the contract curve.
(b) If initial endowments are e4 =
A
(4,0) and eB
(0, 4), what is the
core?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3.arrow_forwardConsider an Edgeworth-box economy, which contains two individuals i and j, and two goods (and 2. The total endowment of good I is 8, and the total endowment of good 2 is 4. Individual i has the Leontief utility U₂C X₁, X₁z) = min (X₂₁, Xiz) for all X₁, Xiz 20, while individual j has the Linear utility U₁ (Xj₁, Xj₂)=Xj₁t Xj₂ for all X₁, Xyzzo, which allocation below this is not Patreto efficient / optimal a. (( X ²1, Xit), (X₁₁ + X₁²₂)) =((2, 2), (6,2)) 6. (( X ₂₁, Xiv), (X; ₁ ; X₁3₂)) = (C0₁0), (814)) c. (CX₁, Xt₂), (X3³₁, X₁₂)) = (( 8₁4), (0, 0)) d. ((x), X₁₂), (X₁, X3₂)) =((4,4), (4,0))arrow_forwardConsider an economy with 2 goods and 2 agents. The Örst agent has the utilityfunction, u (x1; x2) = ln x1 + 2 ln x2, and the other one has u (y1; y2) = 2 ln y1 + ln y2.The aggregate endowments of the 2 goods are given by (50; 100). Suppose there is asocial planner who cares about agents equally.(a) Set up the plannerís problem b) Calculate the first-best outcome (i.e., the social plannerís solution).arrow_forward
- (5) A has utility function u4(x4) = x4 + x and initial endowment w4 = (3,6). Consumer B has utility function uB (xB) = xf · x% and initial endowment wB = (3,6). Consider an exchange economy with two consumers and two goods. Consumer (a) Is the initial endowment a Pareto efficient allocation? Justify your answer. (b) Find a competitive equilibrium (p, xª, x³) for the economy. (c) Construct the contract curve. A picture here is not a complete answer; you need to specify analytically the set of points that are in the contract curve.arrow_forwardThis question is related to equilibrium and its drive? all detail is given in a snap.arrow_forward2. General Equilibrium Consider a market with two goods, x and z, and two consumers, A and B. The utility functions for consumers A and B are as follows UA ÜB 2 1 == XBZB and the initial endowments for each consumer are @ eA = (4,2) еB = (2,6) where consumer B is endowed with 2 unit of good x and 6 units of good z, respectively. a) Draw the Edgeworth Box (Don't worry about the shape of the utility curves. Just pick a general shape that we have used before). b) Derive the contract curve.arrow_forward
- Consider the following pure exchange, Edgeworth box economy. There are two consumers, Adam and Mark, and two goods. Adam has an endowment of 7 units of good 1 and 3 units of good 2 (i.e. wadam = (7, 3)), while Mark has an endowment of 3 units of good 1 and 7 units of good2 (wmark$ = (3,7)). The consumers' utility functions are given by: Uadam = Xa1 + Xa2 and Umark = min{xm1, Xm2) where x¡1 is the consumption of good 1 by consumer (i = adam, mark) (a) Find the set of Pareto optimal allocations of this economy (b) Find the Walrasian equilibrium.arrow_forwardIn a two-good market, a consumer starts with an initial endowment of (x₁, x2) = (15.00, 5.00), while the market prices for these goods are given by (P1, P2) = (7.00, 3.00). The consumer has the following utility function: U 0.52 0.48 - Given this information, what will this consumer's final choice of quantity for each good be? x1 = x2 =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education