
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
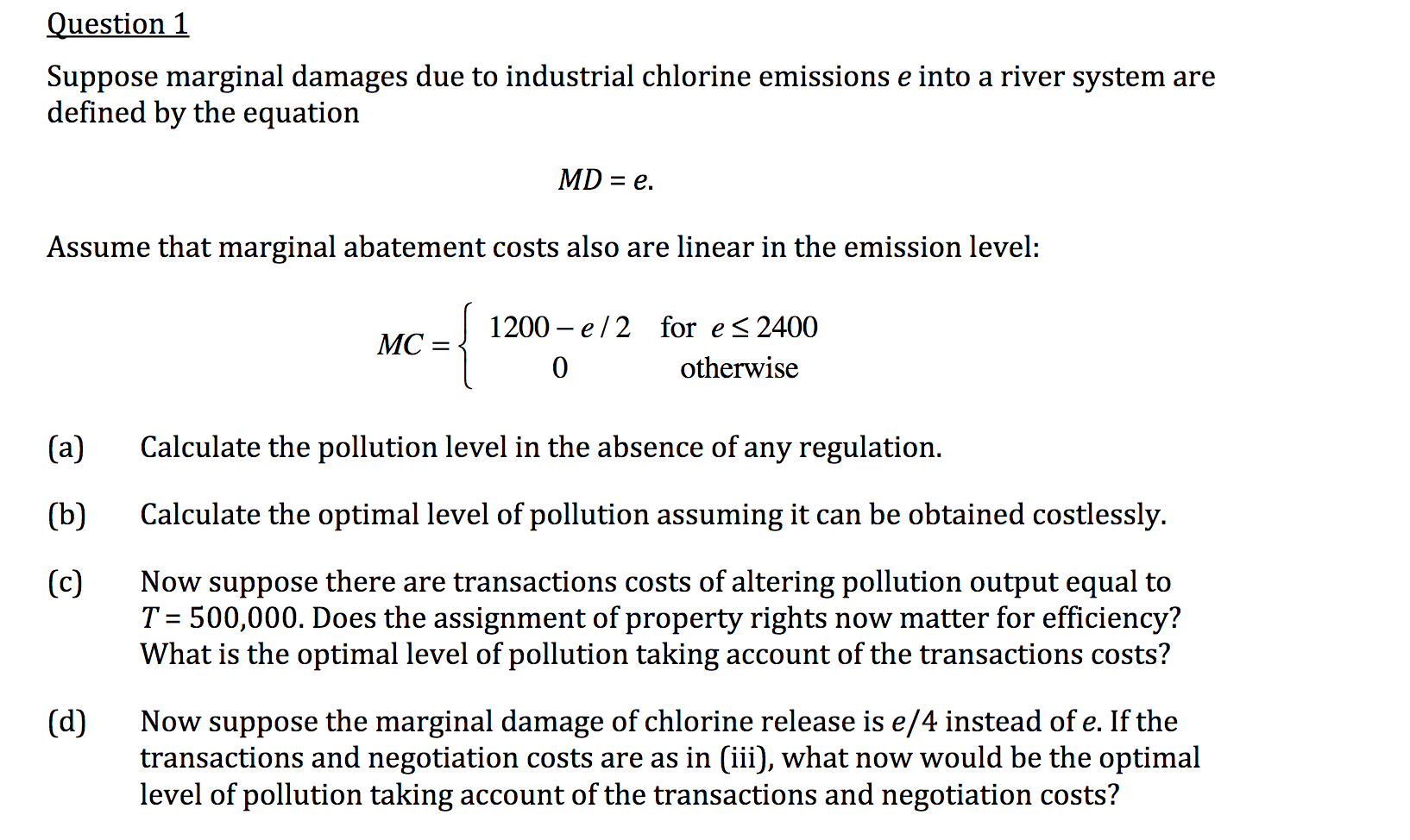
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose marginal damages due to industrial chlorine emissions e into a river system are
defined by the equation
MD = e.
Assume that marginal abatement costs also are linear in the emission level:
1200 – e/2 for e<2400
MC =
otherwise
(a)
Calculate the pollution level in the absence of any regulation.
(b)
Calculate the optimal level of pollution assuming it can be obtained costlessly.
Now suppose there are transactions costs of altering pollution output equal to
T = 500,000. Does the assignment of property rights now matter for efficiency?
What is the optimal level of pollution taking account of the transactions costs?
(c)
Now suppose the marginal damage of chlorine release is e/4 instead of e. If the
transactions and negotiation costs are as in (iii), what now would be the optimal
level of pollution taking account of the transactions and negotiation costs?
(d)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use the model of environmental pollution to model the following changes in a polluting industry to: i) the socially optimal level of pollution; ii) the total abatement costs; and ii) the total damage costs (а) A new technology is invented that allows firms to reducе pollution associated with each level of production output. (b) The government announces a new commitnment to more strictly enforce current environmental regulations. (c) A new study finds the pollutant in question to be more carcinogenic than originally thought.arrow_forwardThe revenues from an emissions-charge approach to controlling climate change would be unusually large in comparison to other pollutants. What circumstances would lead to high revenues?arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Consider two firms with the following marginal abatement costs (MAC) as a function of emissions (E): MAC_1 = 12-2E_1 MAC_2=9-E_2, and assume marginal external damages (MED) from aggregate emissions from the two firms (E_Agg) is: MED = E_Agg. Total external damages at the socially efficient level of aggregate emissions is Answer: 1arrow_forwardPlease drag and drop the markers 1 through 5 below to denote the appropriate position on the diagram that answers the question. a) Show with marker 1 the efficient level of marginal abatement costs. b) Show with marker 2 the marginal abatement costs if each produce must reduce pollution to 7.5 units. c) Denote with marker 3 the area that measures total abatement costs for each polluter. d) Show with marker 4 the marginal abatement costs if sources 1 and 2 merged and were constrained to a maximum total emissions of 15 units. e) Show with marker 5 the total abatement costs if both sources merged and were constrained to a maximum total emissions of 15 units. Marginal Cost (in dollars) MC MC, Quantity of Emissions Reduced A Source 1 10 5 4 13 14 15 15 14 13 12 11 10 8 O Source 2 5arrow_forwardFind Pure Strategy Nash equilibirum then use following values for emissions.arrow_forward
- Please help me with this question ASAParrow_forwardtwo types of consumers( workers an retirees) share a community with a polluting cheese factory. the polution is nonrival and nonexcludable. the total damage to workers is p2 where p is the amount of pollution and the total damage to retirees is 3p2 . thus marginal damage to workers is 2p and marginal damage to retirees is 6p. according to an anlaysis by consulting engineers, the cheese factory saves 20p-p2 by pollluting p, for a marginal savings of 20-2p. a.Find the aggregate(including both types of sonsumers) marginal damage for the public bad. b..graph the marginal savings and aggregate marginal damage curves with pollution on the horizontal axis. c. how much will the cheese factory pollute in the abscence of any regulation or bargaining? what is the societys optimal level of pollution? d. starting from the uncontrolled level of pollution calculated in part(c), find the marginal willingness to pay for pollution abatment, A, for each consumer class. (abatment is the reduction in…arrow_forwardConsider an industry with two firms that emit a uniformly mixed air pollutant (e.g., carbon dioxide). The marginal abatement cost functions for Firm 1 and Firm 2 are: MAC1 = 100 - e1 MAC2 = 100 - 4e2 Aggregate emissions for the industry are denoted as E = e1 + e2. 1. In an unregulated environment how many units of emissions does each firm emit? Firm 1’s unregulated level of emissions ____________ Firm 2’s unregulated level of emissions ____________ Total unregulated level of emissions ______________ Suppose a regulator has a goal of reducing the total level of emissions from the amount from the amount you answered in [1] to 25 units. The regulator would like to achieve the goal of 25 units of total emissions in a cost-effective way. To do so it issues 25 permits, 10 are given to Firm 1 and 15 are given to Firm 2. A firm can only emit a unit of pollution if they have a permit for that unit, otherwise they must abate. After the permits are allocated,…arrow_forward
- Consider a firm that emits pollution into the air. Suppose that the marginal damage costs associated with the emissions are given by MDC -15+ 4 c, where e is the quantity of the emissions. The firm's marginal costs of abatement are given by (a) (b) 390 (c) MAC 1200 - 20 c. Determine the quantity of emissions that the firm would discharge in the absence of government policy. Determine the socially efficient level of emissions. Calculate the total costs to society for both a and b and draw a diagram illustrating these costs.arrow_forwardFirms in a polluting industry can be classified in two groups: newer firms with a cleaner technology that can abate pollution at a lower marginal cost MCLA = (1/2)aL and older firms with dirtier MCHA = aH, where ai is the level of abatement undertaken by firms of type i = L, H. The social marginal benefit of abating pollution from this particular industry is MBA= 120 - A, where A is the aggregate level of abatement in that industry. Suppose that in order to avoid the costly obtention of disaggregate information about individual firms' costs, the government just implements a uniform standard aui = A* / 2. Is this allocation efficient? If not, what is the deadweight loss?arrow_forwardNo hand written solution Afirm has an industrial plant that emits pollutants into a town’s lake. The plant’s marginal abatement function is MAC= 200 – 0.5E and damages caused by its emissions are given by MD = 2E where emissions are in kg. per day. What is the socially efficient level of emissions from this plant? Illustrate this in a graph. As an incentive to reduce emissions to the socially efficient level, government offers to pay the firm for each kg. of emissions it abates per day from this plant. What subsidy per kg. should the government offer? If the plant abates to the socially efficient level of emissions, what total subsidy payment would the firm receive? Identify the area in your graph. How much better or worse off would the firm be compared to if it did no abating? Identify the area in your graph. What would be the net benefit to society if we pay the firm to reduce the plant’s emissions to the socially efficient level? Identify this area in your graph.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education